Abstract
Objective
Although radiofrequency ablation is well validated for treatment of osteoid osteoma, newer technologies, namely cryoablation, have been less thoroughly studied. The purpose is to perform a systematic review and pooled analysis of percutaneous ablation technologies for treatment of osteoid osteoma with subset analysis of intra-articular and spinal tumors.
Material and methods
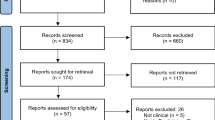
A total of 36 of 79 identified manuscripts met inclusion criteria, comprising 1863 ablations in 1798 patients. Inclusion criteria were (1) retrospective or prospective analysis of thermal ablation of osteoid osteomas in any location, (2) at least 6 months of clinical follow-up, (3) 10 or more patients, (4) patients not included in a second study included in this review, and (5) English language or English translation available. Success rate was defined as all ablations minus technical failures, clinical failures, and recurrences. Subset analysis of intra-articular and spinal tumors was performed.
Results
Overall success rate was 91.9% (95% CI 91–93%). Technical failure, clinical failure, and recurrence rates were 0.3%, 2.1%, and 5.6% respectively. Complications were seen in 2.5% (95% CI 1.9–3.3%) patients. There was no significant difference when comparing radiofrequency ablation and cryoablation (p = 0.92). Success rates for intra-articular (radiofrequency ablation) and spinal tumors (radiofrequency and cryoablation) were 97% and 91.6% respectively.
Conclusion
Percutaneous ablation of osteoid osteomas was highly successful with low complication rates. Efficacy of radiofrequency ablation and cryoablation is similar, which is consequential because cryoablation is associated with decreased pain, predictable nerve regeneration, and theoretical immunotherapy benefits. Treatment of more challenging intra-articular and spinal lesions demonstrated similarly high success and low complication rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noordin S, Allana S, Hilal K, Nadeem N, Lakdawala R, Sadruddin A, et al. Osteoid osteoma: contemporary management. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2018;10(3):7496.
Ghanem I. The management of osteoid osteoma: updates and controversies. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2006;18:36–41.
Rimondi E, Mavrogenis AF, Rossi G, Ciminari R, Malaguti C, Tranfaglia C, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for non-spinal osteoid osteomas in 557 patients. Eur Radiol. 2012;22(1):181–8.
Lindner NJ, Scarborough M, Ciccarelli JM, Enneking WF. CT-controlled thermocoagulation of osteoid osteoma in comparison with traditional methods. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1997;135(6):522–7 German.
Rosenthal DI, Hornicek FJ, Wolfe MW, Jennings LC, Gebhardt MC, Mankin HJ. Percutaneous radiofrequency coagulation of osteoid osteoma compared with operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(6):815–21.
Simon MA. Percutaneous radiofrequency coagulation of osteoid osteoma compared with operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(3):437–8.
Lanza E, Thouvenin Y, Viala P, Sconfienza LM, Poretti D, Cornalba G, et al. Osteoid osteoma treated by percutaneous thermal ablation: when do we fail? A systematic review and guidelines for future reporting. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2014;37(6):1530–9.
Liu DM, Kee ST, Loh CT, McWilliams J, Ho SG, Brower JS, et al. Cryoablation of osteoid osteoma: two case reports. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21(4):586–9.
Aarts BM, Klompenhouwer EG, Rice SL, Imani F, Baetens T, Bex A, et al. Cryoablation and immunotherapy: an overview of evidence on its synergy. Insights Imaging. 2019;10:53.
Johnson C, Mitchell J, Manyapu S, Hawkins C, Singer A, Prologo J. Natural history of motor nerve cryoablation: a retrospective cohort analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019;30(3):S176.
Kostrzewa M, Diezler P, Michaely H, Rathmann N, Attenberger UI, Schoenberg SO, et al. Microwave ablation of osteoid osteomas using dynamic MR imaging for early treatment assessment: preliminary experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014;25(1):106–11.
Basile A, Failla G, Reforgiato A, Scavone G, Mundo E, Messina M, et al. The use of microwaves ablation in the treatment of epiphyseal osteoid osteomas. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2014;37(3):737–42.
Hinshaw JL, Lubner MG, Ziemlewicz TJ, Lee FT, Brace CL. Percutaneous tumor ablation tools: microwave, radiofrequency, or cryoablation—what should you use and why? RadioGraphics. 2014;35:1344–62.
Papagelopoulos PJ, Mavrogenis AF, Kyriakopoulos CK, Benetos IS, Kelekis NL, Andreou J, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of intra-articular osteoid osteoma of the hip. J Int Med Res. 2006;34(5):537–44.
