Abstract
Purpose
Although sorafenib has been approved for treating advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), its high cost, frequent adverse events, and unsatisfactory efficacy remain unresolved. We evaluated the efficacy and safety of the combination treatment of localized concurrent chemoradiation therapy (CCRT) for locally advanced HCC with portal vein thrombosis (PVT) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for intrahepatic metastasis.
Methods
Between January 2006 and June 2011, 30 patients with HCC with portal vein invasion and intrahepatic metastasis were enrolled. After TACE for intrahepatic metastasis, localized CCRT (45 Gy over 5 weeks with conventional fractionation and hepatic artery infusional chemotherapy using 5-fluorouracil as a radiosensitizer, administered during the first and fifth weeks of radiotherapy) was used to treat main HCC with PVT. The modified response evaluation criteria in solid tumors (mRECIST) were used to evaluate tumor response.
Results
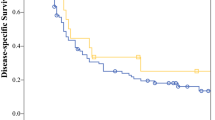
The median age of the patients (26 men, 4 women) was 51 years. Objective response rates were 30.0 % (9/30) and 32.1 % (9/28) in the intention-to-treat and per protocol analyses, respectively. The median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 4.5 and 9.8 months, respectively. Baseline α-fetoprotein (AFP) correlated significantly with PFS (P = 0.008), whereas baseline AFP, completion of the protocol, and overall radiological response influenced OS significantly (all P < 0.05). All adverse events were predictable and manageable with conservative care.
Conclusions
Combination treatment of localized CCRT and TACE was effective and tolerable in patients with locally advanced HCC with PVT and intrahepatic metastasis. This protocol may be an alternative option when sorafenib cannot be prescribed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kudo M (2010) The 2008 Okuda lecture: management of hepatocellular carcinoma: from surveillance to molecular targeted therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25(3):439–452. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06207.x
Yuen MF, Hou JL, Chutaputti A, Asia Pacific Working Party on Prevention of Hepatocellular C (2009) Hepatocellular carcinoma in the Asia pacific region. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24(3):346–353. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05784.x
Kim SU, Kim YR, Kim do Y, Kim JK, Lee HW, Kim BK, Han KH, Chon CY, Moon YM, Ahn SH (2007) Clinical features and treatment outcome of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with inferior vena caval invasion or atrial tumor thrombus. Korean J Hepatol 13(3):387–395
Han KH, Seong J, Kim JK, Ahn SH, Lee do Y, Chon CY (2008) Pilot clinical trial of localized concurrent chemoradiation therapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis. Cancer 113(5):995–1003. doi:10.1002/cncr.23684
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Haussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J, Group SIS (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. The New England Journal of Medicine 359(4):378–390. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, Liu J, Wang J, Tak WY, Pan H, Burock K, Zou J, Voliotis D, Guan Z (2009) Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10(1):25–34. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(08)70285-7
Bruix J, Sherman M, American Association for the Study of Liver D (2011) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 53(3):1020–1022. doi:10.1002/hep.24199
Trevisani F, De Notariis S, Rossi C, Bernardi M (2001) Randomized control trials on chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: is there room for new studies? J Clin Gastroenterol 32(5):383–389
Lo CM, Ngan H, Tso WK, Liu CL, Lam CM, Poon RT, Fan ST, Wong J (2002) Randomized controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 35(5):1164–1171. doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.33156
Llovet JM, Real MI, Montana X, Planas R, Coll S, Aponte J, Ayuso C, Sala M, Muchart J, Sola R, Rodes J, Bruix J, Barcelona Liver Cancer G (2002) Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 359(9319):1734–1739. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08649-x
Park JY, Ahn SH, Yoon YJ, Kim JK, Lee HW, Lee do Y, Chon CY, Moon YM, Han KH (2007) Repetitive short-course hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with high-dose 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 110(1):129–137. doi:10.1002/cncr.22759
Robertson JM, Lawrence TS, Dworzanin LM, Andrews JC, Walker S, Kessler ML, DuRoss DJ, Ensminger WD (1993) Treatment of primary hepatobiliary cancers with conformal radiation therapy and regional chemotherapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology: Official Journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 11(7):1286–1293
Seong J, Keum KC, Han KH, Lee DY, Lee JT, Chon CY, Moon YM, Suh CO, Kim GE (1999) Combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and local radiotherapy of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43(2):393–397
Park JW (2005) Hepatocellular carcinoma in Korea: introduction and overview. The Korean journal of gastroenterology 45(4):217–226
Seong J, Park HC, Han KH, Chon CY, Chu SS, Kim GE, Suh CO (2003) Clinical results of 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy combined with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic patients. Hepatology Research: The Official Journal of the Japan Society of Hepatology 27(1):30–35
