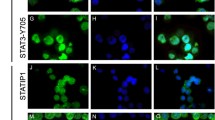
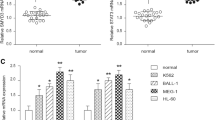
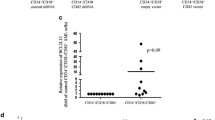
Abstract
Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins are latent cytoplasmic transcription factors that affect several cellular processes including cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Following phosphorylation, STATs are activated, and their upregulated expressions increase in malignancies with playing a role in the development of leukemia. In this study, transfection of K–562 cells with either unmodified or chemically modified anti-STAT3, -STAT5A, -STAT5B siRNAs for duration of 12 days, determining gene silencing at mRNA and protein levels, evaluating apoptosis rate, and detecting JAK/STAT pathway members’ gene expression profiles via array method were aimed. Quantitative RT-PCR and Western blot assays indicated that STAT expressions were downregulated both at mRNA and protein levels, and TUNEL assay showed that leukemic cell apoptosis was induced due to inhibition of STATs. Array analysis resulted with decreases in signal transducer, phosphorylation inducer, and oncogene expressions, whereas increased expressions in STAT inhibitor and apoptosis inducer genes were observed. These results point out that siRNA application could constitute a new and alternative curative method for supporting therapy of CML-diagnosed patients in the future.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melo JV, Hughes TP, Apperley JF (2003) Chronic myeloid leukemia. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 1:132–152
Kantarjian H, Melo JV, Tura S, Giralt S, Talpaz M (2000) Chronic myelogenous leukemia: disease biology and current and future therapeutic strategies. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 1:90–109
Kantarjian H, Talpaz M, Giles F, O'Brien S, Cortes J (2006) New insights into the pathophysiology of chronic myeloid leukemia and imatinib resistance. Ann Intern Med 145(12):913–923
Vaidya S, Ghosh K, Vundinti BR (2011) Recent developments in drug resistance mechanism in chronic myeloid leukemia: a review. Eur J Haematol 87(5):381–393
Valentino L, Pierre J (2006) JAK/STAT signal transduction: regulators and implication in hematological malignancies. Biochem Pharmacol 71(6):713–721
Rawlings JS, Rosler KM, Harrison DA (2004) The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 8):1281–1283
Levy DE, Gilliland DG (2000) Divergent roles of STAT1 and STAT5 in malignancy as revealed by gene disruptions in mice. Oncogene 19(21):2505–2510
Bromberg JF, Horvath CM, Wen Z, Schreiber RD, Darnell JE Jr (1996) Transcriptionally active Stat1 is required for the antiproliferative effects of both interferon alpha and interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(15):7673–7678
Yu H, Jove R (2004) The STATs of cancer—new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer 4(2):97–105
Ilaria RL Jr, Van Etten RA (1996) P210 and P190(BCR/ABL) induce the tyrosine phosphorylation and DNA binding activity of multiple specific STAT family members. J Biol Chem 271(49):31704–31710
Donato NJ, Wu JY, Zhang L, Kantarjian H, Talpaz M (2001) Down-regulation of interleukin-3/granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor beta-chain in BCR-ABL(+) human leukemic cells: association with loss of cytokine-mediated Stat-5 activation and protection from apoptosis after BCR-ABL inhibition. Blood 97(9):2846–2853
Nieborowska-Skorska M, Wasik MA, Slupianek A, Salomoni P, Kitamura T, Calabretta B, Skorski T (1999) Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)5 activation by BCR/ABL is dependent on intact Src homology (SH)3 and SH2 domains of BCR/ABL and is required for leukemogenesis. J Exp Med 189(8):1229–1242
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Moscinski L, Fernández-Luna JL, Nuñez G, Dalton WS, Jove R (1999) Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity 10(1):105–115
Jing N, Tweardy DJ (2005) Targeting Stat3 in cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 16(6):601–607
