Abstract
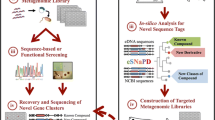
Soil has the largest population of microbes of any habitat, but only about 0.3% of soil microbes are cultivable with current techniques. Cultured soil microbes have been an incredibly productive source of drugs, for example the cancer chemotherapeutics doxorubicin hydrochloride, bleomycin, daunorubicin and mitomycin. Unfortunately, the current yield of new drugs from soil microbes is low due to repeated cultivation of the same small fraction of cultivable microbes. Uncultured soil species represent a tremendous untapped resource of new antineoplastic agents. Methods have recently been developed to access the diversity of secondary metabolites from uncultured soil microbes. Briefly, total DNA is extracted from soil samples, purified, partially digested, and fragments inserted into vectors for expression in readily fermented microbes such as Escherichia coli. Clones expressing enzymatic and antibiotic activities that are encoded by novel sequences have been reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonowitz Y, Cohen G, Martin JF (1992) Penicillin and cephalosporin biosynthetic genes: structure, organization, regulation, and evolution. Annu Rev Microbiol 46:461
Barns SM, Fundyga RE, Jeffries MW, Pace NR (1994) Remarkable archaeal diversity detected in a Yellowstone National Park hot spring environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:1609
Brady SF, Clardy J (2000) Long-chain N-acyl amino acid antibiotics isolated from heterologously expressed environmental DNA. J Am Chem Soc 122:12903
Brady SF, Chao CJ, Handelsman J, Clardy J (2001) Cloning and heterologous expression of a natural product biosynthetic gene cluster from eDNA. Org Lett 3:1981
Brosch R, Gordon SV, Billault A, Garnier T, Eiglmeier K, Soravito C, Barrell BG, Cole ST (1998) Use of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv bacterial artificial chromosome library for genome mapping, sequencing, and comparative genomics. Infect Immun 66:2221
Bull AT, Goodfellow M, Slater JH (1992) Biodiversity as a source of innovation in biotechnology. Annu Rev Microbiol 46:219
Bull AT, Ward AC, Goodfellow M (2000) Search and discovery strategies for biotechnology: the paradigm shift. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:573
Burgmann H, Pesaro M, Widmer F, Zeyer J (2001) A strategy for optimizing quality and quantity of DNA extracted from soil. J Microbiol Methods 45:7
Bycroft BW (1988) Dictionary of antibiotics and related substances. Chapman and Hall, University Press, Cambridge, UK
Chater KF, Bruton CJ (1985) Resistance, regulatory and production genes for the antibiotic methylenomycin are clustered. EMBO J 4:1893
Christian MC, Pluda JM, Ho PTC, Arbuck SG, Murgo AJ, Sausville EA (1997) Promising new agents under development by the Division of Cancer Treatment, Diagnosis, and Centers of the National Cancer Institute. Semin Oncol 24:219
Clark AM (1996) Natural products as a resource for new drugs. Pharm Res 13:1133
Cragg GM, Newman DJ (2000) Antineoplastic agents from natural sources: achievements and future directions. Exp Opin Invest Drugs 9:2783
Distler J, Braun C, Ebert A, Piepersberg W (1987) Gene cluster for streptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces griseus: analysis of a central region including the major resistance gene. Mol Gen Genet 208:204
Donadio S, Staver MJ, McAlpine JB, Swanson SJ, Katz L (1991) Modular organization of genes required for complex polyketide biosynthesis. Science 252:675
Gillespie DE, Brady SF, Bettermann AD, Cianciotto NP, Liles MR, Rondon MR, Clardy J, Goodman RM, Handelsman J (2002) Isolation of antibiotics turbomycin A and B from a metagenomic library of soil microbial DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1
Gillespie DE, Rondon MR, Handelsman J (2004) Metagenomic libraries from uncultured microorganisms. In: Osborn AM (ed) Molecular microbial ecology. BIOS Scientific Publishers, Oxford (in press)
Hammond PM (1995) Described and estimated species numbers: an objective assessment of current knowledge. In: Microbial diversity and ecosystem function: proceedings of the IUBS/IUMS workshop, Egham, UK. University Press, Cambridge, UK, p 29
Handelsman J, Rondon MR, Brady SF, Clardy J, Goodman RM (1998) Molecular biological access to the chemistry of unknown soil microbes: a new frontier for natural products. Chem Biol 5:R245
Handelsman J, Liles M, Mann D, Riesenfeld C, Goodman RM (2002) Cloning the metagenome: culture-independent access to the diversity and functions of the uncultivated microbial world. Methods Microbiol 33:241
Hawksworth DL (1991) The fungal dimension of biodiversity: magnitude, significance, and conservation. Mycol Res 95:641
Henne A, Daniel R, Schmitz RA, Gottschalk G (1999) Construction of environmental DNA libraries in Escherichia coli and screening for the presence of genes conferring utilization of 4-hydroxybutyrate. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3901
Henne A, Schmitz RA, Bömeke M, Gottschalk G, Daniel R (2000) Screening of environmental DNA libraries for the presence of genes conferring lipolytic activity on Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3113
Holben WE, Jansson JK, Chelm BK, Tiedje JM (1988) DNA probe method for the detection of specific microorganisms in the soil bacterial community. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:703
Hopwood DA (1999) Forty years of genetics with Streptomyces: from in vivo through in vitro to in silico. Microbiology 145:2183
