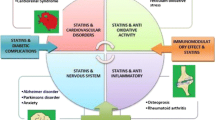
Abstract
The hydroxy-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) are used extensively in the treatment for hyperlipidemia. They have also demonstrated a benefit in a variety of other disease processes, including a wide range of rheumatologic disorders. These secondary actions are known as pleiotropic effects. Our paper serves as a focused and updated discussion on the pleiotropic effects of statins in rheumatologic disorders and emphasizes the importance of randomized, placebo-controlled trials to further elucidate this interesting phenomenon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pignone M, Phillips C, Mulrow C (2000) Use of lipid lowering drugs for primary prevention of coronary heart disease: meta-analysis of randomized trials. BMJ. 321:983–985
Tonkin A, Aylward P, Colquhoun D et al. (1998) Prevention of cardiovascular events and death with pravastatin in patients with coronary heart disease and a broad range of initial cholesterol levels. The long-term intervention with pravastatin in ischaemic disease (LIPID) study group. N Engl J Med 339(19):1349–1357
Endres M (2005) Statins and stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25(9):1093–1110
Liao JK (2002) Beyond lipid lowering: the role of statins in vascular protection. Int J Cardiol 86(1):5–18
Li J, Li JJ, He JG, Nan JL, Guo YL, Xiong CM (2010) Atorvastatin decreases C-reactive protein-induced inflammatory response in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B pathway. Cardiovasc Ther 28(1):8–14
Tandon V, Bano G, Khajuria V, Parihar A, Gupta S (2005) Pleiotropic effects of statins. Indian J Pharmacol 37(2):77–85
Blaschke S, Viereck V, Schwarz G, Klinger HM, Guerluek S, Müller GA (2009) Anti-inflammatory effects of atorvastatin on peripheral blood mononuclear cells and synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 38(4):235–239
Lazzerini PE, Lorenzini S, Selvi E et al. (2007) Simvastatin inhibits cytokine production and nuclear factor-k B activation in interleukin 1-beta stimulated synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol 25(5):696–700
Xu H, Liu P, Liang L et al (2006) RhoA-mediated, tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced activation of NF-kappaB in rheumatoid synoviocytes: inhibitory effect of simvastatin. Arthritis Rheum 54(11):3441–3451
Connor AM, Berger S, Narendran A, Keystone EC (2006) Inhibition of protein geranylgeranylation induces apoptosis in synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther 8(4):R94
Nagashima T, Okazaki H, Yudoh K, Matsuno H, Minota S (2006) Apoptosis of rheumatoid synovial cells by statins through the blocking of protein geranylgeranylation: a potential therapeutic approach to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54(2):579–586
Yokota K, Miyoshi F, Miyazaki T et al (2008) High concentration simvastatin induces apoptosis in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 35(2):193–200
Tikiz C, Utuk O, Pirildar T et al (2005) Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and statin treatment on inflammatory markers and endothelial functions in patients with long-term rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 32(11):2095–2101
Haruna Y, Morita Y, Yada T, Satoh M, Fox DA, Kashihara N (2007) Fluvastatin reverses endothelial dysfunction and increased vascular oxidative stress in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 56(6):1827–1835
Kinderlerer AR, Steinberg R, Johns M et al (2006) Statin-induced expression of CD59 on vascular endothelium in hypoxia: a potential mechanism for the anti-inflammatory actions of statins in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 8(4):R130
Paumelle R, Blanquart C, Briand O et al (2006) Acute antiinflammatory properties of statins involve peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha via inhibition of the protein kinase C signaling pathway. Circ Res 98(3):361–369
Lin H, Xiao Y, Chen G et al. (2010) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor simvastatin suppresses Toll-like receptor 2 ligand-induced activation of nuclear factor kappa B by preventing RhoA activation in monocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatol Int. 15 May 2010. (in press)
