Abstract
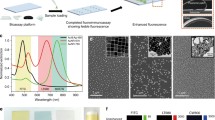
Amplification of fluorescence is a nanoscale phenomenon which is particularly pronounced in close proximity to metal nanostructures. Due to its sharp distance dependence, it is ideally suited to monitor biorecognition reactions. Using this effect we have been able to demonstrate ultrasensitive bioassays. Two types of metal nanostructures have been employed, nanometric silver islands deposited over an ultrathin metal mirror and silver fractal structures. For the first type, metal mirrors (aluminum, gold, or silver protected with a thin silica layer) were coated with SIFs and an immunoassay (model assay for rabbit IgG or myoglobin immunoassay) was performed on this surface using fluorescently labeled antibodies. Our results show that SIFs alone (on a glass surface not coated with metal) enhance the immunoassay signal approximately 3 to 10-fold. Using a metal mirror instead of glass as support for SIFs leads to up to 50-fold signal enhancement. The second type of metal nanostructures, silver fractals, were produced by electrochemical reduction of silver nitrate deposited on sapphire covered with a thin conductive film of indium tin oxide. These structures were used as a substrate for a model rabbit IgG bioassay. The fluorescence resulting from the binding of antibody labeled with Rhodamine was highly nonuniform with distinctive hot spots. These highly fluorescent regions were correlated with areas of higher Ag thickness and coverage. Such high values of fluorescence amplification in both types of nanostructures have been interpreted by using time-resolved fluorescence data and by considering the radiative properties of plasmons in the environments which promote plasmon coupling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.R. Lakowicz, J. Malicka, I. Gryczynski, Z. Gryczynski, C.D. Geddes, Appl. Phys. 36, 240 (2003)
J.R. Lakowicz, Y. Shen, S. D’Auria, J. Malicka, J. Fang, Z. Gryczynski, I. Gryczynski, Anal. Biochem. 301, 261 (2002)
B. Lamprecht, J.R. Krenn, G. Schider, H. Ditlbacher, M. Salerno, N. Felidj, A. Leitner, F.R. Aussenegg, Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 51 (2001)
H.X. Xu, Phys. Lett. A 312, 411 (2003)
J. Zhang, J. Malicka, I. Gryczynski, J.R. Lakowicz, J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 7643 (2005)
J.R. Lakowicz, J. Malicka, S. D’Auria, I. Gryczynski, Anal. Biochem. 320, 13 (2003)
F. Xie, M. Baker, E. Goldys, J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 23085 (2006)
E. Matveeva, Z. Gryczynski, J. Malicka, I. Gryczynski, J.R. Lakowicz, Anal. Biochem. 334, 303 (2004)
E.G. Matveeva, I. Gryczynski, J. Malicka, Z. Gryczynski, E. Goldys, J. Howe, K.W. Berndt, J.R. Lakowicz, J. Fluoresc. 15, 865 (2005)
J.R. Lakowicz, I. Gryczynski, J. Malicka, J. Lukomska, S. Makowiec, E. Matveeva, K. Nowaczyk, Z. Gryczynski, Biophys. J. 88, 163A (2005)
H.R. Stuart, D.G. Hall, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 5663 (1998)
Y. Sawada, A. Dougherty, P. Gollub, Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 1260 (1986)
C.D. Geddes, A. Parfenov, D. Roll, I. Gryczynski, J. Malicka, J.R. Lakowicz, J. Fluoresc. 13, 267 (1995)
A. Doron, E. Katz, I. Willner, Langmuir 11, 1313 (1995)
J.R. Lakowicz, J. Malicka, S. Dauria, I. Gryczynski, Anal. Biochem. 320, 13 (2003)
J.-H. Song, T. Atay, S. Shi, H. Urabe, A.V. Nurmikko, Nano Lett. 5, 1557 (2005)
E. Matveeva, Z. Gryczynski, J.R. Lakowicz, J. Immunol. Methods 302, 26 (2005)
F. De Martini, G. Innocenti, G.R. Jacobovitz, P. Mataloni, Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 2955 (1987)
U. Dorner, P. Zoller, Phys. Rev. A 66, 023816-1 (2002)
J. Eschner, Lett. Nature 413, 495 (2001)
www.rsoftdesign.com, Feb. 2007
E.C. Le Ru, P.G. Etchegoin, http://arxiv.org/abs/physics/0509154
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
87.64.Ni; 81.07.-b; 87.14.-g
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldys, E., Barnett, A., Xie, F. et al. Plasmon-enhanced fluorescence near metallic nanostructures: biochemical applications. Appl. Phys. A 89, 265–271 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-4100-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-4100-z