Abstract
Objective
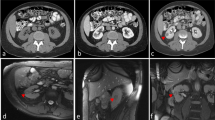
To determine whether MRI allows safe and accurate guidance for biopsies of renal masses.
Materials and methods
Between May 2010 and September 2013, 26 patients (15 men and 11 women) with 26 renal masses underwent MRI-guided percutaneous biopsy. For each patient, we retrospectively collected the epidemiological, procedural and histopathological data.
Results
Mean size of tumour was 3.6 cm (range 0.6 – 9 cm). Mean procedure time was 48 minutes (range 37 – 70 min). Malignancy was found in the percutaneous samples in 81 % (21/26) of the masses. All these cases were considered as true positive biopsies. Benignity was found in the percutaneous samples in 5/26 (19 %) of the masses but was confirmed only in 3 cases. The other 2 cases included one false negative case and one undetermined biopsy, as patient was lost to follow-up. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) and accuracy of this study were 95.4 %, 100 %, 100 %, 75 % and 96 %, respectively
Conclusion
MRI-guidance is safe and accurate to target renal masses.
Key Points
• Percutaneous interventions can be performed with MRI-guidance
• MRI offers real-time multiplanar imaging capabilities without radiation
• MRI-guidance allows to target renal tumours



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- US:
-
ultrasound
- CT:
-
computed tomography
- CBCT:
-
cone beam computed tomography
- SRMs:
-
small renal masses
- NPV:
-
negative predictive value
- PPV:
-
positive predictive value
- TP:
-
true positive
- TN:
-
true negative
- FP:
-
false positive
- FN:
-
false negative
References
Volpe A, Panzarella T, Rendon RA et al (2004) The natural history of incidentally detected small renal masses. Cancer 100:738–745
Pedrosa I, Sun MR, Spencer M et al (2008) MR imaging of renal masses: correlation with findings at surgery and pathologic analysis. Radiographics 28(4):985–1003
Hindman N, Ngo L, Genega EM et al (2012) Angiomyolipoma with minimal fat: can it be differentiated from clear cell renal carcinoma by using standard MR techniques? Radiology 265(2):468–77
Martinez-Piñeiro L, Alvarez Maestro M (2010) Challenging the EAU guidelines: role of biopsy and management of small renal tumours. Eur Urol Suppl 9:450–453
Salem S, Ponsky LE, Abouassaly R et al (2013) Image-guided biopsy of small renal masses in the era of ablative therapies. Int J Urol 20:580–584
Neuzillet Y, Lechevallier E, Andre M et al (2004) Accuracy and clinical role of fine needle percutaneous biopsy with computerized tomography guidance of small (less than 4.0 cm) renal masses. J Urol 171:1802–1805
Volpe A, Mattar K, Finelli A et al (2008) Contemporary results of percutaneous biopsy of 100 small renal masses: a single center experience. J Urol 180:2333–2337
Wang R, Wolf JS Jr, Wood DP Jr et al (2009) Accuracy of percutaneous core biopsy in management of small renal masses. Urology 73:586–590, discussion 590–591
Caoili EM, Bude RO, Higgins EJ et al (2002) Evaluation of sonographically guided percutaneous core biopsy of renal masses. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:373–378
Eshed I, Elias S, Sidi AA (2004) Diagnostic value of CT-guided biopsy of indeterminate renal masses. Clin Radiol 59:262–267
Kühn J-P, Langner S, Hegenscheid K et al (2010) Magnetic resonance-guided upper abdominal biopsies in a high-field wide-bore 3-T MRI system: feasibility, handling, and needle artefacts. Eur Radiol 20:2414–2421
Braak SJ, van Melick HHE, Onaca MG et al (2012) 3D cone-beam CT guidance, a novel technique in renal biopsy–results in 41 patients with suspected renal masses. Eur Radiol 22:2547–2552
Chawla SN, Crispen PL, Hanlon AL et al (2006) The natural history of observed enhancing renal masses: meta-analysis and review of the world literature. J Urol 175:425–431