Weitz-Schmidt G, Welzenbach K, Brinkmann V et al (2001) Statins selectively inhibit leukocyte function antigen-1 by binding to a novel regulatory integrin site. Nat Med 7(6):687–692
McCarey DW, McInnes IB, Madhok R et al (2004) Trial of atorvastatin in rheumatoid arthritis (TARA): double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 363(9426):2015–2021
Shirinsky IV, Zheltova OI, Solovyova NY, Kozlov VA (2009) Shirinsky versus changes in disease activity, cytokine production, and proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis after simvastatin treatment. Scand J Rheumatol 38(1):23–27
Mäki-Petäjä KM, Booth AD, Hall FC et al (2007) Ezetimibe and simvastatin reduce inflammation, disease activity, and aortic stiffness and improve endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Coll Cardiol 50(9):852–858
Okamoto H, Koizumi K, Kamitsuji S et al (2007) Beneficial action of statins in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a large observational cohort. J Rheumatol 34(5):964–968
Bansback N, Ara R, Ward S, Anis A, Choi HK (2009) Statin therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: a cost-effectiveness and value-of-information analysis. Pharmacoeconomics 27(1):25–37
Chodick G, Amital H, Shalem Y et al (2010) Persistence with statins and onset of rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based cohort study. PLoS Med 7(9):e1000336
Jick SS, Choi H, Li L, McInnes IB, Sattar N (2009) Hyperlipidaemia, statin use and the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68(4):546–551
Orozco P (2004) Atherogenic lipid profile and elevated lipoprotein (a) are associated with lower bone mineral density in early postmenopausal overweight women. Eur J Epidemiol 19(12):1105–1112
Hanayama R, Shimizu H, Nakagami H et al (2009) Fluvastatin improves osteoporosis in fructose-fed insulin resistant model rats through blockade of the classical mevalonate pathway and antioxidant action. Int J Mol Med 23(5):581–588
Ahn KS, Sethi G, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB (2008) Simvastatin, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, suppresses osteoclastogenesis induced by receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand through modulation of NF-kappaB pathway. Int J Cancer 123(8):1733–1740
Staal A, Frith JC, French MH et al (2003) The ability of statins to inhibit bone resorption is directly related to their inhibitory effect on HMG-CoA reductase activity. J Bone Miner Res 18(1):88–96
Chen PY, Sun JS, Tsuang YH, Chen MH, Weng PW, Lin FH (2010) Simvastatin promotes osteoblast viability and differentiation via Ras/Smad/Erk/BMP-2 signaling pathway. Nutr Res 30(3):191–199
Maeda T, Matsunuma A, Kurahashi I, Yanagawa T, Yoshida H, Horiuchi N (2004) Induction of osteoblast differentiation indices by statins in MC3T3–E1 cells. J Cell Biochem 92(3):458–471
Li X, Cui Q, Kao C, Wang GJ, Balian G (2003) Lovastatin inhibits adipogenic and stimulates osteogenic differentiation by suppressing PPARgamma2 and increasing Cbfa1/Runx2 expression in bone marrow mesenchymal cell cultures. Bone 33(4):652–659
Chan MH, Mak TW, Chiu RW, Chow CC, Chan IH, Lam CW (2001) Simvastatin increases serum osteocalcin concentration in patients treated for hypercholesterolemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(9):4556–4559
Uyar Y, Baytur Y, Inceboz U, Demir BC, Gumuser G, Ozbilgin K (2009) Comparative effects of risedronate, atorvastatin, estrogen and SERMs on bone mass and strength in ovariectomized rats. Maturitas 63(3):261–267
Du Z, Chen J, Yan F, Xiao Y (2009) Effects of simvastatin on bone healing around titanium implants in osteoporotic rats. Clin Oral Implants Res 20(2):145–150
Wang JW, Xu SW, Yang DS, Lv RK (2007) Locally applied simvastatin promotes fracture healing in ovariectomized rat. Osteoporos Int 18(12):1641–1650
Hatzigeorgiou C, Jackson JL (2005) Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors and osteoporosis: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 16(8):990–998
