Abstract
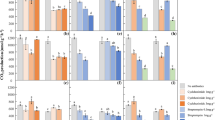
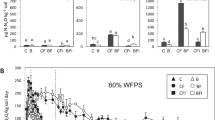
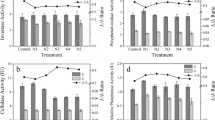
The present work aims at evaluating the effect of cycloheximide at concentrations of between 0.5 and 5mgg–1 on N2O and NO3 – production in two slightly alkaline soils, sampled from deciduous woodland and arable cultivation. In the first experiment, peptone was used as the “inducing substrate” for heterotrophic activity, and soil was incubated with cycloheximide (at different concentrations) and/or acetylene (1mll–1) to block induced eukaryotic protein synthesis and ammonia monooxygenase activity, respectively. Peptone addition stimulated N2O and NO3 – production significantly in woodland soil, whereas arable soil showed no significant N2O emissions and low NO3 – production. Low cycloheximide concentrations drastically reduced N2O emissions in woodland soil, suggesting a potential role of fungi in N2O emissions. However, acetylene was equally effective in blocking N2O emissions and part of NO3 – production, so that a possible role of ammonia monooxygenase in an organic-inorganic pathway of N nitrification in fungal metabolism can be hypothesized. A second experiment was carried out on the woodland soil to check if low cycloheximide concentrations had non-target biocidal effects on soil microorganisms. Attention was focused on the range of concentrations which had reduced N2O emission in the woodland soil. The results suggested that at concentrations of cycloheximide between 0.5 and 2mgg–1 any biocidal effect on microbial biomass was negligible in the first 48h; therefore only selective inhibition of protein synthesis could be expected. The whole nitrifier population seemed to be particularly sensitive to cycloheximide concentrations higher than 2.5mgg–1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 July 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castaldi, S., Smith, K. Effect of cycloheximide on N2O and NO3– production in a forest and an agricultural soil. Biol Fertil Soils 27, 27–34 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050395
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050395