Shingleton WB, Sewell PE Jr (2001) Percutaneous renal tumor cryoablation with magnetic resonance imaging guidance. J Urol 165:773–776
Kariniemi J, Blanco Sequeiros R, Ojala R, Tervonen O (2005) MRI-guided abdominal biopsy in a 0.23-T open-configuration MRI system. Eur Radiol 15:1256–1262
Brennan SB (2014) Breast magnetic resonance imaging for the interventionalist: magnetic resonance imaging–guided vacuum-assisted breast biopsy. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol 17:40–48
Eshed I, Althoff CE, Hamm B, Hermann K-GA (2007) Claustrophobia and premature termination of magnetic resonance imaging examinations. J Magn Reson Imaging JMRI 26:401–404
Ahrar K, Ahrar JU, Javadi S et al (2013) Real-time magnetic resonance imaging-guided cryoablation of small renal tumors at 1.5 T. Investig Radiol 48:437–444
Stattaus J, Maderwald S, Forsting M et al (2008) MR-guided core biopsy with MR fluoroscopy using a short, wide-bore 1.5-Tesla scanner: feasibility and initial results. J Magn Reson Imaging JMRI 27:1181–1187
Miki K, Shimomura T, Yamada H et al (2006) Percutaneous cryoablation of renal cell carcinoma guided by horizontal open magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Urol 13:880–884
Fischbach F, Bunke J, Thormann M et al (2011) MR-guided freehand biopsy of liver lesions with fast continuous imaging using a 1.0-T open MRI scanner: experience in 50 patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34:188–192
Rofsky NM, Yang BM, Schlossberg P et al (1998) MR-guided needle aspiration biopsies of hepatic masses using a closed bore magnet. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22:633–637
Schmidbauer J, Remzi M, Memarsadeghi M et al (2008) Diagnostic accuracy of computed tomography-guided percutaneous biopsy of renal masses. Eur Urol 53:1003–1011
Kang SK, Kim D, Chandarana H (2011) Contemporary imaging of the renal mass. Curr Urol Rep 12:11–17
Schmidt AJ, Kee ST, Sze DY et al (1999) Diagnostic yield of MR-guided liver biopsies compared with CT- and US-guided liver biopsies. J Vasc Interv Radiol JVIR 10:1323–1329
Krücker J, Xu S, Venkatesan A et al (2011) Clinical utility of real-time fusion guidance for biopsy and ablation. J Vasc Interv Radiol JVIR 22:515–524
Kroeze SGC, Huisman M, Verkooijen HM et al (2012) Real-time 3D fluoroscopy-guided large core needle biopsy of renal masses: a critical early evaluation according to the IDEAL recommendations. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35:680–685
Hoffmann R, Thomas C, Rempp H et al (2012) Performing MR-guided biopsies in clinical routine: factors that influence accuracy and procedure time. Eur Radiol 22:663–671
Maurer MH, Schreiter N, de Bucourt M et al (2013) Cost comparison of nerve root infiltration of the lumbar spine under MRI and CT guidance. Eur Radiol 23:1487–1494
Lee SW, Lee MH, Yang HJ et al (2013) Experience of ultrasonography-guided percutaneous core biopsy for renal masses. Korean J Urol 54:660–665
Reichelt O, Gajda M, Chyhrai A et al (2007) Ultrasound-guided biopsy of homogenous solid renal masses. Eur Urol 52:1421–1426
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank Marion VAZEL for her help in coordinating the clinical study.
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Afshin Gangi. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. This study has received funding by French state funds managed by the ANR within the Investissements d'Avenir programme (Labex CAMI) under reference ANR-11-LABX-0004. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: retrospective, observational, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garnon, J., Schlier, A., Buy, X. et al. Evaluation of percutaneous biopsies of renal masses under MRI-guidance: a retrospective study about 26 cases. Eur Radiol 25, 617–623 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3449-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3449-6