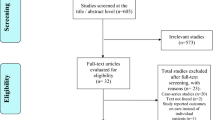
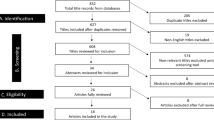
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease affecting up to 1% of the worldwide population. RA is associated with multiple extra-articular manifestations (EAMs). Middle ear, cochlea and the auditory nerve are suspected sites of RA activity and hearing loss is a possible novel EAM of RA. Objective was to investigate the association of RA with the different subtypes of hearing loss. This systematic review was performed according to the PRISMA guidelines. A random effects model meta-analysis was conducted and the I2 was used to assess heterogeneity. Twelve studies comprising 20,022 RA patients and 79,244 controls were included in this systematic review. All studies were observational and were rated to a moderate rate of bias. RA patients had nearly fourfold increased odds of sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) compared with controls (OR 3.42; 95% CI 2.50–4.69; I2 = 13). RA patients also had a significantly increased risk of SNHL (RR 2.28; 95% CI 1.88–2.76; I2 = 0). RA patients did not have increased odds of conductive hearing loss (CHL) and mixed hearing loss (MHL) (OR 1.36; 95% CI 0.52–3.55; I2 = 22); (OR 2.73; 95% CI 0.78–9.58; I2 = 0%). RA is significantly associated with SNHL. RA is not associated with CHL and MHL. Early screening of RA patients with pure tone audiometry should be considered.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
MacGregor AJ, Snieder H, Rigby AS et al (2000) Characterizing the quantitative genetic contribution to rheumatoid arthritis using data from twins. Arthritis Rheum 43:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1%3c30:AID-ANR5%3e3.0.CO;2-B
Gregersen PK, Silver J, Winchester RJ (1987) The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 30:1205–1213. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780301102
The Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium (2007) Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 447:661–678. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05911
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB (2016) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet (Lond, Engl) 388:2023–2038. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8
Myasoedova E, Crowson CS, Turesson C et al (2011) Incidence of extraarticular rheumatoid arthritis in Olmsted County, Minnesota, in 1995–2007 versus 1985–1994: a population-based study. J Rheumatol 38:983–989. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.101133
Cimmino MA, Salvarani C, Macchioni P et al (2000) Extra-articular manifestations in 587 Italian patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 19:213–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00006853
Lobo FS, Dossi MO, Batista L, Shinzato MM (2016) Hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: association with anti-citrullinated protein antibodies. Clin Rheumatol 35:2327–2332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3278-x
Halligan CS, Bauch CD, Brey RH et al (2006) Hearing loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Laryngoscope 116:2044–2049. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000241365.54017.32
Takatsu M, Higaki M, Kinoshita H et al (2005) Ear involvement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Otol Neurotol Off Publ Am Otol Soc Am Neurotol Soc Eur Acad Otol Neurotol 26:755–761. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mao.0000178138.19848.bd
Ozturk A, Yalcin S, Kaygusuz I et al (2004) High-frequency hearing loss and middle ear involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Otolaryngol 25:411–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2004.06.001
Ozcan M, Karakus MF, Gunduz OH et al (2002) Hearing loss and middle ear involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 22:16–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-002-0185-z
Reiter D, Konkle DF, Myers AR et al (1980) Middle ear immittance in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Otolaryngol 106:114–117. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1980.00790260046013
Galarza-Delgado DA, Villegas Gonzalez MJ, Riega Torres J et al (2018) Early hearing loss detection in rheumatoid arthritis and primary Sjogren syndrome using extended high frequency audiometry. Clin Rheumatol 37:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3959-0
Golub JS, Brickman AM, Ciarleglio AJ et al (2019) Association of subclinical hearing loss with cognitive performance. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2019.3375
Michalowsky B, Hoffmann W, Kostev K (2019) Association between hearing and vision impairment and risk of dementia: results of a case-control study based on secondary data. Front Aging Neurosci 11:363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2019.00363
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M et al (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ 350:g7647
Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC et al (2011) The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 343:d5928. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d5928
Sterne JA, Hernan MA, Reeves BC et al (2016) ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 355:i4919
Sterne JAC, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JPA et al (2011) Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 343:d4002. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d4002
The Cochrane Collaboration (2014) Review manager (RevMan) [computer program]. Version 5.3. The Nordic Cochrane Centre, Copenhagen
Garcia Callejo FJ, Conill Tobias N, Munoz Fernandez N et al (2007) Hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 58:232–238
Ahmadzadeh A, Daraei M, Jalessi M et al (2017) Hearing status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Laryngol Otol 131:895–899. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215117001670
