Abstract
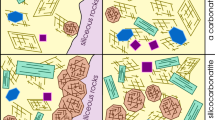
Zeolites are aluminosilicate minerals with multiple channels and cages. They are widely used in industry; further, owing to its increasing demand, the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites from natural minerals/rocks has attracted great attention. This study aims to discuss the crystal growth mechanisms of zeolites from pumice. Pumice is a widely available porous volcanic glass (mainly consisting of 65–75% SiO2 and 9–20% Al2O3) that can be used in the fabrication of zeolites. In this study, zeolite was formed from pumice via a hydrothermal method with varying alkaline concentrations, reaction times and temperatures, and addition of NaCl. Zeolite Na-P1 was synthesized under conditions of 0.1 or 0.5 M at 150 °C. The feldspar phase (albite) initially occurred, followed by the zeolite phase (zeolite Na-P1). Phillipsite was an unstable intermediate product during this synthesis process. Based on these results, we suggest that the phase transformation sequence follows the order of albite, phillipsite, and zeolite Na-P1. Moreover, it can be speculated that an increase in cation concentration can induce a rapid occurrence of the zeolite phase (zeolite Na-P1). Raman spectrometry analyses provided insights into the formation mechanism of zeolite structures, indicating differences related to the number of sodium ions. Both zeolite Na-P1 and phillipsite are composed of four- and eight-membered rings, and the former is mainly grown with four-membered rings as the main structure. This study provides a low-cost and simple synthetic method for producing zeolite Na-P1 and phillipsite, which can be used as indicator minerals for marine/lake facies and in environmental treatment.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adisaputra MK, Kusnida D (2010) Paleocene postgenetic accumulation of nannoplankton on the phillipsite minerals in Roo Rise, Indian Ocean. Indones J Geosci 5(1):49–56. https://doi.org/10.17014/ijog.v5i1.92
Akporiaye DE (1994) Systematic evaluation and classification of zeolite frameworks based on constituent sheets. Stud Surf Sci Catal 84:575–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2991(08)64160-9
Andrade FRD, Yogi MTAG, Gomes EB, Shinzato MC (2020) Extent of zeolite synthesis via alkaline fusion from tailings dam sediments. Environ Earth Sci 79(16):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09118-9
Aygun Z, Aygun M (2016) Spectroscopic analysis of Ahlat stone (ignimbrite) and pumice formed by volcanic activity. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 166:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.05.018
Burriesci N, Arcoraci C, Giordano N, Antonucci PL (1985) Zeolites from pumice and tuff as evaluation of pozzolanic cement constituents. Zeolites 5(2):96–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/0144-2449(85)90080-6
Cardoso AM, Paprocki A, Ferret LS, Azevedo CMN, Pires M (2015) Synthesis of zeolite Na-P1 under mild conditions using Brazilian coal flyash and its application in wastewater treatment. Fuel 139:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.08.016
Che T, Liu ZD, Yonezawa Y, Sukenaga S, Ando M, Shibata H, Sasaki Y, Okubo T, Wakihara T (2020) Unique crystallization behavior in zeolite synthesis under external high pressures. Chem Commun 20(56):2811–2814. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc09966b
Chen HF, Lo HJ, Song SR, Fang JN, Chen YL, Li LJ, Lee YT (2002) The synthesis of phillipsite. Western Pacific Earth Sci 2(4):381–392
Cocks PA, Pope CG (1998) Salt effects on the synthesis of some aluminous zeolites. Zeolites 15(8):701–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/0144-2449(95)00076-I
Correcher V, Gomez-Ros JM, Dogan T, García-Guinea J, Topaksu M (2017) Optical, spectral and thermal properties of natural pumice glass. Radiat Phys Chem 130:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2016.08.002
Dutta PK, Shieh DC, Puri M (1988) Correlation of framework Raman bands of zeolites with structure. Zeolites 8(4):306–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-2449(88)80127-1
Esaifan M, Hourani M, Khoury H, Rahier H, Wastiels J (2017) Synthesis of hydroxysodalite zeolite by alkali-activation of basalt powder rich in calc-plagioclase. Adv Powder Technol 28(2):473–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2016.11.002
Franus W, Wdowin M, Franus M (2014) Synthesis and characterization of zeolites prepared from industrial fly ash. Environ Monit Assess 186:5721–5729. https://link.springer.com/article/https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3815-5
Fukasawa T, Horigome A, Karisma AD, Maeda N, Huang AN, Fukui K (2018) Utilization of incineration fly ash from biomass power plants for zeolite synthesis from coal fly ash by microwave hydrothermal treatment. Adv Powder Technol 29(3):450–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.06.023
