Abstract
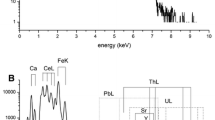
In this work, several individual grains of uranium minerals—uraninite with high content of Ca, Ca-rich boltwoodite, growths of uranophane with β-uranophane, and weeksite—from different uranium deposits were studied by a scanning nuclear microprobe. Particle-induced X-ray emission technique provided by the microprobe (µ-PIXE) was carried out to obtain a concentration and 2D distribution of elements in these minerals. In addition, energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (SEM-EDS) provided by a scanning electron microscope was used. The types of minerals were determined by X-ray diffraction methods. Results of this study improved the understanding of trace elemental composition of the uranium minerals depending on their origin. Obtained signatures could be linked then to the sample provenance. Such data are important for nuclear forensics to identify the ore types and even specific ore bodies, when only small samples may be available for analysis. In this study, the µ-PIXE technique was used for obtaining the 2D distribution of trace elements that are not commonly measured by SEM-EDS at the relevant concentrations. The detected levels and precisions of elements determination by µ-PIXE were also defined. Using µ-PIXE, several micro mineral inclusions such as phosphate with high level of V and Si were identified. The age of the uranium minerals was estimated due to a significant content of radiogenic Pb that provides an additional parameter for determination of the main attributive characteristics of the minerals. This work also showed that due to its high elemental sensitivity the nuclear microprobe can be a new analytical tool for creating a nuclear forensic database from the known uranium deposits and a subsequent analysis of the intercepted illicit materials.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla HM (1996) Geochemical and mineralogical studies at Um Ara rare metals prospect, Southeastern Desert, Egypt. PhD Thesis, Hokkaido Univ Sapporo, Japan 178
Belevtsev Y, Koval V (1995) Genetic types and regularities of location Uranium deposits in Ukraine. In: Naukova Dumka press, Kiev (Russian).
Burns PC (2003) Advances in Understanding of the Crystal Chemistry of Hexavalent Uranium. MRS Proc 802:DD3.2. https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-802-DD3.2
Calligaro T, Coquinot Y, Pichon L, Moignard B (2011) Advances in elemental imaging of rocks using the AGLAE external microbeam. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 269:2364–2372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2011.02.074
Campbell JL, Boyd NI, Grassi N et al (2010) The Guelph PIXE software package IV. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 268:3356–3363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2010.07.012
Dai Z, Ren C, Zhang J et al (1995) Comparison of quantitative PIXE and EPMA microanalysis of mineral samples. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 104:489–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-583X(95)00473-4
Dawood YH (2001) Uranium-series disequilibrium dating of secondary uranium ore from the south Eastern Desert of Egypt. Appl Radiat Isot 55:881–887. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-8043(01)00139-7
Eppich GR, Williams RW, Gaffney AM et al (2013) 235U–231 Pa age dating of uranium materials for nuclear forensic investigations. J Anal At Spectrom 28:666. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ja50041a
Eremenko G, Ilmenev E, Azimi N (1977) Viksite group minerals: occurence in Afghanistan. Trans Acad Sci USSR (in Russ 237:1191–1193
Johansson S, Campbell J, Malmqvist K (1995) Particle Induced X-ray Emission spectrometry (PIXE). Wiley, New York
Keegan E, Kristo MJ, Colella M et al (2014) Nuclear forensic analysis of an unknown uranium ore concentrate sample seized in a criminal investigation in Australia. Forensic Sci Int 240:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2014.04.004
Kertész Z, Furu E, Angyal A et al (2015) Characterization of uranium and thorium containing minerals by nuclear microscopy. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 306:283–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4175-5
Kristo MJ, Tumey SJ (2013) The state of nuclear forensics. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 294:656–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2012.07.047
Kristo MJ, Keegan E, Colella M et al (2015) Nuclear forensic analysis of uranium oxide powders interdicted in Victoria, Australia. Radiochim Acta 103:487–500. https://doi.org/10.1515/ract-2014-2363
Magilin DV, Ponomarev AG, Rebrov VA et al (2009) Performance of the Sumy nuclear microprobe with the integrated probe-forming system. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 267:2046–2049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2009.03.015
Mayer K, Wallenius M, Varga Z (2013) Nuclear Forensic Science: Correlating Measurable Material Parameters to the History of Nuclear Material. Chem Rev 113:884–900. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300273f
Ohnuki T, Kozai N, Samadfam M et al (2001) Analysis of uranium distribution in rocks by micro-PIXE. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 181:586–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-583X(01)00381-0
Ortega R, Deves G, Maire R (2003) Nuclear microprobe analysis of uranium-rich speleothems: Methodological aspects. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 210:455–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-583X(03)01075-9
Ram R, Charalambous FA, Mcmaster S et al (2013) Chemical and micro-structural characterisation studies on natural uraninite and associated gangue minerals. Miner Eng 45:159–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2013.02.004
Ryan CG (2011) PIXE and the nuclear microprobe: Tools for quantitative imaging of complex natural materials. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 269:2151–2162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2011.02.046
Sie SH (1997) Nuclear microprobe in geological applications: Where do we go from here? Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 130:592–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-583X(97)00257-7
Stohl FV, Smith DK (1981) The crystal chemistry of the uranyl silicate minerals. Am Mineral 66:610–625
Suzuki K, Adachi M (1991) Precambrian provenance and Silurian metamorphism of the Tsubonosawa paragneiss in the South Kitakami terrane, Northeast Japan, revealed by the chemical Th-U-total Pb isochron ages of monazite, zircon and xenotime. Geochem J 25:357–376. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.25.357
Švedkauskaite-LeGore J, Mayer K, Millet S et al (2007) Investigation of the isotopic composition of lead and of trace elements concentrations in natural uranium materials as a signature in nuclear forensics. Radiochim Acta 95:601–605. https://doi.org/10.1524/ract.2007.95.10.601
Valter A, Knight K (2011) Characterization of Uranium Mineralogy in Ukrainian Ores. Mineral J 75:2059
Valter A, Englebrecht A, Magilin D et al (2013) Evaluation of a calcium-rich uraninite composition by electron and proton microprobe. Mineral J 35:48–53
Valter AA, Dikiy NP, Dovbnia AN et al (2015) The nuclear-physical dating of the formation of uranium ores in the Hanneshin deposit (Afghanistan) by mineral weeksite. Reports Natl Acad Sci Ukr 57–64. https://doi.org/10.15407/dopovidi2015.03.057
Wallenius M, Mayer K, Ray I (2006) Nuclear forensic investigations: Two case studies. Forensic Sci Int 156:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2004.12.029
Ziegler JF, Ziegler MD, Biersack JP (2010) SRIM - The stopping and range of ions in matter (2010). Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact with Mater Atoms 268:1818–1823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2010.02.091
Acknowledgements
The authors thank S. M. Romanenko, who fulfilled the main part of SEM and EPMA investigations. We also want to acknowledge the staff of the accelerator analytic facilities in IAP NAS of Ukraine for assistance with μ-PIXE measurements, especially the head of the Accelerator Division N. M. Marchenko. Over the course of our experiments, the authors were grateful for the constant support and attention from the organizer and originator of the PIXE facility at IAP NASU, prof. V. Y. Storizhko. This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract DE-AS52-07NA27344.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valter, A.A., Knight, K.B., Eremenko, G.K. et al. Spatial investigation of some uranium minerals using nuclear microprobe. Phys Chem Minerals 45, 533–547 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-017-0940-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-017-0940-z