Uzzan B, Cohen R, Nicolas P, Cucherat M, Perret GY (2007) Effects of statins on bone mineral density: a meta-analysis of clinical studies. Bone 40(6):1581–1587
Yue J, Zhang X, Dong B, Yang M (2010) Statins and bone health in postmenopausal women: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Menopause 17(5):1071–1079
Bauer DC, Mundy GR, Jamal SA et al (2004) Use of statins and fracture: results of 4 prospective studies and cumulative meta-analysis of observational studies and controlled trials. Arch Intern Med 164(2):146–152
Pérez-Castrillón JL, Vega G, Abad L et al (2008) Effect of the TNFalpha-308 G/A polymorphism on the changes produced by atorvastatin in bone mineral density in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Ann Nutr Metab 53(2):117–121
Pérez-Castrillón JL, Vega G, Abad L et al. (2009) Atorvastatin and BMD in coronary syndrome. Role of Lys656Asn polymorphism of leptin receptor gene. Endocr J 56(2):221–225
Bakhireva LN, Shainline MR, Carter S et al (2010) Synergistic effect of statins and postmenopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of skeletal fractures in elderly women. Pharmacotherapy 30(9):879–887
Tanriverdi HA, Barut A, Sarikaya S (2005) Statins have additive effects to vertebral bone mineral density in combination with risedronate in hypercholesterolemic postmenopausal women. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 120(1):63–68
De Leo V, Morgante G, la Marca A, Lanzetta D, Cobellis L, Petraglia F (2003) Combination of statins and hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women is associated with increased bone mineral density. Gynecol Endocrinol 17(4):329–332
Amuro H, Ito T, Miyamoto R et al (2010) Statins, inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, function as inhibitors of cellular and molecular components involved in type I interferon production. Arthritis Rheum 62(7):2073–2085
Ferreira GA, Teixeira AL, Sato EI (2010) Atorvastatin therapy reduces interferon-regulated chemokine CXCL9 plasma levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 19(8):927–934
Jury EC, Isenberg DA, Mauri C, Ehrenstein MR (2006) Atorvastatin restores Lck expression and lipid raft-associated signaling in T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 177(10):7416–7422
Shimazu H, Kinoshita K, Hino S et al (2010) Effect of combining ACE inhibitor and statin in lupus-prone mice. Clin Immunol 136(2):188–196
Woo JM, Lin Z, Navab M et al (2010) Treatment with apolipoprotein A-1 mimetic peptide reduces lupus-like manifestations in a murine lupus model of accelerated atherosclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther 12(3):R93
Aprahamian T, Bonegio R, Rizzo J et al (2006) Simvastatin treatment ameliorates autoimmune disease associated with accelerated atherosclerosis in a murine lupus model. J Immunol 177(5):3028–3034
Lawman S, Mauri C, Jury EC, Cook HT, Ehrenstein MR (2004) Atorvastatin inhibits autoreactive B cell activation and delays lupus development in New Zealand black/white F1 mice. J Immunol 173(12):7641–7646
Petri MA, Kiani AN, Post W, Christopher-Stine L, Magder LS (2010) Lupus atherosclerosis prevention study (LAPS). Ann Rheum Dis 70(5):760–765
Ferreira GA, Navarro TP, Telles RW, Andrade LE, Sato EI (2007) Atorvastatin therapy improves endothelial-dependent vasodilation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: an 8 weeks controlled trial. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46(10):1560–1565
Belmont HM, Lydon E (2005) Avascular necrosis prevention with lipitor in lupus erythematosus. Lupus 14(10):869–870
Del Papa N, Cortiana M, Vitali C et al (2008) Simvastatin reduces endothelial activation and damage but is partially ineffective in inducing endothelial repair in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 35(7):1323–1328
Abou-Raya A, Abou-Raya S, Helmii M (2007) Statins as immunomodulators in systemic sclerosis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1110:670–680
Kuwana M (2006) Potential benefit of statins for vascular disease in systemic sclerosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 18(6):594–600
Louneva N, Huaman G, Fertala J, Jiménez SA (2006) Inhibition of systemic sclerosis dermal fibroblast type I collagen production and gene expression by simvastatin. Arthritis Rheum 54(4):1298–1308
