Abstract
Objective
A screening survey for osteoporotic fractures in men and women in Hong Kong represents the first large-scale prospective population-based study on bone health in elderly (≥65 years) Chinese men and women. This study aims to identify the prevalence and potential risk factors of lumbar spondylolisthesis in these subjects.
Methods
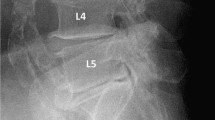
The lateral lumbar radiographs of 1,994 male and 1,996 female patients were analysed using the Meyerding classification.
Results
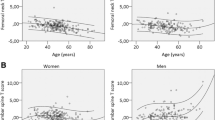
Amongst the men, 380 (19.1 %) had at least one spondylolisthesis and 43 (11.3 %) had slips at two or more levels; 283 had anterolisthesis, 85 had retrolisthesis, whereas 12 subjects had both anterolisthesis and retrolisthesis. Amongst the women, 499 (25.0 %) had at least one spondylolisthesis and 69 (13.8 %) had slips at two or more levels; 459 had anterolisthesis, 34 had retrolisthesis, whereas 6 subjects had both anterolisthesis and retrolisthesis. Advanced age, short height, higher body mass index (BMI), higher bone mineral density (BMD) and degenerative arthritis are associated with spondylolisthesis. Lower Physical Activity Scale for the Elderly (PASE) score was associated with spondylolisthesis in men; higher body weight, angina and lower grip strength were associated with spondylolisthesis in women.
Conclusion
The male/female ratio of lumbar spondylolisthesis prevalence was 1:1.3 in elderly Chinese. Men are more likely to have retrolisthesis.
Key Points
• The prevalence of spondylolisthesis is 19.1 % in elderly Chinese men.
• The prevalence of spondylolisthesis is 25.0 % in elderly Chinese women.
• Men are more likely to have retrolisthesis.
• Anterolisthesis is most commonly seen at the L4/L5 level.
• Retrolisthesis is most commonly seen at the L3/L4 level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiltse LL, Newman PH, Macnab I (1976) Classification of spondylolisis and spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 23–294
Fredrickson BE, Baker D, McHolick WJ et al (1984) The natural history of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 66:699–707
Beutler WJ, Fredrickson BE, Murtland A et al (2003) The natural history of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: 45-year follow-up evaluation. Spine 28:1027–1035
North American Spine Society (2008) Clinical guidelines for multidisciplinary spine care. Diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. North American Spine Society, Burr Ridge
Rosenberg NJ (1975) Degenerative spondylolisthesis. Predisposing factors J Bone Joint Surg Am 57:467–474
Moller H, Sundin A, Hedlund R (2000) Symptoms, signs, and functional disability in adult spondylolisthesis. Spine 25:683–690
Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Olson PR et al (2006) United States’ trends and regional variations in lumbar spine surgery: 1992–2003. Spine 31:2707–2714
Deyo RA, Gray DT, Kreuter W et al (2005) United States trends in lumbar fusion surgery for degenerative conditions. Spine 30:1441–1445
Fischgrund JS, Mackay M, Herkowits HN et al (1997) 1997 Volvo award winner in clinical studies. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation. Spine 22:2807–2812
Kornblum MB, Fischgrund JS, Herkowitz HN et al (2004) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective long-term study comparing fusion and pseudarthrosis. Spine 29:726–733
Vibert BT, Sliva CD, Herkowitz HN (2006) Treatment of instability and spondylolisthesis: surgical versus nonsurgical treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 443:222–227
Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD et al (2007) Surgical versus nonsurgical treatment for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. N Engl J Med 356:2257–2270
Chen JC, Chan WP, Katz JN et al (2004) Occupational and personal factors associated with acquired lumbar spondylolisthesis of urban taxi drivers. Occup Environ Med 61:992–998
Jacobsen S, Sonne-Holm S, Rovsing H et al (2007) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: an epidemiological perspective: The Copenhagen Osteoarthritis Study. Spine 32:120–125
Vogt MT, Rubin D, Valentin RS et al (1998) Lumbar olisthesis and lower back symptoms in elderly white women. The study of osteoporotic fractures. Spine 23:2640–2647
Kauppila LI, Eustace S, Kiel DP et al (1998) Degenerative displacement of lumbar vertebrae. A 25-year follow-up study in Framingham. Spine 23:1868–1873
