Abstract
To cherish the memory of the late Professor Duzheng YE on what would have been his 100th birthday, and to celebrate his great accomplishment in opening a new era of Tibetan Plateau (TP) meteorology, this review paper provides an assessment of the atmospheric heat source (AHS) over the TP from different data resources, including observations from local meteorological stations, satellite remote sensing data, and various reanalysis datasets. The uncertainty and applicability of these heat source data are evaluated. Analysis regarding the formation of the AHS over the TP demonstrates that it is not only the cause of the atmospheric circulation, but is also a result of that circulation. Based on numerical experiments, the review further demonstrates that land–sea thermal contrast is only one part of the monsoon story. The thermal forcing of the Tibetan–Iranian Plateau plays a significant role in generating the Asian summer monsoon (ASM), i.e., in addition to pumping water vapor from sea to land and from the lower to the upper troposphere, it also generates a subtropical monsoon–type meridional circulation subject to the angular momentum conservation, providing an ascending-air large-scale background for the development of the ASM.
摘要
值叶笃正先生诞辰100周年之际, 为了纪念他在青藏高原气象学方面的研究工作, 和创造性的开启了青藏高原气象学这一门学科的伟大贡献, 我们撰写了这篇研究综述文章, 主要回顾了对近几十年来青藏高原大气热源研究的评估工作. 这些工作基于多种资料源, 包括局地的台站观测资料, 卫星遥感资料, 和各种再分析资料. 本文指出了这些热源资料的不确定性和可用性. 对高原大气热源形成的分析表明, 热源本身不仅仅是大气环流变化的诱因, 并且它同时也是大气环流变化的结果. 基于一系列数值试验, 本文指出了海陆热力差异仅仅是亚洲夏季风形成的部分原因, 而青藏-伊朗高原的热力强迫作用对亚洲夏季风的形成具有至关重要的作用: 它不但将海洋的水汽从对流层低层抽吸到大陆上空对流层高层, 而且在角动量守恒的约束下, 它还导致了副热带经向季风环流的形成, 这给亚洲夏季风的发展提供了大尺度背景.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessandri, C., and N. VenturiGinori, 1931: Meteorologia, Aerologia e Pireliometria. Spedizione Italiana de Filippi, Serie I, Bologna, 3.(In Italian)
Chen, L. X., and W. Li, 1981: The summer atmospheric heat budget in the Asian monsoon area. Collection of the National Conference on the Tropical Summer Monsoon, Vol. I., Yunnan People’s Press, 86–101. (in Chinese)
Chen, L. X., and W. Li, 1982: Structure of the monthly mean atmospheric heat source in the Asian monsoon area. Collection of the National Conference on the Tropical Summer Monsoon, Vol. II., Yunnan People’s Press, 246–258. (in Chinese)
Chen, L. X., E. R. Reiter, and Z. Q. Feng, 1985: The atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau: May August 1979. Mon. Wea. Rev., 113(10), 1771–1790, doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1985)113<1771:TAHSOT>2.0.CO;2.
Chen, L. X., F. Schmidt, and W. Li, 2003: Characteristics of the atmospheric heat source and moisture sink over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during the Second TIPEX of summer 1998 and their impact on surrounding monsoon. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 83(1–2), 1–18, doi: 10.1007/s00703-002-0546-x.
Chu, P. C., 1957a: The steady state perturbations of the westerlies by the large-scale heat sources, sinks and earth’s orography (I)—The distribution of heat sources and sinks in lower troposphere over northern hemisphere. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 28, 122–140, doi: 10.11676/qxxb1957.011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chu, P. C., 1957b: The steady state perturbations of the westerlies by the large-scale heat sources and sinks and earth’s orography (II). Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 28, 198–224. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chu, P. C., 1957c: Role of large-scale mountain in the formation of temperature field. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 28, 315–318. (in Chinese)
Duan, A. M., and G. X. Wu, 2008: Weakening trend in the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Part I: Observations. J. Climate, 21(13), 3149–3164, doi: 10.1175/2007JCLI1912.1.
