Abstract
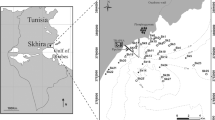
Macrobenthic faunal associations, hydrography and sediment structure were examined at 14 stations in the Kara Sea. The stations were located in an area influenced by huge runoff from the Ob and Yenisei Rivers and in areas influenced by Barents Sea water. Sampling depths varied from 17 to 43 m, with one station at 195 m. The sediments were predominantly muddy but some stations were sandy. Three hundred and eighty-seven taxa were identified and Polychaeta, Crustacea and Mollusca were the most conspicuous. Species number, abundance and biomass varied widely among stations, and were generally higher in the more marine waters. Boreal-arctic species predominated, but an increase of arctic species from marine to the estuarine areas was evident. Five faunal associations were delineated by cluster analysis and suggested quite heterogeneous sampling areas. The most conspicuous species of each faunal association were Spiochaetopterus typicus, Tridonta borealis, Serripes groenlandicus, Portlandia arctica, and Marenzelleria arctia, respectively. The sedimentation rate, as well as depth, sediment structure and salinity, apparently influenced the main differences in the fauna.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 29 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jørgensen, L., Pearson, T., Anisimova, N. et al. Environmental influences on benthic fauna associations of the Kara Sea (Arctic Russia). Polar Biol 22, 395–416 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003000050435
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003000050435