Huang C-M, Chen H-J, Huang P-H et al (2018) Retrospective cohort study on risk of hearing loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using claims data. BMJ Open 8:e018134. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018134
Jeong J, Lim H, Lee K et al (2019) High risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in several autoimmune diseases according to a population-based national sample cohort study. Audiol Neurootol 24:224–230. https://doi.org/10.1159/000502677
Raut VV, Cullen J, Cathers G (2001) Hearing loss in rheumatoid arthritis. J Otolaryngol 30:289–294. https://doi.org/10.2310/7070.2001.19580
Dikici O, Muluk NB, Tosun AK, Unlusoy I (2009) Subjective audiological tests and transient evoked otoacoustic emissions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: analysis of the factors affecting hearing levels. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266:1719–1726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-009-0975-y
Rosenberg JN, Moffat DA, Ramsden RT et al (1978) Middle ear function in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 37:522–524. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.37.6.522
Bhatt KA, Liberman MC, Nadol JBJ (2001) Morphometric analysis of age-related changes in the human basilar membrane. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110:1147–1153. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940111001212
Viana LM, O’Malley JT, Burgess BJ et al (2015) Cochlear neuropathy in human presbycusis: confocal analysis of hidden hearing loss in post-mortem tissue. Hear Res 327:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2015.04.014
Zhu T, Feng L (2013) Comparison of anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides, anti-glucose-6-phosphate isomerase and anti-keratin antibodies and rheumatoid factor in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese patients. Int J Rheum Dis 16:157–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.12040
Li L, Deng C, Chen S et al (2016) Meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of anti-carbamylated protein antibody for rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 11:e0159000. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159000
Makol A, Crowson CS, Wetter DA et al (2014) Vasculitis associated with rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study. Rheumatology (Oxf) 53:890–899. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ket475
Voskuyl AE, Zwinderman AH, Westedt ML et al (1996) Factors associated with the development of vasculitis in rheumatoid arthritis: results of a case-control study. Ann Rheum Dis 55:190–192. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.55.3.190
Ashok Murthy V, Mohan Kumar J (2012) Rheumatoid factor and hearing loss. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 64:364–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0401-9
Bayazit YA, Yilmaz M, Gunduz B et al (2007) Distortion product otoacoustic emission findings in Behcet’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 69:233–238. https://doi.org/10.1159/000101544
Di Stadio A, Ralli M (2017) Systemic lupus erythematosus and hearing disorders: literature review and meta-analysis of clinical and temporal bone findings. J Int Med Res 45:1470–1480. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060516688600
Souliotis VL, Vlachogiannis NI, Pappa M et al (2019) DNA damage response and oxidative stress in systemic autoimmunity. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010055
Bougea A, Anagnostou E, Konstantinos G et al (2015) A systematic review of peripheral and central nervous system involvement of rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, primary Sjogren’s syndrome, and associated immunological profiles. Int J Chronic Dis 2015:910352. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/910352
Barbieri MA, Cicala G, Cutroneo PM et al (2019) Ototoxic adverse drug reactions: a disproportionality analysis using the italian spontaneous reporting database. Front Pharmacol 10:1161. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01161
Kyle ME, Wang JC, Shin JJ (2015) Impact of nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents and acetaminophen on sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review. Otolaryngol neck Surg Off J Am Acad Otolaryngol Neck Surg 152:393–409. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599814564533
Magaro M, Zoli A, Altomonte L et al (1990) Sensorineural hearing loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 8:487–490
Acknowledgements
We do not have any financial relationship to this article.
Funding
We did not receive any funding to conduct this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CN conceptualized, proposed and designed the study. FC and AI searched the literature, screened and selected the eligible studies.CN and TP assessed the quality of the studies included. CN and TP analyzed the data and carried out the statistical analyses. CN and TP contributed in drafting the manuscript, and all other authors reviewed it critically. All authors revised the final manuscript and approved it for publication submission. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to quality of the work are appropriately examined and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We do not have any conflict of interest to declare.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed to publish in Rheumatology International Journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaitidis, N., Theocharis, P., Festas, C. et al. Association of rheumatoid arthritis with hearing loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 40, 1771–1779 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-020-04609-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-020-04609-1