Abou-Raya A, Abou-Raya S, Helmii M (2008) Statins: potentially useful in therapy of systemic sclerosis-related Raynaud’s phenomenon and digital ulcers. J Rheumatol 35(9):1801–1808
Kuwana M, Okazaki Y, Kaburaki J (2009) Long-term beneficial effects of statins on vascular manifestations in patients with systemic sclerosis. Mod Rheumatol 19(5):530–535
Simopoulou T, Malizos KN, Poultsides L, Tsezou A (2010) Protective effect of atorvastatin in cultured osteoarthritic chondrocytes. J Orthop Res 28(1):110–115
Sverdrup FM, Yates MP, Vickery LE et al (2010) Protein geranylgeranylation controls collagenase expression in osteoarthritic cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 18(7):948–955
Litinsky I, Golan I, Yaron M, Yaron I, Caspi D, Elkayam O (2009) Simvastatin induces apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Open Rheumatol J. 3:35–40
Lazzerini PE, Capecchi PL, Nerucci F et al (2004) Simvastatin reduces MMP-3 level in interleukin 1beta stimulated human chondrocyte culture. Ann Rheum Dis 63(7):867–869
Rabinowitz JL, Gregg JR, Nixon JE, Schumacher HR (1979) Lipid composition of the tissues of the human knee joints. I—Observations in normal joints (articular cartilage, meniscus, ligaments, synovial fluid, synovium, intra-articular fat pad and bone marrow). Clin Orthop Relat Res (143):260–265
Pritchett JW (2007) Statins and dietary fish oils improve lipid composition in bone marrow and joints. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 456:233–237
Akasaki Y, Matsuda S, Nakayama K, Fukagawa S, Miura H, Iwamoto Y (2009) Mevastatin reduces cartilage degradation in rabbit experimental osteoarthritis through inhibition of synovial inflammation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 17(2):235–243
Akasaki Y, Matsuda S, Iwamoto Y (2009) Progress of research in osteoarthritis. The anti-inflammatory effects of intra-articular injected statin on experimental osteoarthritis. Clin Calcium 19(11):1653–1662
López-Pedrera C, Ruiz-Limón P, Aguirre MA et al. (2010) Global effects of fluvastatin on the prothrombotic status of patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 70(4):675–682
Jajoria P, Murthy V, Papalardo E, Romay-Penabad Z, Gleason C, Pierangeli SS (2009) Statins for the treatment of antiphospholipid syndrome? Ann N Y Acad Sci 1173:736–745
Meroni PL, Raschi E, Testoni C et al (2001) Statins prevent endothelial cell activation induced by antiphospholipid (anti-beta2-glycoprotein I) antibodies: effect on the proadhesive and proinflammatory phenotype. Arthritis Rheum 44(12):2870–2878
Redecha P, Franzke CW, Ruf W, Mackman N, Girardi G (2008) Neutrophil activation by the tissue factor/factor VIIa/PAR2 axis mediates fetal death in a mouse model of antiphospholipid syndrome. J Clin Invest 118(10):3453–3461
Ferrara DE, Liu X, Espinola RG et al (2003) Inhibition of the thrombogenic and inflammatory properties of antiphospholipid antibodies by fluvastatin in an in vivo animal model. Arthritis Rheum 48(11):3272–3279
Vasiuk IuA, Perlamutrov IuN, Shkol’nik MN, Shkol’nik EL (2010) Possibilities of atorvastatin in complex management of extensive psoriasis in patients with arterial hypertension. Kardiologiia. 50(3):37–46
Naseri M, Hadipour A, Sepaskhah M, Namazi MR (2010) The remarkable beneficial effect of adding oral simvastatin to topical betamethasone for treatment of psoriasis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Niger J Med 19(1):58–61
Hamaoka A, Hamaoka K, Yahata T et al (2010) Effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on continuous post-inflammatory vascular remodeling late after Kawasaki disease. J Cardiol 56(2):245–253
Huang SM, Weng KP, Chang JS et al (2008) Effects of statin therapy in children complicated with coronary arterial abnormality late after kawasaki disease: a pilot study. Circ J 72(10):1583–1587
van Denderen JC, Peters MJ, van Halm VP et al (2006) Statin therapy might be beneficial for patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 65(5):695–696
