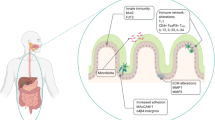
Abstract
Many studies have been performed to determine the interaction between bacterial species and cancer. However, there has been no attempts to demonstrate a possible relationship between Enterobacter spp. and colon cancer so far. Therefore, in the present study, it is aimed to investigate the effects of Enterobacter strains on colon cancer. Bacterial proteins were isolated from 11 Enterobacter spp., one Morganella morganii, and one Escherichia coli strains, and applied onto NCM460 (Incell) and CRL1790 (ATCC) cell lines. Cell viability and proliferation were determined in MTS assay. Flow Cytometry was used to detect CD24 level and apoptosis. Real-Time PCR studies were performed to determine NFKB and Bcl2 expression. Graphpad Software was used for statistical analysis. The results showed that proteins, isolated from the Enterobacter spp., have significantly increased cell viability and proliferation, while decreasing the apoptosis of the cell lines tested. The data in the present study indicated that Enterobacter strains might promote colon cancer. Moreover, Enterobacter spp. could be a clinically important factor for colon cancer initiation and progression. Studies can be extended on animal models in order to develop new strategies for treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Macfarlane GT, Fite A, McBain AJ, Gilbert P, Macfarlane S (2007) Mucosa-associated bacterial diversity in relation to human terminal ileum and colonic biopsy samples. Appl Environ Microb 73(22):7435–7442. doi:10.1128/Aem.01143-07
Balish E, Warner T (2002) Enterococcus faecalis induces inflammatory bowel disease in interleukin-10 knockout mice. Am J Pathol 160(6):2253–2257
Biarc J, Nguyen IS, Pini A, Gosse F, Richert S, Thierse D, Van DA, Leize-Wagner E, Raul F, Klein JP, Scholler-Guinard M (2004) Carcinogenic properties of proteins with pro-inflammatory activity from Streptococcus infantarius (formerly S. bovis). Carcinogenesis 25(8):1477–1484. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgh091
Breathnach SARA, Shad S, Jownally MS, Law R, Chin CP, Kaufmann EM, Smith JE (2006) An outbreak of wound infection in cardiac surgery patients caused by Enterobacter cloacae arising from cardioplegia ice. J Hosp Infect 64:124–128
Bronner PMCC, Reed CJ, Furth EE (1995) The Bcl2 protooncogene and the gastrointestinal epithelial tumor progression model. AJP January 146(1):20–26
Buyer JS (2002) Rapid sample processing and fast gas chromatography for identification of bacteria by fatty acid analysis. J Microbiol Meth 51(2):209–215. doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(02)00081-7
Choi YXH, Lee S, Park MS, Kim JW, Kim H, Kim S (2006) Enhanced CD24 expression in colorectal cancer correlates with prognostic factors. Korean J Pathol 40:103–111
Cotter TG (2009) Apoptosis and cancer: the genesis of a research field. Nat Rev Cancer 9(7):501–507
Datasheet BT FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit 1
Dolcet XLD, Pallares J, Matras-Guiu X (2005) NFKB in development and progression of human cancer. Virchows Arch 446:475–482
Faherty CS, Maurelli AT (2008) Staying alive: bacterial inhibition of apoptosis during infection. Trends Microbiol 16(4):173–180
Grimont F, Grimont PA (2006) The genus Enterobacter. The prokaryotes. Springer, New York, pp 197–214
Hao LW, Lee YK (2004) Microflora of the gastrointestinal tract: a review. Methods in molecular biology, public health microbiology methods and protocols, vol 268. Humana Press, Totowa
Higgins DG, Bleasby AJ, Fuchs R (1992) CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci CABIOS 8(2):189–191
Huerta S, Goulet EJ, Livingston EH (2006) Colon cancer and apoptosis. Am J Surg 191(4):517–526
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP-phylogeny inference package (Version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Kojima M, Morisaki T, Sasaki N, Nakano K, Mibu R, Tanaka M, Katano M (2004) Increased nuclear factor-kB activation in human colorectal carcinoma and its correlation with tumor progression. Anticancer Res 24(2B):675–682
Laurila AL, Anttila T, Laara E, Bloigu A, Virtamo J, Albanes D, Leinonen M, Saikku P (1997) Serological evidence of an association between Chlamydia pneumoniae infection and lung cancer. Int J Cancer 74(1):31–34. doi:10.1002/(Sici)1097-0215(19970220)74
