Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this investigation was to examine the association between cognition disorders and microstructural white matter (WM) changes in maintenance hemodialysis end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients.
Methods
Twenty-six maintenance hemodialysis ESRD patients and 28 healthy controls underwent diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE), Trial Marking Test-A&B (TMT-A&B), and white matter hyperintensity (WMH) assessment. Tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) analyses was performed to evaluate WM changes in the patients. Relationships between behavioural performances, clinical data, and the DTI index were tested, respectively, by correlation analysis at the voxel level.
Results
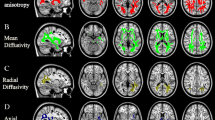
ESRD patients showed significant decreased fractional anisotropy (FA) in 14 WM regions, and increased mean diffusivity (MD) and radial diffusivity (RD) in widespread regions. Significant positive correlations between FA values and MMSE scores were found in the right anterior corona radiata and the left anterior thalamic radiation; significant negative correlations between the TMT-B time consumption and FA values were identified in the bilateral superior longitudinal fasciculus. Positive linear relationships between MD, RD values, and the duration of hemodialysis were found in several WM regions.
Conclusion
Structural damages to radiation and associative fibre tracts, caused by brain oedema and WM demyelination, may account for the cognitive deficits in ESRD patients.
Key Points
• Lower FA, higher MD and RD values were found in ESRD patients.
• Cognitive deficits in ESRD patients mainly focused on executive dysfunction.
• Cognitive impairment in ESRD patients may be associated with damages to WM.
• MD and RD are valuable in monitoring WM alteration in ESRD patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- DTI:
-
Diffusion tensor imaging
- FA:
-
Fractional anisotropy
- MD:
-
Mean diffusivity
- AD:
-
Axial diffusivity
- RD:
-
Radial diffusivity
- MMSE:
-
Mini Mental State Examination
- TMT:
-
Trial Marking Test
References
Zhang L, Wang F, Wang L et al (2012) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet 379:815–822
Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA et al (2007) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 298:2038–2047
Madan P, Kalra OP, Agarwal S, Tandon OP (2007) Cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22:440–444
Murray AM (2008) Cognitive impairment in the aging dialysis and chronic kidney disease populations: an occult burden. Adv Chron Kidney Dis 15:123–132
Kurella M, Chertow GM, Luan J, Yaffe K (2004) Cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease. J Am Geriatr Soc 52:1863–1869
Etgen T, Sander D, Chonchol M et al (2009) Chronic kidney disease is associated with incident cognitive impairment in the elderly: the INVADE study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:3144–3150
Weiner DE, Bartolomei K, Scott T et al (2009) Albuminuria, cognitive functioning, and white matter hyperintensities in homebound elders. Am J Kidney Dis 53:438–447
Yaffe K, Ackerson L, Kurella Tamura M et al (2010) Chronic kidney disease and cognitive function in older adults: findings from the chronic renal insufficiency cohort cognitive study. J Am Geriatr Soc 58:338–345
Chen CL, Lai PH, Chou KJ, Lee PT, Chung HM, Fang HC (2007) A preliminary report of brain edema in patients with uremia at first hemodialysis: evaluation by diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:68–71
Chou MC, Hsieh TJ, Lin YL et al (2013) Widespread white matter alterations in patients with end-stage renal disease: a voxelwise diffusion tensor imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:1945–1951
Kim HS, Park JW, Bai DS et al (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging findings in neurologically asymptomatic patients with end stage renal disease. NeuroRehabilitation 29:111–116
Hsieh TJ, Chang JM, Chuang HY et al (2009) End-stage renal disease: in vivo diffusion-tensor imaging of silent white matter damage. Radiology 252:518–525
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H et al (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31:1487–1505
Jones DK, Symms MR, Cercignani M, Howard RJ (2005) The effect of filter size on VBM analyses of DT-MRI data. Neuroimage 26:546–554
Cascio CJ, Gerig G, Piven J (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging: application to the study of the developing brain. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 46:213–223
Qi R, Zhang LJ, Zhong J et al (2013) Grey and white matter abnormalities in minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a study combining voxel-based morphometry and tract-based spatial statistics. Eur Radiol 23:3370–3378