Hugenholtz P, Goebel BM, Pace NR (1998) Impact of culture-independent studies on the emerging phylogenetic view of bacterial diversity. J Bacteriol 180:4765
Hugenholtz P, Pitulle C, Hershberger KL, Pace NR (1998) Novel division level bacterial diversity in a Yellowstone hot spring. J Bacteriol 180:366
Kaeberlein T, Lewis K, Epstein SS (2002) Isolating “uncultivable” microorganisms in pure culture in a simulated natural environment. Science 296:1127
Khosla C (2000) Natural product biosynthesis: a new interface between enzymology and medicine. J Org Chem 65:8127
Liles MR, Manske BF, Bintrim SB, Handelsman J, Goodman RM (2003) A census of rRNA genes and linked genomic sequences within a soil metagenomic library. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2684
Lomovskaya N, Doi-Katayama Y, Filippini S, Nastro C, Fonstein L, Gallo M, Colombo AL, Hutchinson CR (1998) The Streptomyces peucetius dpsY and dnrX genes govern early and late steps of daunorubicin and doxorubicin biosynthesis. J Bacteriol 180:2379
MacNeil IA, Tiong CL, Minor C, August PR, Grossman TH, Loiacono KA, Lynch BA, Phillips T, Narula S, Sundaramoorthi R, Tyler A, Aldredge T, Long H, Gilman M, Holt D, Osburne MS (2001) Expression and isolation of antimicrobial small molecules from soil DNA libraries. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 3:301
Majernik A, Gottschalk G, Daniel R (2001) Screening of environmental DNA libraries for the presence of genes conferring Na+(Li+)/H+ antiporter activity on Escherichia coli: characterization of the recovered genes and the corresponding gene products. J Bacteriol 183:6645
Martín JF (1992) Clusters of genes for the biosynthesis of antibiotics: regulatory genes and overproduction of pharmaceuticals. J Ind Microbiol 9:73
Martín JF, Liras P (1989) Organization and expression of genes involved in the biosynthesis of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites. Annu Rev Microbiol 43:173
Pace NR (1997) A molecular view of microbial diversity and the biosphere. Science 276:734
Quaiser A, Ochsenreiter T, Klenk H-P, Kletzin A, Treusch AH, Meurer G, Eck J, Sensen CW, Schleper C (2002) First insight into the genome of an uncultivated crenarchaeote from soil. Environ Microbiol 4:603
Ritz K, Griffiths BS, Torsvik VL, Hendriksen NB (1997) Analysis of soil and bacterioplankton community DNA by melting profiles and reassociation kinetics. FEMS Microbiol Lett 149:151
Rondon MR, Raffel SJ, Goodman RM, Handelsman J (1999) Toward functional genomics in bacteria: analysis of gene expression in Escherichia coli from a bacterial artificial chromosome library of Bacillus cereus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:6451
Rondon MR, August PR, Bettermann AD, Brady SF, Grossman TH, Liles MR, Loiacono KA, Lynch BA, MacNeil IA, Minor C, Tiong CL, Gilman M, Osburne MS, Clardy J, Handelsman J, Goodman RM (2000) Cloning the soil metagenome: a strategy for accessing the genetic and functional diversity of uncultured microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2541
Sheng Y, Mancino V, Birren B (1995) Transformation of Escherichia coli with large DNA molecules by electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res 23:1990
Shizuya H, Birren B, Kim U-J, Mancino V, Slepak T, Tachiiri Y, Simon M (1992) Cloning and stable maintenance of 300-kilobase-pair fragments of human DNA in Escherichia coli using an F-factor-based vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:8794
Sosio M, Giusino FA, Cappellano C, Bossi E, Puglia AM, Donadio S (2000) Artificial chromosomes for antibiotic-producing actinomycetes. Nat Biotechnol 18:343
Stackebrandt E, Liesack W, Goebel BM (1993) Bacterial diversity in a soil sample from a subtropical Australian environment as determined by 16S rDNA analysis. FASEB J 7:232
Steffan RJ, Goksøyr J, Bej AK, Atlas RM (1988) Recovery of DNA from soils and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2908
Stein JL, Marsh TL, Wu KY, Shizuya H, DeLong EF (1996) Characterization of uncultivated prokaryotes: isolation and analysis of a 40-kilobase-pair genome fragment from a planktonic marine archaeon. J Bacteriol 178:591
Torsvik V, Goksøyr J, Daae FL (1990) High diversity in DNA of soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:782
Torsvik V, Sørheim R, Goksøyr J (1996) Total bacterial diversity in soil and sediment communities—a review. J Ind Microbiol 17:170
Van den Hondel, CAMJJ, Punt PJ, van Gorcom RFM (1991) Heterologous gene expression in filamentous fungi. In: Bennett JW, Lasure LL (eds) More gene manipulations in fungi. Academic Press, San Diego, p 396
Whitman WB, Coleman DC, Wiebe WJ (1998) Prokaryotes: the unseen majority. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:6578
Zhou J, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:316
Zhou J, Davey ME, Figueras JB, Rivkina E, Gillichinsky D, Tiedje JM (1997) Phylogenetic diversity of a bacterial community determined from Siberian tundra soil DNA. Microbiology 143:3913
Acknowledgements
This paper is dedicated to Professor G.R. Pettit, who pioneered another productive source of antineoplastic agents, marine natural products.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pettit, R.K. Soil DNA libraries for anticancer drug discovery. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 54, 1–6 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-004-0771-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-004-0771-8