Fukui K, Arai K, Kanayama K, Yoshida H (2006) Phillipsite synthesis from fly ash prepared by hydrothermal treatment with microwave heating. Adv Powder Technol 17(4):369–382. https://doi.org/10.1163/156855206777866164
Gualtieri AF, Passaglia E, Galli E (2002) Ion exchange selectivity of Phillipsite. Stud Surf Sci Catal 142:1705–1712. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2991(02)80343-3
Hall A (1998) Zeolitization of volcaniclastic sediments; the role of temperature and pH. J Sediment Res 68(5):739–745. https://doi.org/10.1163/156855206777866164
Hernández RS (2018) Complete transformation of aluminum waste into zeolite and its use in the removal of pollutants from aqueous solution. PhD Thesis of Universidad Carlos III de Madrid e-Archivo. https://core.ac.uk/reader/288499879
Hussein MM, Khader KM, Musleh SM (2014) Characterization of raw zeolite and surfactant-modified zeolite and their use in removal of selected organic pollutants from water. Int J Chem Sci 12(3):815–844. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269039105
Ji WX, Zhang SY, Zhao PD, Zhang SS, Feng N, Lan LP, Zhang XG, Sun YG, Li YY, Ma YL (2020) Green synthesis method and application of NaP zeolite prepared by coal gasification coarse slag from Ningdong, China. Appl Sci 10:2694–2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10082694
Król M, Morawska J, Mozgawa W, Pichór W (2014) Low-temperature synthesis of zeolite from perlite waste—Part I: review of methods and phase compositions of resulting products. Mater Sci Pol 32(3):503–513. https://doi.org/10.2478/s13536-014-0216-y
Liu Y, Wang G, Lu W, Li X, Luo Q, Na P (2019) Zeolite P synthesis based on fly ash and its removal of Cu (II) and Ni (II) ions. Chin J Chem Eng 27(2):341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2018.03.032
Okada K, Kuboyama K, Takei T, Kameshima Y, Yasumori A, Yoshimura M (2000) In situ zeolite NaX coating on glass fibers by soft solution process. Micropor Mesopor Mat 37:99–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(99)00198-5
Ostrooumov M (2017) Raman and infrared reflection spectroscopic study of mineralogical composition of iron-manganese nodules (Pacific and Indian Oceans). Inter J Exp Spectrosc Techniq 2(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.35840/2631-505X/8512
Ottana R, Saija LM, Burriesci N, Giordano N (1982) Hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites from pumice in alkaline and saline environment. Zeolites 2(4):295–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-2449(82)80073-0
Plessis PWD, Ojumu TV, Petrik LF (2013) Waste minimization protocols for the process of synthesizing zeolites from South African coal fly ash. Mater 6:1688–1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6051688
Ren XU, Qu RY, Liu SJ, Zhao HT, Wu WH, Song H, Zheng CH, Wu SC, Gao X (2020) Synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash for the removal of harmful gaseous pollutants: a review. Aerosol Air Qual Res 20:1127–1144. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2019.12.0651
Rodrigues M, Souza AG, Santos IMG (2016) Brazilian kaolin wastes: synthesis of zeolite p at low-temperature. Chem Sci Inter J 12(4):1–11. https://doi.org/10.9734/ACSJ/2016/22771
Rujiwatra A (2004) A selective preparation of phillipsite and sodalite from perlite. Mater Lett 58(14):2012–2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2003.12.015
Wu D, Zhang BH, Yan L, Kong HN, Wang XZ (2006) Effect of some additives on synthesis of zeolite from coal fly ash. Int J Miner Process 80(2):266–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2006.05.005
Yu Y, Xiong G, Li C, Xiao FS (2001) Characterization of aluminosilicate zeolites by UV Raman spectroscopy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 46(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(01)00271-2
Yuan P, He HP, Wu DQ, Wang DQ, Chen LJ (2004) Characterization of diatomaceous silica by Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 60(12):2941–2945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2004.02.005
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Wei-The Jiang and Prof. Jennifer Kung of the Department of Earth Sciences in National Cheng Kung University for the help with XRD measurements and Raman analyses, respectively. We sincerely thank to the Ministry of Science and Technology for the financial support [MOST 107-2116-M-006-002].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, TL., Chen, YH. & Hsu, WD. Phase transition pathway of hydrothermal zeolite synthesis. Phys Chem Minerals 48, 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-020-01125-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-020-01125-3