Abstract
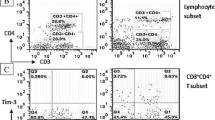
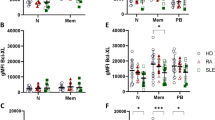
An increased level of apoptotic material and B cell activation leading to autoantibody production are hallmarks of systemic lupus erythematoses (SLE). Increased FAS expression, apoptosis, and CD154-mediated signaling, enabling T–B cell interaction are involved in the pathogenesis of SLE. This study addresses the expression profile of CD154 and FAS in the peripheral blood of patients with SLE, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and normal healthy control donors. Surface markers on peripheral blood T and B cells from patients and healthy control donors were assessed using flow cytometry. The expression of CD154 and FAS were significantly increased in T and B cells of SLE patients as compared to healthy control donors and RA patients. In SLE and RA patients, FAS expression strongly correlated with CD154 expression on T cells, which was not found in healthy control donors. FAS expression was also associated with the occurrence of anti-DNA antibodies. We demonstrate high CD154 and FAS expression as a characteristic feature of SLE. This pattern may reflect simultaneous activation of apoptosis and activation of B–T cell interaction in SLE.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afford SC, Ahmed-Choudhury J, Randhawa S, Russell C, Youster J, Crosby HA, Eliopoulos A, Hubscher SG, Young LS, Adams DH (2001) CD40 activation-induced, Fas-dependent apoptosis and NF-kappaB/AP-1 signaling in human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells. FASEB J 15:2345–2354. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0088com
Aleksandrova EN, Novikov AA, Popkova TV, Reshetniak TM, Novikova DS, Kliukvina NG, Il’ina AE, Mach ES, Volkov AV, Nasonov EL (2006) Soluble CD40 ligand in systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome. Ter Arkh 78:35–39
Boumpas DT, Furie R, Manzi S, Illei GG, Wallace DJ, Balow JE, Vaishnaw A (2003) A short course of BG9588 (anti-CD40 ligand antibody) improves serologic activity and decreases hematuria in patients with proliferative lupus glomerulonephritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:719–727. doi:10.1002/art.10856
Desai-Mehta A, Lu L, Ramsey-Goldman R, Datta SK (1996) Hyperexpression of CD40 ligand by B and T cells in human lupus and its role in pathogenic autoantibody production. J Clin Invest 97:2063–2073. doi:10.1172/JCI118643
Gaipl US, Voll RE, Sheriff A, Franz S, Kalden JR, Herrmann M (2005) Impaired clearance of dying cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 4:189–194. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2004.10.007
Grammer AC, Bergman MC, Miura Y, Fujita K, Davis LS, Lipsky PE (1995) The CD40 ligand expressed by human B cells costimulates B cell responses. J Immunol 154:4996–5010
Haas JP, Grunke M, Frank C, Kolowos W, Dirnecker D, Leipold G, Hieronymus T, Lorenz HM, Herrmann M (1998) Increased spontaneous in vitro apoptosis in double negative T cells of humans with a fas/apo-1 mutation. Cell Death Differ 5:751–757. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400426
Hirose S, Yan K, Abe M, Jiang Y, Hamano Y, Tsurui H, Shirai T (1997) Precursor B cells for autoantibody production in genomically Fas-intact autoimmune disease are not subject to Fas-mediated immune elimination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9291–9295. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.17.9291
Kato K, Santana-Sahagun E, Rassenti LZ, Weisman MH, Tamura N, Kobayashi S, Hashimoto H, Kipps TJ (1999) The soluble CD40 ligand sCD154 in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 104:947–955. doi:10.1172/JCI7014
Lederer JA, Perez VL, DesRoches L, Kim SM, Abbas AK, Lichtman AH (1996) Cytokine transcriptional events during helper T cell subset differentiation. J Exp Med 184:397–406. doi:10.1084/jem.184.2.397
Lipsky PE (2001) Systemic lupus erythematosus: an autoimmune disease of B cell hyperactivity. Nat Immunol 2:764–766. doi:10.1038/ni0901-764
Lorenz HM, Grunke M, Hieronymus T, Herrmann M, Kuhnel A, Manger B, Kalden JR (1997) In vitro apoptosis and expression of apoptosis-related molecules in lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheum 40:306–317. doi:10.1002/art.1780400216
Nakamura M, Tanaka Y, Satoh T, Kawai M, Hirakata M, Kaburaki J, Kawakami Y, Ikeda Y, Kuwana M (2006) Autoantibody to CD40 ligand in systemic lupus erythematosus: association with thrombocytopenia but not thromboembolism. Rheumatology (Oxford) 45:150–156. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kei118
Schattner EJ, Elkon KB, Yoo DH, Tumang J, Krammer PH, Crow MK, Friedman SM (1995) CD40 ligation induces Apo-1/Fas expression on human B lymphocytes and facilitates apoptosis through the Apo-1/Fas pathway. J Exp Med 182:1557–1565. doi:10.1084/jem.182.5.1557
Suzuki N, Ichino M, Mihara S, Kaneko S, Sakane T (1998) Inhibition of Fas/Fas ligand-mediated apoptotic cell death of lymphocytes in vitro by circulating anti-Fas ligand autoantibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 41:344–353. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199802)41:2<344::AID-ART19>3.0.CO;2-J
Vakkalanka RK, Woo C, Kirou KA, Koshy M, Berger D, Crow MK (1999) Elevated levels and functional capacity of soluble CD40 ligand in systemic lupus erythematosus sera. Arthritis Rheum 42:871–881. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199905)42:5<871::AID-ANR5>3.0.CO;2-J
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by “Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft” SFB 643 (project B5), by the Interdisciplinary Centre for Clinical Research (IZKF) (project number A4 and N2) at the University Hospital of the University of Erlangen–Nuremberg, by the European Commissions [E.U. (QLK3-CT-2002-02017_APOCLEAR)], by the Lupus Erythemathodes Selbsthilfegemeinschaft e.V., by the “Responsif GmbH” Erlangen, by the “Doktor Robert Pfleger” Foundation, Bamberg, by the ELAN-Fond of the university of Erlangen Nuremberg (Pro.-Nr. 53410026), A grand dedicated to Maria Elena Manea and Doru Deica by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. E. Manea and R. B. Mueller contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manea, M.E., Mueller, R.B., Dejica, D. et al. Increased expression of CD154 and FAS in SLE patients’ lymphocytes. Rheumatol Int 30, 181–185 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-0933-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-0933-4