Allen SD, Saiffuddin A. Imaging of intra-articular osteoid osteoma. Clin Radiol. 2003;58:845–52.
Albisinni U, Bazzocchi A, Bettelli G, Facchini G, Castiello E, Cavaciocchi M, et al. Treatment of osteoid osteoma of the elbow by radiofrequency thermal ablation. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2014;23(1):e1–7.
Albisinni U, Facchini G, Spinnato P, Gasbarrini A, Bazzocchi A. Spinal osteoid osteoma: efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation. Skelet Radiol. 2017;46(8):1087–94.
Martel J, Bueno A, Nieto-Morales ML, Ortiz EJ. Osteoid osteoma of the spine: CT-guided monopolar radiofrequency ablation. Eur J Radiol. 2009;71(3):564–9.
Morassi LG, Kokkinis K, Evangelopoulos DS, Karargyris O, Vlachou I, Kalokairinou K, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of spinal osteoid osteoma under CT guidance. Br J Radiol. 2014;87(1038):20140003.
Lindquester WS, Crowley JJ, Hawkins CM. Percutaneous thermal ablation for treatment of osteoid osteoma: a systematic review and analysis. Poster session presented at: Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe Annual Meeting; 7–11 Sept. 2019.
Institute of Health Economics (IHE). Quality appraisal of case series studies checklist. Edmonton (AB): Institute of Health Economics; 2014. Available from: http://ihe.ca/research-programs/rmd/cssqac-about
Moga C, Guo B, Schopflocher D, Harstall C. Development of a quality appraisal tool for case series studies using a modified Delphi technique. Institute of Health Economics: Edmonton; 2012.
Coupal TM, Mallinson PI, Munk PL, Liu D, Clarkson P, Ouellette H. CT-guided percutaneous cryoablation for osteoid osteoma: initial experience in adults. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;202(5):1136–9.
Santiago E, Pauly V, Brun G, Guenoun D, Champsaur P, Le Corroller T. Percutaneous cryoablation for the treatment of osteoid osteoma in the adult population. Eur Radiol. 2018;28(6):2336–44.
Shah J, Gill A, Laporte J, Whitmore M, Bertino F, Prologo JD, et al. Long-term results and durability of cryoablation of osteoid osteoma in the pediatric and adolescent population. Pediatr Radiol. 2019;49(Suppl 1):S75.
Abboud S, Kosmas C, Novak R, Robbin M. Long-term clinical outcomes of dual-cycle radiofrequency ablation technique for treatment of osteoid osteoma. Skelet Radiol. 2016;45(5):599–606.
Akhlaghpoor S, Aziz Ahari A, Arjmand Shabestari A, Alinaghizadeh MR. Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma in atypical locations: a case series. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(7):1963–70.
Al-Omari MH, Ata KJ, Al-Muqbel KM, Mohaidat ZM, Haddad WH, Rousan LA. Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma using tissue impedance as a parameter of osteonecrosis. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2012;56(4):384–9.
Becce F, Theumann N, Rochette A, Larousserie F, Campagna R, Cherix S, et al. Osteoid osteoma and osteoid osteoma-mimicking lesions: biopsy findings, distinctive MDCT features and treatment by radiofrequency ablation. Eur Radiol. 2010;20(10):2439–46.
Bourgault C, Vervoort T, Szymanski C, Chastanet P, Maynou C. Percutaneous CT-guided radiofrequency thermocoagulation in the treatment of osteoid osteoma: a 87 patient series. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(3):323–7.
Cantwell CP, O'Byrne J, Eustace S. Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma with cooled probes and impedance-control energy delivery. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186(5 Suppl):S244–8.
Cheng EY, Naranje SM, Ritenour ER. Radiation dosimetry of intraoperative cone-beam compared with conventional CT for radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(9):735–42.
Cioni R, Armillotta N, Bargellini I, Zampa V, Cappelli C, Vagli P, et al. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma: long-term results. Eur Radiol. 2004;14(7):1203–8.
Daniilidis K, Martinelli N, Gosheger G, Hoell S, Henrichs M, Vogt B, et al. Percutaneous CT-guided radio-frequency ablation of osteoid osteoma of the foot and ankle. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(12):1707–10.
Donkol RH, Al-Nammi A, Moghazi K. Efficacy of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma in children. Pediatr Radiol. 2008;38(2):180–5.
Garge S, Keshava SN, Moses V, Chiramel GK, Ahmed M, Mammen S, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma in common and technically challenging locations in pediatric population. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2017;27(1):88–91.
Ghanem I, Collet L-M, Kharrat K, Samaha E, Deramon H, Mertl P, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency coagulation of osteoid osteoma in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2003;12(4):244–52.