Duan, A. M., and G. X. Wu, 2009: Weakening trend in the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Part II: Connection with climate warming. J. Climate, 22, 4197–4212, doi: 10.1175/2009JCLI2699.1.
Duan, A. M., M. R. Wang, and Z. X. Xiao, 2014: Uncertainties in quantitatively estimating the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 7, 28–33, doi: 10.1080/16742834.2014.11447131.
Flohn, H., 1957: Large-Scale aspects of the “summer monsoon” in South and East Asia. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 75, 180–186, doi: 10.2151/jmsj1923.35A.0 180.
He, J. H., H. M. Xu, S. S. Zhong, Y. F. Gong, L. P. Li, and B. Zhang, 2011: Characteristics of the Atmospheric Heating Source Over the Tibetan Plateau, Its Impacts and Potential Mechanism. Beijing, China Meteor. Press, 243 pp. (in Chinese)
Held, I. M., 1983: Stationary and quasi-stationary eddies in the extratropical troposphere: Theory. Large-Scale Dynamical Principles in the Atmosphere, B. Hoskins and R. Pearce, Eds., Academic Press, 127–168.
Held, I. M., and A. Y. Hou, 1980: Nonlinear axially symmetric circulations in a nearly inviscid atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 37(3), 515–533, doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1980)037<0515: NASCIA>2.0.CO;2.
Jiang, X.W., Y. Q. Li, S. Yang, K. Yang, and J.W. Chen, 2016: Interannual variation of summer atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan plateau and the role of convection around the western maritime continent. J. Climate, 29, 121–138, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0181.1.
Kuo, H. L., and Y. F. Qian, 1982: Numerical simulation of the development of mean monsoon circulation in July. Mon. Wea. Rev., 110, 1879–1897, doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1982)110 <1879:NSOTDO>2.0.CO;2.
Li, C. F., and M. Yanai, 1996: The onset and interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon in relation to land–sea thermal contrast. J. Climate, 9, 358–375, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<0358:TOAIVO>2.0.CO;2.
Liang, X. Y., Y. M. Liu, and G. X. Wu, 2005: The role of landsea distribution in the formation of the Asian summer monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L03708, doi: 10.1029/2004GL 021587.
Liu, Y. M., B. Hoskins, and M. Blackburn, 2007: Impact of Tibetan orography and heating on the summer flow over Asia (125th anniversary issue of the meteorological society of Japan). J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 85B, 1–19.
Liu, Y. M., G. X. Wu, J. L. Hong, B. W. Dong, A. M. Duan, Q. Bao, and L. J. Zhou, 2012: Revisiting Asian monsoon formation and change associated with Tibetan Plateau forcing: II. Change. Climate Dyn., 39(5), 1183–1195, doi: 10.1007/s00382-012-1335-y.
Luo, H. B., and M. Yanai, 1984: The large-scale circulation and heat sources over the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas during the early summer of 1979. Part II: Heat and moisture budgets. Mon. Wea. Rev., 112, 966–989, doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1984)112<0966:TLSCAH>2.0.CO;2.
Ma, Y., and Coauthors, 2014a: Combining MODIS, AVHRR and in situ data for evapotranspiration estimation over heterogeneous landscape of the Tibetan Plateau. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 14, 1507–1515, doi: 10.5194/acp-14-1507-2014.
Ma, Y. M., and Coauthors, 2014b: Using MODIS and AVHRR data to determine regional surface heating field and heat flux distributions over the heterogeneous landscape of the Tibetan Plateau. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 117(3-4), 643–652, doi: 10.1007/s00704-013-1035-5.
Molnar, P., and K. A. Emanuel, 1999: Temperature profiles in radiative-convective equilibrium above surfaces at different heights. J. Geophys. Res., 104(D20), 24265–24271, doi: 10.1029/1999JD900485.
Pan, W. J., J. Y. Mao, and G. X. Wu, 2013: Characteristics and mechanism of the 10-20-day oscillation of spring rainfall over southern China. J. Climate, 26, 5072–5087, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00618.1.
