Abstract.
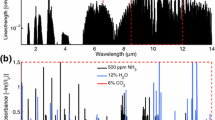
An industrial trace-ammonia sensor based on photoacoustic spectroscopy and CO2 lasers has been developed for measuring ammonia with a 1σ detection limit of 220 parts-per-trillion (ppt) in an integration time of 30 s. The instrument response time for measuring ammonia was 200 s, limited by adsorption effects due to the polar nature of ammonia. The minimum detectable fractional absorbance was 2.0×10-7, and the minimum normalized detectable absorption coefficient for this system was 2.4×10-7 W cm-1/\(\surd\Box H\Box \)z. The 9R(30) transition of the CO2 laser at 9.22 μm with 2 W of output power was used to probe the strong sR(5,K) multiplet of ammonia at the same wavelength. This sensor was demonstrated with an optically multiplexed configuration for simultaneous measurement in four cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 April 2002 / Revised version: 31 May 2002 / Published online: 21 August 2002
RID="*"
ID="*"Corresponding author. Fax: +1-310/458-0171, E-mail: webber@pranalytica.com
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pushkarsky, M., Webber, M., Baghdassarian, O. et al. Laser-based photoacoustic ammonia sensors for industrial applications. Appl Phys B 75, 391–396 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-002-0967-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-002-0967-8