Benekli M, Baumann H, Wetzler M (2009) Targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway in leukemias. J Clin Oncol 27(26):4422–4432
Whitehead KA, Langer R, Anderson DG (2009) Knocking down barriers: advances in siRNA delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8(2):129–138
Chiu YL, Rana TM (2003) siRNA function in RNAi: a chemical modification analysis. RNA 9(9):1034–1048
Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J, Jove R (2000) STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene 19(21):2474–2488
Schindler T, Bornmann W, Pellicena P, Miller WT, Clarkson B, Kuriyan J (2000) Structural mechanism for STI-571 inhibition of abelson tyrosine kinase. Science 289(5486):1938–1942
Crombez L, Aldrian-Herrada G, Konate K, Nguyen QN, McMaster GK, Brasseur R, Heitz F, Divita G (2009) A new potent secondary amphipathic cell-penetrating peptide for siRNA delivery into mammalian cells. Mol Ther 17(1):95–103
Buettner R, Mora LB, Jove R (2002) Activated STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for therapeutic intervention. Clin Cancer Res 8(4):945–954
Chai SK, Nichols GL, Rothman P (1997) Constitutive activation of JAKs and STATs in BCR-Abl-expressing cell lines and peripheral blood cells derived from leukemic patients. J Immunol 159(10):4720–4728
Kosova B, Tezcanli B, Ekiz HA, Cakir Z, Selvi N, Dalmizrak A, Kartal M, Gunduz U, Baran Y (2010) Suppression of STAT5A increases chemotherapeutic sensitivity in imatinib-resistant and imatinib-sensitive K562 cells. Leuk Lymphoma 51(10):1895–1901
Nowicki MO, Pawlowski P, Fischer T, Hess G, Pawlowski T, Skorski T (2003) Chronic myelogenous leukemia molecular signature. Oncogene 22(25):3952–3963
Piva R, Pellegrino E, Mattioli M, Agnelli L, Lombardi L, Boccalatte F, Costa G, Ruggeri BA, Cheng M, Chiarle R, Palestro G, Neri A, Inghirami G (2006) Functional validation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase signature identifies CEBPB and BCL2A1 as critical target genes. J Clin Invest 116(12):3171–3182
Quentmeier H, Geffers R, Jost E, Macleod RA, Nagel S, Röhrs S, Romani J, Scherr M, Zaborski M, Drexler HG (2008) SOCS2: inhibitor of JAK2V617F-mediated signal transduction. Leukemia 22(12):2169–2175
Guerzoni C, Bardini M, Mariani SA, Ferrari-Amorotti G, Neviani P, Panno ML, Zhang Y, Martinez R, Perrotti D, Calabretta B (2006) Inducible activation of CEBPB, a gene negatively regulated by BCR/ABL, inhibits proliferation and promotes differentiation of BCR/ABL-expressing cells. Blood 107(10):4080–4089
Ulger C, Toruner GA, Alkan M, Mohammed M, Damani S, Kang J, Galante A, Aviv H, Soteropoulos P, Tolias PP, Schwalb MN, Dermody JJ (2003) Comprehensive genome-wide comparison of DNA and RNA level scan using microarray technology for identification of candidate cancer-related genes in the HL-60 cell line. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 147(1):28–35
Segatto O, Anastasi S, Alemà S (2011) Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signalling by inducible feedback inhibitors. J Cell Sci 124(11):1785–1793
Shim MS, Kwon YJ (2010) Efficient and targeted delivery of siRNA in vivo. FEBS J 277(23):4814–4827
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Vildan Bozok ÇETİNTAŞ, Phd (Ege University Medical School, of Medical Biology Department) for the great help in creating figures of the manuscript. This work was supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey, by the Turkish Society of Hematology, and Ege University Medical School Scientific Research Projects (TUBITAK 105S459, THD 200–02/08 and APAK 2010-TIP–004 respectively, to BK).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 273 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaymaz, B.T., Selvi, N., Gündüz, C. et al. Repression of STAT3, STAT5A, and STAT5B expressions in chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K–562 with unmodified or chemically modified siRNAs and induction of apoptosis. Ann Hematol 92, 151–162 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1575-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1575-2