Plumb, R. A., and A. Y. Hou, 1992: The response of a zonally symmetric atmosphere to subtropical thermal forcing: Threshold behavior. J. Atmos. Sci., 49, 1790–1799, doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1992)049<1790:TROAZS>2.0.CO;2.
Schneider, E. K., 1977: Axially symmetric steady-state models of the basic state for instability and climate studies. Part II. Nonlinear calculations. J. Atmos. Sci., 34(2): 280–296, doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1977)034<0280:ASSSMO>2.0.CO;2.
Schneider, E. K., 1987: A simplified model of the modified Hadley circulation. J. Atmos. Sci., 44(22), 3311–3328, doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1987)044<3311:ASMOTM>2.0.CO;2.
Schneider, E. K., and R. S. Lindzen, 1977: Axially symmetric steady-state models of the basic state for instability and climate studies. Part I. Linearized calculations. J. Atmos. Sci., 34(2): 263–279, doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1977)034<0263: ASSSMO>2.0.CO;2.
Seto, R., T. Koike, and M. Rasmy, 2013: Analysis of the vertical structure of the atmospheric heating process and its seasonal variation over the Tibetan Plateau using a land data assimilation system. J. Geophys. Res., 118, 12 403–12 421, doi: 10.1002/2013JD020072.
Tamura, T., K. Taniguchi, and T. Koike, 2010: Mechanism of upper tropospheric warming around the Tibetan Plateau at the onset phase of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Geophys. Res., 115(D2), D02106, doi: 10.1029/2008JD011678.
Taniguchi, K., and T. Koike, 2007: Increasing atmospheric temperature in the upper troposphere and cumulus convection over the eastern part of the Tibetan Plateau in the pre-monsoon season of 2004. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan., 85A, 271–294, doi: 10.2151/jmsj.85A.271.
Taniguchi, K., T. Tamura, T. Koike, K. Ueno, and X. D. Xu, 2012: Atmospheric conditions and increasing temperature over the Tibetan Plateau during early spring and the premonsoon season in 2008. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan., 90C, 17–32, doi: 10.2151/jmsj.2012-C02.
Tian, S. F., and T. Yasunari, 1998: Climatological aspects and mechanism of spring persistent rains over central China. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan., 76(1), 57–71.
Wan, R. J., and G. X. Wu, 2007: Mechanism of the Spring Persistent Rains over southeastern China. Sciences in China D: Earth Sciences, 50, 130–144.
Webster, P. J., V. O. Maga˜na, T. N. Palmer, J. Shukla, R. A. Tomas, M. Yanai, and T. Yasunari, 1998: Monsoons: Processes, predictability, and the prospects for prediction. J. Geophys. Res., 103, 14 451–14 510, doi: 10.1029/97JC02719.
Wu, G. X., and Y. S. Zhang, 1998: Tibetan plateau forcing and the timing of the monsoon onset over South Asia and the South China Sea. Mon. Wea. Rev., 126, 913–927, doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1998)126<0913:TPFATT>2.0.CO;2.
Wu, G. X., H. F. Zhuo, Z. Q. Wang, and Y. M. Liu, 2016b: Two types of summertime heating over the Asian large-scale orography and excitation of potential-vorticity forcing I. Over Tibetan Plateau. Science China Earth Sciences, 59(10), 1996–2008, doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-5328-2.
Wu, G. X., B. He, Y. M. Liu, Q. Bao, and R. C. Ren, 2015b: Location and variation of the summertime upper-troposphere temperature maximum over South Asia. Climate Dyn., 45, 2757–2774, doi: 10.1007/s00382-015-2506-4.
Wu, G. X., W. P. Li, H. Guo, H. Liu, J. S. Xue, and Z. Z. Wang, 1997: Sensible heat driven air-pump over the Tibetan Plateau and its impacts on the Asian Summer Monsoon. Collections on the Memory of Zhao Jiuzhang, Y. Duzheng, Ed., Science Press, 116–126. (in Chinese)
Wu, G. X., Y. M. Liu, B. He, Q. Bao, A. M. Duan, and F. F. Jin, 2012b: Thermal controls on the Asian summer monsoon. Scientific Reports, 2, 404, doi: 10.1038/srep00404.