Hage AN, Chick JFB, Gemmete JJ, Grove JJ, Srinivasa RN. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of osteoid osteoma in children and adults: a comparative analysis in 92 patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018;41(9):1384–90.
Hoffmann RT, Jakobs TF, Kubisch CH, Trumm CG, Weber C, Duerr H-R, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of osteoid osteoma-5-year experience. Eur J Radiol. 2010;73(2):374–9.
Karagöz E, Özel D, Özkan F, Özel BD, Özer Ö, Coşkun ZÜ. Effectiveness of computed tomography guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation therapy for osteoid osteoma: initial results and review of the literature. Pol J Radiol. 2016;81:295–300.
Mylona S, Patsoura S, Galani P, Karapostolakis G, Pomoni A, Thanos L. Osteoid osteomas in common and in technically challenging locations treated with computed tomography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Skelet Radiol. 2010;39(5):443–9.
Neumann D, Berka H, Dorn U, Neureiter D, Thaler C. Follow-up of thirty-three computed-tomography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermoablations of osteoid osteoma. Int Orthop. 2012;36(4):811–5.
Peyser A, Applbaum Y, Khoury A, Liebergall M, Atesok K. Osteoid osteoma: CT-guided radiofrequency ablation using a water-cooled probe. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14(2):591–6.
Peyser A, Applbaum Y, Simanovsky N, Safran O, Lamdan R. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation of pediatric osteoid osteoma utilizing a water-cooled tip. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(10):2856–61.
Rosenthal DI, Hornicek FJ, Torriani M, Gebhardt MC, Mankin HJ. Osteoid osteoma: percutaneous treatment with radiofrequency energy. Radiology. 2003;229(1):171–5.
Ruiz Santiago F, Castellano García Mdel M, Guzmán Álvarez L, Martínez Montes JL, Ruiz García M, Tristán Fernández JM. Percutaneous treatment of bone tumors by radiofrequency thermal ablation. Eur J Radiol. 2011;77(1):156–63.
Schmidt D, Clasen S, Schaefer JF, Rempp H, Duda S, Trübenbach J, et al. CT-guided radiofrequency (RF) ablation of osteoid osteoma: clinical long-term results. Rofo. 2011;183(4):381–7.
Shields DW, Sohrabi S, Crane EO, Nicholas C, Mahendra A. Radiofrequency ablation for osteoid osteoma-recurrence rates and predictive factors. Surgeon. 2018;16(3):156–62.
Soong M, Jupiter J, Rosenthal D. Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma in the upper extremity. J Hand Surg [Am]. 2006;31(2):279–83.
Sung K-S, Seo J-G, Shim JS, Lee YS. Computed-tomography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermoablation for the treatment of osteoid osteoma-2 to 5 years follow-up. Int Orthop. 2009;33(1):215–8.
Vanderschueren GM, Obermann WR, Dijkstra SPD, Taminiau AHM, Bloem JL, van Erkel AR. Radiofrequency ablation of spinal osteoid osteoma: clinical outcome. Spine. 2009;34(9):901–4.
Thacker PG, Callstrom MR, Curry TB, Mandrekar JN, Atwell TD, Goetz MP, et al. Palliation of painful metastatic disease involving bone with imaging-guided treatment: comparison of patients’ immediate response to radiofrequency ablation and cryoablation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(2):510–5.
Napoli A, Bazzocchi A, Scipione R, Anzidei M, Saba L, Ghanouni P, et al. Noninvasive therapy for osteoid osteoma: a prospective developmental study with MR imaging-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound. Radiology. 2017;285(1):186–96. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017162680 Epub 2017 Jun 7.
Bing F, Vappou J, de Mathelin M, Gangi A. Targetability of osteoid osteomas and bone metastases by MR-guided high intensity focused ultrasound (MRgHIFU). Int J Hyperth. 2018;35(1):471–9.
Funding
Marnie Bertolet (assistant professor in the department of Epidemiology) and Liwen Wu (graduate student in the department of biostatistics) of the Graduate School of Public Health at the University of Pittsburgh aided in the statistical analysis through funding from the Clinical and Translational Science Institute at the University of Pittsburgh (National Institutes of Health (NIH) Clinical and Translational Science Award (CTSA) program, grant UL1 TR001857).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This retrospective study was determined to be exempted by the Institutional Review Board and was performed in compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindquester, W.S., Crowley, J. & Hawkins, C.M. Percutaneous thermal ablation for treatment of osteoid osteoma: a systematic review and analysis. Skeletal Radiol 49, 1403–1411 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03435-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03435-7