Zikou AK, Kosmidou M, Astrakas LG, Tzarouchi LC, Tsianos E, Argyropoulou MI (2014) Brain involvement in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging study. Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3242-6
Kamagata K, Motoi Y, Tomiyama H et al (2013) Relationship between cognitive impairment and white-matter alteration in Parkinson’s disease with dementia: tract-based spatial statistics and tract-specific analysis. Eur Radiol 23:1946–1955
Kloppenborg RP, Nederkoorn PJ, Geerlings MI, van den Berg E (2014) Presence and progression of white matter hyperintensities and cognition: a meta-analysis. Neurology 82:2127–2138
Lu L, Bigler ED (2000) Performance on original and a Chinese version of Trail Making Test Part B: a normative bilingual sample. Appl Neuropsychol 7:243–246
Salat DH, Tuch DS, Greve DN et al (2005) Age-related alterations in white matter microstructure measured by diffusion tensor imaging. Neurobiol Aging 26:1215–1227
Feng L, Chong MS, Lim WS, Ng TP (2012) The Modified Mini-Mental State Examination test: normative data for Singapore Chinese older adults and its performance in detecting early cognitive impairment. Singap Med J 53:458–462
Scheltens P, Barkhof F, Leys D et al (1993) A semiquantative rating scale for the assessment of signal hyperintensities on magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurol Sci 114:7–12
Nichols TE, Holmes AP (2002) Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: a primer with examples. Hum Brain Mapp 15:1–25
Palmer CA (2002) Neurologic manifestations of renal disease. Neurol Clin 20:23–34, v
Smogorzewski MJ (2001) Central nervous dysfunction in uremia. Am J Kidney Dis 38:S122–S128
Arismendi-Morillo G, Fernandez-Abreu M (2010) Ultrastructural cutaneous microvascular pathology of young adults aged up to 50 years with chronic kidney disease and vascular cognitive impairment. Ultrastruct Pathol 34:214–218
Tarhan NC, Agildere AM, Benli US, Ozdemir FN, Aytekin C, Can U (2004) Osmotic demyelination syndrome in end-stage renal disease after recent hemodialysis: MRI of the brain. AJR Am J Roentgenol 182:809–816
Carpenter PA, Just MA, Reichle ED (2000) Working memory and executive function: evidence from neuroimaging. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10:195–199
Fletcher P, McKenna PJ, Friston KJ, Frith CD, Dolan RJ (1999) Abnormal cingulate modulation of fronto-temporal connectivity in schizophrenia. Neuroimage 9:337–342
Spence SA, Liddle PF, Stefan MD et al (2000) Functional anatomy of verbal fluency in people with schizophrenia and those at genetic risk. Focal dysfunction and distributed disconnectivity reappraised. Br J Psychiatry 176:52–60
Liang X, Wen J, Ni L et al (2013) Altered pattern of spontaneous brain activity in the patients with end-stage renal disease: a resting-state functional MRI study with regional homogeneity analysis. PLoS One 8:e71507
Martinez-Vea A, Salvado E, Bardaji A et al (2006) Silent cerebral white matter lesions and their relationship with vascular risk factors in middle-aged predialysis patients with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 47:241–250
Conijn MM, Kloppenborg RP, Algra A et al (2011) Cerebral small vessel disease and risk of death, ischemic stroke, and cardiac complications in patients with atherosclerotic disease: the Second Manifestations of ARTerial disease-Magnetic Resonance (SMART-MR) study. Stroke 42:3105–3109
Silbert LC, Nelson C, Howieson DB, Moore MM, Kaye JA (2008) Impact of white matter hyperintensity volume progression on rate of cognitive and motor decline. Neurology 71:108–113
Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Cercignani M (2009) About “axial” and ‘radial” diffusivities. Magn Reson Med 61:1255–1260
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2014M552596 for Kai Liu). The scientific guarantor of this publication is Gang Sun. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. This study has received funding by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2014M552596 for Kai Liu). No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained from the ethics committee of Jinan Military General Hospital, and written informed consent was obtained from all subjects (patients) in this study. Methodology: retrospective, case-control study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ruijie Zhang and Kai Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Liu, K., Yang, L. et al. Reduced white matter integrity and cognitive deficits in maintenance hemodialysis ESRD patients: A diffusion-tensor study. Eur Radiol 25, 661–668 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3466-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3466-5