Abstract
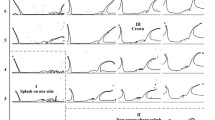
The impact process of spherical hollow droplets impinging onto a solid surface has been experimentally studied. Formation of a counter-jet in a wide range of Reynolds and Weber numbers was revealed, this jet being similar to a Worthington jet. For characterizing the regime of liquid flow in the hollow droplet, we propose using the Euler number. Theoretically, the problem was treated using a simple model of axisymmetric liquid flow. The obtained results proved to be consistent with experimental data.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Eu = P g0/ρU 2p :
-
Euler number
- Re = ρD p U p /μ :
-
Reynolds number
- We = ρD p U 2p /σ :
-
Weber number
- D cont :
-
Mean diameter of the circumference round which the droplet shell contacts the spreading liquid layer (m)
- D p :
-
Droplet diameter (m)
- D s :
-
Splat diameter (m)
- E tot(t), E kin(t), E surf(t):
-
Total, kinetic, and surface energy of spreading droplet at time t (J)
- E visc(t):
-
Viscous loss of energy in droplet flow by time t (J)
- m p :
-
Droplet mass (kg)
- P g0 :
-
Initial pressure in gas cavity (Pa)
- t d = D p /U p :
-
Characteristic time of droplet deformation (s)
- U p :
-
Droplet velocity (m/s)
- U jet :
-
Counter-jet velocity (m/s)
- u z, u r :
-
Vertical and radial velocities of liquid flow in spreading layer (m/s)
- V tot(t):
-
Total liquid volume having entered the spreading layer by time t (m3)
- V disk(t):
-
Liquid volume having entered the peripheral spreading disk by time t (m3)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity of liquid (Pa s)
- ρ :
-
Liquid density (kg/m3)
- σ :
-
Liquid surface tension (N/m)
- Δp :
-
Droplet shell thickness (m)
- δ p = Δp/D p :
-
Relative droplet shell thickness
- β = (1 − 2δ p)3 :
-
Part of droplet volume occupied by gas
References
Benjamin TJ, Ellis AT (1966) The collapse of cavitation bubbles and the pressures thereby produced against solid boundaries. Phil Trans R Soc Lond A 260(1110):221–240
Blake JR, Gibson DC (1987) Cavitation bubbles near boundaries. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 19:99–123
Chandra S, Fauchais P (2009) Formation of solid splats during thermal spray deposition. J Therm Spray Tech 18(2):148–180
Fantassi S, Vardelle M, Vardelle A, Fauchais P (1993) Influence of the velocity of plasma-sprayed particles on splat formation. J Therm Spray Tech 2(4):379–384
Fauchais P, Fukumoto M, Vardelle A, Vardelle M (2004) Knowledge concerning splat formation: an invited review. J Therm Spray Tech 13(3):337–360
Grigor’ev IS, Meilikhova EZ (eds) (1991) Physical quantities: a reference book. Energoatomizdat, Moscow (in Russian)
Gulyaev IP (2009) Synthesis and processing of hollow particles in plasma flows. Dissertation, Novosibirsk, ITAM SB RAS (in Russian)
Gulyaev IP, Solonenko OP, Gulyaev PYu, Smirnov AV (2009) Hydrodynamic features of the impact of a hollow spherical drop on a flat surface. Tech Phys Lett 35(10):885–888
Lavrentiev MA (1957) Cumulative charge and principles of its operation. Uspekhi Matematicheskih Nauk 12(4):41–56 (in Russian)
Lavrentiev MA, Shabat BV (1977) Hydrodynamic problems and their mathematical models. Nauka, Moscow (in Russian)
Madejski J (1976) Solidification of droplets on a cold surface. Heat Mass Transf 19:1009–1013
Mayer BB (1989) Accumulation effect in simple experiments. Nauka, Moskow (in Russian)
Moreau C, Cielo P, Lamontagne M, Dallaire S, Vardelle M (1990) Impacting particle temperature monitoring during plasma spray deposition. Meas Sci Technol 1:807–815
Moreau C, Cielo P, Lamontagne M (1992) Flattening and solidification of thermally sprayed particles. J Therm Spray Tech 1(4):317–323
Ogawa A, Utsuno K, Mutou M, Kouzen S, Shimotake Y, Satou Y (2006) Morphological study of cavity and worthington jet formations for Newtonian and Non-Newtonian liquids. Particul Sci Technol 24(2):181–225
Prosperetti A, Oguz HN (1993) The impact of drops on liquid surfaces and the underwater noise of rain. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 25:577–602
Rioboo R, Tropea C, Marengo M (2001) Outcomes from a drop impact on solid surfaces. At Sprays 11:155–165
Shinoda K, Kojima Y, Yoshida T (2005) In situ measurement system for deformation and solidification phenomena of Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia droplets impinging on quartz glass substrate under plasma-spraying conditions. J Therm Spray Tech 14(4):511–517
Shinoda K, Murakami H, Kuroda S, Oki S, Takehara K, Etoh TG (2007) High-speed thermal imaging of Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia droplet impinging on substrate in plasma spraying. Appl Phys Lett 90(19). Article no. 194103
Solonenko OP, Mikhalchenko AA, Kartaev EV (2005) Splat formation under YSZ hollow droplet impact onto substrate. In: Proceedings of ITSC’05, 2–4 May, Bazel, Switzerland
Solonenko OP, Gulyaev IP, Smirnov AV (2008a) Plasma processing and deposition of powdered metal oxides consisting of hollow spherical particles. Tech Phys Lett 34(12):1050–1052
Solonenko OP, Smirnov AV, Gulyaev IP (2008b) Spreading and solidification of hollow molten droplet under its impact onto substrate: computer simulation and experiment. Proceedings of AIP, Melville, New York 982:561–568
Solonenko OP, Gulyaev IP, Smirnov AV (2011) Thermal plasma processes for production of hollow spherical powders: theory and Experiment. J Therm Sci Tech 6(2):219–234
Thoroddsen ST, Etoh TG, Takehara K (2008) High-speed imaging of drops and bubbles. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 40:257–285
Vardelle M, Vardelle A, Fauchais P, Moreau C (1994) Pyrometer system for monitoring the particle impact on a substrate during a plasma spray process. Meas Sci Technol 5(3):205–212
Vardelle M, Vardelle A, Leger AC, Fauchais P, Gobin D (1995) Influence of particle parameters at impact on splat formation and solidification in plasma spraying processes. J Therm Spray Tech 4(1):50–58
Worthington AM (1908) A study of splashes. Longmans, Green, London
Xu L, Zhang WW, Nagel SR (2005) Drop splashing on a dry smooth surface. Phys Rev Lett 94:184505
Yarin AL (2006) Drop impact dynamics: splashing, spreading, receding, bouncing. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 38:159–192
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gulyaev, I.P., Solonenko, O.P. Hollow droplets impacting onto a solid surface. Exp Fluids 54, 1432 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-012-1432-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-012-1432-z