Lax AJ (2005) Bacterial toxins and cancer: a case to answer? Nat Rev Microbiol 3(4):343–349. doi:10.1038/Nrmicro1130
Lax AJ, Thomas W (2002) How bacteria could cause cancer: one step at a time. Trends Microbiol 10(6):293–299. doi:10.1016/S0966-842x(02)02360-0
Levine DS, Haggitt RC (1989) Normal histology of the colon. Am J Surg Pathol 13(11):966–984. doi:10.1097/00000478-198911000-00008
Lu H, Ouyang W, Huang C (2006) Inflammation, a key event in cancer development. Mol Cancer Res 4(4):221–233
Martin MHCJ, Hart AC, Mpofu C, Nayar M, Singh R, Englyst H, Williams FH, Rhodes MJ (2004) Enhanced Esherichia coli adherence and invasion in Crohn’s disease and colon cancer. Gastroenterology 127:80–93
Newman JV, Kosaka T, Sheppard BJ, Fox JG, Schauer DB (2001) Bacterial infection promotes colon tumorigenesis in Apc(Min/+) mice. J Infect Dis 184(2):227–230. doi:10.1086/321998
Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP, Chang Y, Vogelman JH, Orentreich N, Sibley RK (1991) Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. New Engl J Med 325(16):1127–1131. doi:10.1056/Nejm199110173251603
Pincus HD (2006) Microbial identification using the Biomerieux Vitek 2 system. Encyclopedia of rapid microbiological methods. Parenteral Drug Association, Bethesda
Riss TL, Moravec RA (1992) Comparison of MTT, XTT and a novel tetrazolium compound for MTS for in vitro proliferation and chemosensitivity assays. Mol Biol Cell 3:184
Rupnarain C, Dlamini Z, Naicker S, Bhoola K (2004) Colon cancer: genomics and apoptotic events. Biol Chem 385(6):449–464
Sagiv E, Memeo L, Karin A, Kazanov D, Jacob-Hirsch J, Mansukhani M, Rechavi G, Hibshoosh H, Arber N (2006) CD24 is a new oncogene, early at the multistep process of colorectal cancer carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 131(2):630–639
Sanders W, Sanders CC (1997) Enterobacter spp.: pathogens poised to flourish at the turn of the century. Clin Microbiol Rev 10(2):220–241
Shishodia S, Aggarwal BB (2004) Nuclear factor-κB: a friend or a foe in cancer? Biochem Pharmacol 68(6):1071–1080
Sinicrope FA, Hart J, Michelassi F, Lee JJ (1995) Prognostic value of bcl-2 oncoprotein expression in stage II colon carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 1(10):1103–1110
Terzić J, Grivennikov S, Karin E, Karin M (2010) Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology 138(6):2101–2114
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22(22):4673–4680
Wang S, Liu Z, Wang L, Zhang X (2009) NF-kappaB signaling pathway, inflammation and colorectal cancer. Cell Mol Immunol 6(5):327–334
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16s ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173(2):697–703
Wilkins A, Kemp K, Ginty M, Hares K, Mallam E, Scolding N (2009) Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor which promotes neuronal survival in vitro. Stem Cell Res 3(1):63–70
Wong RSY (2011) Apoptosis in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-30-87
Wright SC, Zhong J, Larrick JW (1994) Inhibition of apoptosis as a mechanism of tumor promotion. Faseb J 8(9):654–660
Yalvac ME, Yarat A, Mercan D, Rizvanov AA, Palotas A, Sahin F (2013) Characterization of the secretome of human tooth germ stem cells (hTGSCs) reveals neuro-protection by fine-tuning micro-environment. Brain Behav Immun 32:122–130
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Ali Umman Doğan, Nilsu Atay, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Dilek Telci, Prof. Dr. Ufuk Hasdemir, Prof. Dr. Necmettin Sökücü, Prof. Dr. Adile Çevikbaş, and Assoc. Prof. Dr. Ümran Soyoğul Gürer for their help and support. The authors are grateful to INCELL Corporation, LLC for providing NCM460 Cell Lines. The authors also would like to thank Yeditepe University, Genetics and Bioengineering Department and Istanbul Technical University, Scientific Research Foundations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yurdakul, D., Yazgan-Karataş, A. & Şahin, F. Enterobacter Strains Might Promote Colon Cancer. Curr Microbiol 71, 403–411 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0867-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0867-x