Lencioni R, Llovet JM (2010) Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 30(1):52–60. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1247132
Kim DY, Ryu HJ, Choi JY, Park JY, Lee DY, Kim BK, Kim SU, Ahn SH, Chon CY, Han KH (2012) Radiological response predicts survival following transarterial chemoembolisation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 35(11):1343–1350. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2012.05089.x
Ando E, Yamashita F, Tanaka M, Tanikawa K (1997) A novel chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombosis of the main trunk of the portal vein. Cancer 79(10):1890–1896
Shim JH, Lee HC, Kim SO, Shin YM, Kim KM, Lim YS, Suh DJ (2012) Which response criteria best help predict survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma following chemoembolization? A validation study of old and new models. Radiology 262(2):708–718. doi:10.1148/radiol.11110282
Llovet JM, Di Bisceglie AM, Bruix J, Kramer BS, Lencioni R, Zhu AX, Sherman M, Schwartz M, Lotze M, Talwalkar J, Gores GJ, Panel of Experts in HCCDCT (2008) Design and endpoints of clinical trials in hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 100(10):698–711. doi:10.1093/jnci/djn134
Cuesta L, Betlloch I, Toledo F, Latorre N, Monteagudo A (2011) Severe sorafenib-induced hand-foot skin reaction. Dermatol Online J 17(5):14
Lee HC (2008) Systemic chemotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma—Korean experience. Oncology 75(Suppl 1):114–118. doi:10.1159/000173432
Park HC, Seong J, Han KH, Chon CY, Moon YM, Suh CO (2002) Dose-response relationship in local radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 54(1):150–155
Ando E, Tanaka M, Yamashita F, Kuromatsu R, Yutani S, Fukumori K, Sumie S, Yano Y, Okuda K, Sata M (2002) Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: analysis of 48 cases. Cancer 95(3):588–595. doi:10.1002/cncr.10694
Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Ohmori S, Shiraki K, Nakano T, Ikoma J, Adachi Y, Takeda K (2002) Radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment response based on tumor size and morphology. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology JVIR 13(12):1225–1232
Fujiyama S, Tanaka M, Maeda S, Ashihara H, Hirata R, Tomita K (2002) Tumor markers in early diagnosis, follow-up and management of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 62(Suppl 1):57–63
Shim JH, Lee HC, Won HJ, Shin YM, Kim KM, Lim YS, Suh DJ (2012) Maximum number of target lesions required to measure responses to transarterial chemoembolization using the enhancement criteria in patients with intrahepatic hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 56(2):406–411. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2011.04.028
Iwasa S, Ikeda M, Okusaka T, Ueno H, Morizane C, Nakachi K, Mitsunaga S, Kondo S, Hagihara A, Shimizu S, Satake M, Arai Y (2011) Transcatheter arterial infusion chemotherapy with a fine-powder formulation of cisplatin for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma refractory to transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41(6):770–775. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyr037
Nagano H, Wada H, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Eguchi H, Tanemura M, Tomimaru Y, Osuga K, Umeshita K, Doki Y, Mori M (2011) Long-term outcome of combined interferon-alpha and 5-fluorouracil treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with major portal vein thrombosis. Oncology 80(1–2):63–69. doi:10.1159/000328281
Siringo S, Burroughs AK, Bolondi L, Muia A, Di Febo G, Miglioli M, Cavalli G, Barbara L (1995) Peptic ulcer and its course in cirrhosis: an endoscopic and clinical prospective study. J Hepatol 22(6):633–641
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (A102065) and by a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry for Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (0620390).
Conflict of interest
None to declare from all authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. S. Park and S. U. Kim are co-first authors of this article, and have contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

280_2012_1993_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary figure 1. CT findings of PR (A), SD (B), and PD (C) after localized CCRT and TACE (arterial phase). A: After treatment, the diameter of main HCC with PVT showing arterial enhancement significantly decreased (PR) and intrahepatic metastatic HCCs showed compact lipiodolization (CR, white arrow). A hemangioma was noted at segment 4. B: Although intrahepatic metastatic lesion showed compact lipiodolization after treatment (CR, white arrow), the diameter of main HCC with PVT showing arterial enhancement did not decreased (from 7.5 to 7.2 cm; 4.0% decrease; SD) enough to meet the criteria of PR. Thus, overall response was SD. C: After treatment, the diameter of main HCC with PVT showing arterial enhancement increased (from 11.8 to 14.5 cm; 22.4% increase; PD) although intrahepatic metastatic lesion showed compact lipiodolization (CR, white arrow). Thus, overall response was PD. (JPEG 131 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, M.S., Kim, S.U., Park, J.Y. et al. Combination treatment of localized concurrent chemoradiation therapy and transarterial chemoembolization in locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with intrahepatic metastasis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 71, 165–173 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-1993-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-1993-9