Abstract
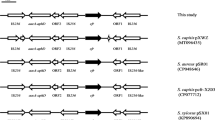
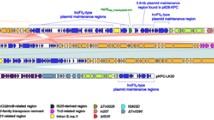
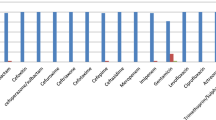
From June, 2012 to November, 2013 five linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus cohnii isolates were identified in our hospital in Beijing, China. The investigation of the resistance mechanisms confirmed that the cfr-carrying plasmids were the main cause of linezolid resistance in those clinical isolates. Moreover, all the five isolates had ribosomal protein L3 mutations, which had different coordinate effect on cfr-mediated linezolid resistance directly through the substitution of serine 158 by phenylalanine or tyrosine in L3 protein. In this study, two types of plasmids (p432, p438) (Accession No. KM114207) were found, which share high sequence identity with previously reported cfr-carrying pRM01 and pMHZ plasmids originated from northern and southern China, showing wide regional dissemination in China. The stability of linezolid resistance was studied by passaging single colonies serially on antibiotic-free blood medium, which showed that the susceptible derivatives emerged until the passages 39–42 with the elimination of cfr-carrying plasmid. Thus the high stability of this plasmid may pose a risk for the transmission among patients or even cause an outbreak in clinical settings.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mendes RE, Deshpande LM, Farrell DJ, Spanu T, Fadda G, Jones RN (2010) Assessment of linezolid resistance mechanisms among Staphylococcus epidermidis causing bacteraemia in Rome, Italy. J Antimicrob Chemother 65:2329–2335
Long KS, Poehlsgaard J, Kehrenberg C, Schwarz S, Vester B (2006) The Cfr rRNA methyltransferase confers resistance to phenicols, lincosamides, oxazolidinones, pleuromutilins, and streptogramin A antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:2500–2505
Toh SM, Xiong L, Arias CA, Villegas MV, Lolans K, Quinn J, Mankin AS (2007) Acquisition of a natural resistance gene renders a clinical strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus resistant to the synthetic antibiotic linezolid. Mol Microbiol 64:1506–1514
Zhao C, Sun H, Wang H, Liu Y, Hu B, Yu Y, Sun Z, Chu Y, Cao B, Liao K, Lei J, Hu Z, Zhang L, Zhang X, Xu Y, Wang Z, Chen M (2012) Antimicrobial resistance trends among 5608 clinical Gram-positive isolates in China: results from the Gram-Positive Cocci Resistance Surveillance program (2005-2010). Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 73:174–181
CLSI (2012) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twenty-second informational supplement. CLSI document M100-S22. 32:70
Murchan S, Kaufmann ME, Deplano A, de Ryck R, Struelens M, Zinn CE, Fussing V, Salmenlinna S, Vuopio-Varkila J, El Solh N, Cuny C, Witte W, Tassios PT, Legakis N, van Leeuwen W, van Belkum A, Vindel A, Laconcha I, Garaizar J, Haeggman S, Olsson-Liljequist B, Ransjo U, Coombes G, Cookson B (2003) Harmonization of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis protocols for epidemiological typing of strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a single approach developed by consensus in 10 European laboratories and its application for tracing the spread of related strains. J Clin Microbiol 41:1574–1585
Wang Y, Zhang W, Wang J, Wu C, Shen Z, Fu X, Yan Y, Zhang Q, Schwarz S, Shen J (2012) Distribution of the multidrug resistance gene cfr in Staphylococcus species isolates from swine farms in China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:1485–1490
Chen H, Wu W, Ni M, Liu Y, Zhang J, Xia F, He W, Wang Q, Wang Z, Cao B, Wang H (2013) Linezolid-resistant clinical isolates of enterococci and Staphylococcus cohnii from a multicentre study in China: molecular epidemiology and resistance mechanisms. Int J Antimicrob Agents 42:317–321
Liu Y, Wang Y, Schwarz S, Li Y, Shen Z, Zhang Q, Wu C, Shen J (2013) Transferable multiresistance plasmids carrying cfr in Enterococcus spp. from swine and farm environment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:42–48
Wilson DN, Schluenzen F, Harms JM, Starosta AL, Connell SR, Fucini P (2008) The oxazolidinone antibiotics perturb the ribosomal peptidyl-transferase center and effect tRNA positioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13339–13344
Yang XJ, Chen Y, Yang Q, Qu TT, Liu LL, Wang HP, Yu YS (2013) Emergence of cfr-harbouring coagulase-negative staphylococci among patients receiving linezolid therapy in two hospitals in China. J Med Microbiol 62:845–850
Miller K, Dunsmore CJ, Fishwick CW, Chopra I (2008) Linezolid and tiamulin cross-resistance in Staphylococcus aureus mediated by point mutations in the peptidyl transferase center. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:1737–1742
Locke JB, Morales G, Hilgers M, G CK, Rahawi S, Jose Picazo J, Shaw KJ, Stein JL (2010) Elevated linezolid resistance in clinical cfr-positive Staphylococcus aureus isolates is associated with co-occurring mutations in ribosomal protein L3. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:5352–5355
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Project Grant [2012AA02A511] from National High Technology Research and Development Program, China, and Project Grant [Z121107005112003] from the Applied Research Program of Capital Clinical Features, Wujieping Medical Foundation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hongtao Xu and Rui Tian contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Tian, R., Li, Y. et al. Ribosomal Protein L3 Mutations are Associated with cfr-Mediated Linezolid Resistance in Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus cohnii . Curr Microbiol 70, 840–845 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0793-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0793-y