Abstract
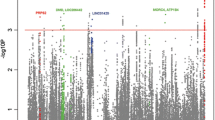
The aim of the study is to explore additional susceptibility factors for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in Chinese Hans. Based on our previous GWAS of SLE, we performed a multistage replication study involving 3,152 cases and 7,050 controls from China to identify additional susceptibility loci for SLE by using the Sequenom MassArray system. All Chinese Han samples used in this study were obtained from doctors through collaboration with multiple hospitals in two geographic regions (central and southern China). Single-marker association analyses were performed using logistic regression with gender as a covariate in each case–control cohort. The joint analysis of all combined samples was performed using logistic regression with gender and sample cohorts as covariates. The significant association evidence for rs906868 (OR = 1.14, 95 % CI 1.08–1.20, P combined = 7.71 × 10−10) and rs7579944 (OR = 1.13, 95 % CI 1.07–1.19, P combined = 5.55 × 10−9) was observed, which located at 2p23.1. In this region, limb bud and heart development homolog (LBH) was the only gene indicated, suggesting LBH might be a susceptibility gene for SLE, although its function was still unknown. The results indicated that the SNP rs7579944, rs906868 at 2p23.1 showed significant association with SLE. The genes LBH which located in this loci might be the predisposing genes of SLE.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olson JM, Song Y, Dudek DM et al (2002) A genome screen of systemic lupus erythematosus using affected-relative-pair linkage analysis with covariates demonstrates genetic heterogeneity. Genes Immun 3(Suppl 1):S5–S12
Lau CS, Yin G, Mok MY (2006) Ethnic and geographical differences in systemic lupus erythematosus: an overview. Lupus 15:715–719
Zeng QY, Chen R, Darmawan J et al (2008) Rheumatic diseases in China. Arthritis Res Ther 10:R17
Danchenko N, Satia JA, Anthony MS (2006) Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison of worldwide disease burden. Lupus 15:308–318
Deapen D, Escalante A, Weinrib L et al (1992) A revised estimate of twin concordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 35:311–318
Graham RR, Ortmann WA, Langefeld CD et al (2002) Visualizing human leukocyte antigen class II risk haplotypes in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Hum Genet 71:543–553
Graham RR, Ortmann W, Rodine P et al (2007) Specific combinations of HLA-DR2 and DR3 class II haplotypes contribute graded risk for disease susceptibility and autoantibodies in human SLE. Eur J Hum Genet 15:823–830
Graham RR, Kozyrev SV, Baechler EC et al (2006) A common haplotype of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) regulates splicing and expression and is associated with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 38:550–555
Remmers EF, Plenge RM, Lee AT et al (2007) STAT4 and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 357:977–986
Hom G, Graham RR, Modrek B et al (2008) Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N Engl J Med 358:900–909
Harley JB, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA et al (2008) Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet 40:204–210
Kozyrev SV, Abelson AK, Wojcik J et al (2008) Functional variants in the B-cell gene BANK1 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 40:211–216
Graham RR, Cotsapas C, Davies L et al (2008) Genetic variants near TNFAIP3 on 6q23 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 40:1059–1061
Han JW, Zheng HF, Cui Y et al (2009) Genome-wide association study in a Chinese Han population identifies nine new susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 41:1234–1237
Gateva V, Sandling JK, Hom G et al (2009) A large-scale replication study identifies TNIP1, PRDM1, JAZF1, UHRF1BP1 and IL10 as risk loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 41:1228–1233
Chen J, Zheng H, Bei JX et al (2009) Genetic structure of the Han Chinese population revealed by genome-wide SNP variation. Am J Hum Genet 85:775–785
Xu S, Yin X, Li S et al (2009) Genomic dissection of population substructure of Han Chinese and its implication in association studies. Am J Hum Genet 85:762–774
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Zhang XJ, Huang W, Yang S et al (2009) Psoriasis genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility variants within LCE gene cluster at 1q21. Nat Genet 41:205–210
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Ai J, Wang Y, Tan K et al (2008) A human homolog of mouse Lbh gene, hLBH, expresses in heart and activates SRE and AP-1 mediated MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Biol Rep 35:179–187
English J, Pearson G, Wilsbacher J et al (1999) New insights into the control of MAP kinase pathways. Exp Cell Res 253:255–270
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81:807–869
Wong CK, Wong PT, Tam LS et al (2009) Activation profile of intracellular mitogen-activated protein kinases in peripheral lymphocytes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Immunol 29:738–746
Lee TP, Leu SJ, Huang JC et al (2009) Anti-ribosomal phosphoprotein autoantibody triggers interleukin-10 overproduction via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent signalling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages. Immunology 127:91–102
Acknowledgments
We thank all the participants of the study. This study was funded by the National Natural Youth Science Foundation (81101185) and An hui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (11040606Q13).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ze-Ying Yu, Wen-Sheng Lu, Xian-bo Zuo and Jian Hu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, ZY., Lu, WS., Zuo, Xb. et al. One novel susceptibility locus associate with systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese Han population. Rheumatol Int 33, 2079–2083 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2697-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2697-0