Kalichman L, Kim DH, Li L et al (2009) Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: Prevalence and association with low back pain in the adult community-based population. Spine 34:199–205
Denard PJ, Holton KF, Miller J et al (2010) Lumbar spondylolisthesis among elderly men: prevalence, correlates and progression. Spine 35:1072–1078
Fitzgerald J, Newman P (1976) Degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 58:184–192
Herkowitz H, Kurz L (1991) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73:802–808
Leung SS, Woo J, Ho S, Lam TH, Janus ED (1998) Hong Kong adult dietary survey, 1995. Aust J Nutrit Diet 55(Suppl 1):S11–S13
Liu B, Woo J, Tang N, Ng K, Ip R, Au A (2001) Assessment of total energy expenditure in a Chinese population by a physical activity questionnaire: examination of validity. Int J Food Sci Nutr 52:269–282
Meyerding HW (1932) Spondyloptosis. Surg Gynaecol Obstet 54:371–377
Valkenburg HA, Haanen HCM (1982) The epidemiology of low back pain. In: White AA (ed) Proceedings from the American Association of Orthopaedic Surgeons Symposium on Low Back Pain. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Rosemont, pp 9–22
Iguchi T, Wakami T, Kurihara A, Kasahara K, Yoshiya S, Nishida K (2002) Lumbar multilevel degenerative spondylolisthesis: radiological evaluation and factors related to anterolisthesis and retrolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech 15:93–99
Herkowitz HN (1995) Spine update. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis Spine 20:1084–1090
Butler D, Trafimow JH, Andersson GBJ et al (1990) Discs degenerate before facets. Spine 15:111–113
Grobler L, Robertson P, Novotny J (1993) Etiology of spondylolisthesis. Assessment of the role played by of lumbar facet joint morphology Spine 18:80–91
Love T, Fagan A, Fraser R (1999) Degenerative spondylolisthesis. Developmental or acquired? J Bone Joint Surg Br 81:670–674
Matsunaga S, Sakou TMY (1990) Natural history of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Pathogenesis and natural course of the slippage Spine 15:1204–1210
McAfee P, Yuan H (1982) Computed tomography in spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 166:62–71
Sanderson PL, Fraser RD (1996) The influence of pregnancy on the development of degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 78:951–954
Porter RW, Hibbert C (1989) Vertebral displacement in spondylolisthesis. Clin Biomech 4:58–63
Imada K, Matsui H, Tsuji H (1995) Oophorectomy predisposes to degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77:126–130
Wang YX, Griffith JF, Ma HT, Kwok AW, Leung JC, Yeung DK, Ahuja AT, Leung PC (2011) Relationship between gender, bone mineral density, and disc degeneration in the lumbar spine: a study in elderly subjects using an eight-level MRI-based disc degeneration grading system. Osteoporos Int 22:91–96
Wang YX, Griffith J (2010) Effect of menopause on lumbar disk degeneration: potential etiology. Radiology 257:318–320
Wang YX, Griffith JF, Zeng XJ, Deng M, Kwok AW, Leung JC, Ahuja AT, Kwok T, Leung P (2013) Prevalence and sex difference of lumbar disc space narrowing in elderly Chinese men and women: osteoporotic fractures in men (Hong Kong) and osteoporotic fractures in women (Hong Kong) studies. Arthritis Rheum 65:1004–1010
Newman P, Stone K (1963) The etiology of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg 45-B:39–59
Mariconda M, Galasso O, Imbimbo L et al (2007) Relationship between alterations of the lumbar spine, visualized with magnetic resonance imaging, and occupational variables. Eur Spine J16:255–266
Farfan HF, Osteria V, Lamy C (1976) The mechanical etiology of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Related Res 117:40–55
Griffith JF, Kumta SM, Huang Y (2011) Hard arteries, weak bones. Skeletal Radiol 40:517–521
Farfan HF (1980) The pathological anatomy of degenerative spondylolisthesis. A cadaver study Spine 5:412–418
Lowe RW, Hayes TD, Kaye J et al (1976) Standing roentgenograms in spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 10:80–84
Hu SS, Tribus CB, Diab M, Ghanayem AJ (2008) Spondylolisthesis and spondylolysis. Instr Course Lect 57:431–445
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Institute of Health R01 Grant AR049439-01A1 and the Research Grants Council Earmarked Grant CUHK 4101/02 M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, LC., Wang, YX.J., Gong, JS. et al. Prevalence and risk factors of lumbar spondylolisthesis in elderly Chinese men and women. Eur Radiol 24, 441–448 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-3041-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-3041-5