Inanc MT, Kalay N, Heyit T et al (2010) Effects of atorvastatin and lisinopril on endothelial dysfunction in patients with Behçet’s disease. Echocardiography 27(8):997–1003
Hashimoto T, Toya Y, Kihara M et al (2008) Behçet’s disease complicated by IgA nephropathy with nephrotic syndrome. Clin Exp Nephrol 12(3):224–227
ten Cate R, Nibbering PH, Bredius RG (2004) Therapy-refractory systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis successfully treated with statins. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43(7):934–935
Rosenson RS (2004) Current overview of statin-induced myopathy. Am J Med 116(6):408–416
Sailler L, Pereira C, Bagheri A et al (2008) Increased exposure to statins in patients developing chronic muscle diseases: a 2-year retrospective study. Ann Rheum Dis 67(5):614–619
Sen D, Rosenstein ED, Kramer N (2010) ANCA-positive vasculitis associated with simvastatin/ezetimibe: expanding the spectrum of statin-induced autoimmunity? Int J Rheum Dis 13(3):e29–e31
Haroon M, Devlin J (2008) A case of ANCA-associated systemic vasculitis induced by atorvastatin. Clin Rheumatol 27(Suppl 2):S75–S77
Noel B (2007) Lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases related to statin therapy: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 21(1):17–24
Goëb V, Guillemant N, Vittecoq O, Le Loët X (2004) Cerivastatin-induced polymyalgia rheumatica-like illness. Clin Rheumatol 23(2):179
Yamamoto M, Ikeda M, Kodama H, Sano S (2008) Transition of psoriasiform drug eruption to psoriasis de novo evidenced by histopathology. J Dermatol 35(11):732–736
Adams AE, Bobrove AM, Gilliam AC (2010) Statins and “chameleon-like” cutaneous eruptions: simvastatin-induced acral cutaneous vesiculobullous and pustular eruption in a 70-year-old man. J Cutan Med Surg 14(5):207–211
Adams AE, Bobrove AM, Gilliam AC (2010) Statins inhibit the antirheumatic effects of rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: results from the Dutch rheumatoid arthritis monitoring (DREAM) registry. Ann Rheum Dis 70(5):877–878
Aronow C, Diamond B. A double blind, placebo controlled, phase II, randomized study of lovastatin therapy in the treatment of mildly active rheumatoid arthritis. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Clinialtrials gov NCT00302952
Ming Li EK. Effects of HMG-coA reductase inhibitor on progression of carotid intima-media thickness and arterial stiffness in rheumatoid arthritis. The Chinese University of Hong Kong. Clinicaltrial gov NCT00555230
Ansell BJ. Effects of atorvastatin on disease activity and HDL cholesterol anti-inflammatory properties in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The University of California, Los Angeles. Clinicatrial gov NCT00356473
Pfizer, Inc. Phase 2 study of the effects of open-label CP-690,550 and double-blind atorvastatin on lipids in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Clinicaltrial gov NCT01059864
Abdou NI. Statins and Lupus: effects of statins on clinical lupus parameters, serological markers and toll-like receptors. St. Luke’s Hospital. Clinicaltrial gov NCT00519363
Lai NS. An open labeled pilot study of atorvastatin in systemic lupus erythematosus. Buddhist Dalin Chi Tzu General Hospital. Clinicaltrial gov NCT00432354
Schanberg LE. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to test the safety and efficacy of lipitor (atorvastatin) in reducing the progression of carotid IMT in early childhood SLE. Duke University. Clinicaltrial gov NCT00065806
Belmont HM. Atorvastatin to prevent avascular necrosis of bone in steroid treated exacerbated systemic lupus erythematosus. New York University. Clinicaltrial gov NCT00412841
Erkan D, Pierangeli S. Effects of fluvastatin on proinflammatory and prothrombotic markers in antiphospholipid syndrome patients. Hospital for Special Surgery. Clinicaltrial gov NCT00674297
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mihos, C.G., Artola, R.T. & Santana, O. The pleiotropic effects of the hydroxy-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors in rheumatologic disorders: a comprehensive review. Rheumatol Int 32, 287–294 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2008-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2008-6