Wu, G. X., B. Hu, Y. M. Liu, Q. Bao, R. C. Ren, and B. Q. Liu, 2016a: Recent progresses on dynamics of the Tibetan Plateau and Asian summer monsoon. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 40(1), 22–32, doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1504.15129. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu, G. X., Y. M. Liu, X. Zhu, W. Li, R. C. Ren, A. M. Duan, and X. Liang, 2009: Multi-scale forcing and the formation of subtropical desert and monsoon. Annales Geophysicae, 27, 3631–3644, doi: 10.5194/angeo-27-3631-2009.
Wu, G. X., Y. M. Liu, B. W. Dong, X. Y. Liang, A. M. Duan, Q. Bao, and J. J. Yu, 2012a: Revisiting Asian monsoon formation and change associated with Tibetan Plateau forcing: I. Formation. Climate Dyn., 39(5), 1169–1181, doi: 10.1007/s00382-012-1334-z.
Wu, G. X., and Coauthors, 2007: The influence of mechanical and thermal forcing by the Tibetan Plateau on Asian climate. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 8(4), 770–789, doi: 10.1175/JHM609.1.
Wu, G. X., and Coauthors, 2015a: Tibetan Plateau climate dynamics: Recent research progress and outlook. National Science Review, 2(1), 100–116, doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwu045.
Yanai, M., C. F. Li, and Z. S. Song, 1992: Seasonal heating of the Tibetan Plateau and its effects on the evolution of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 70, 319–351, doi: 10.2151/jmsj1965.70.1B 319.
Yang, J. C., and S. W. Lo, 1957: Study of the circulation and heating feature over the Tibetan Plateau based on surface observation. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 28, 264–274, doi: 10.11676/qxxb1957.022. (in Chinese)
Yang, K., Y. Y. Chen, and J. Qin, 2009: Some practical notes on the land surface modeling in the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 13, 687–701, doi: 10.5194/hess-13-687-2009.
Yang, K., X. F. Guo, and B. Y. Wu, 2011b: Recent trends in surface sensible heat flux on the Tibetan Plateau. Science China Earth Sciences, 54, 19–28, doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4036-6.
Yang, K., X. F. Guo, J. He, J. Qin, and T. Koike, 2011a: On the climatology and trend of the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau: An experiments-supported revisit. J. Climate, 24, 1525–1541, doi: 10.1175/2010JCLI3848.1.
Yeh, T. C., S. W. Lo, and P. C. Chu, 1957: The wind structure and heat balance in the lower troposphere over Tibetan plateau and its surrounding. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 28, 108–121, doi: 10.11676/qxxb1957.010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu, J. J., Y. M. Liu, and G. X. Wu, 2011a: An analysis of the diabatic heating characteristic of atmosphere over the Tibetan Plateau in winter I: Climatology. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 69(1), 79–88, doi: 10.11676/qxxb2011.007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu, J. J., Y. M. Liu, and G. X. Wu, 2011b: An analysis of the diabatic heating characteristic of atmosphere over the Tibetan Plateau in winter II: Interannual variation. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 69(1), 89–98, doi: 10.11676/qxxb2011.008. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang, J. J., G. W. Sun, and B. D. Chen, 1991: Research on Atmospheric Low-Frequency Variations over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Meteorological Press, 1–109. (in Chinese)
Zhao, P., and L. X. Chen, 2001: Interannual variability of atmospheric heat source/sink over the Qinghai–Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau and its relation to circulation. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 106–116, doi: 10.1007/s00376-001-0007-3.
Zhou, T. J., D. Y. Gong, J. Li, and B. Li, 2009: Detecting and understanding the multi-decadal variability of the East Asian summer monsoon recent progress and state of affairs. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 18(4), 455–467, doi: 10.1127/0941-2948/2009/0396.
Zhu, X. Y., Y. M. Liu, and G. X. Wu, 2012: An assessment of summer sensible heat flux on the Tibetan Plateau from eight data sets. Science China Earth Sciences, 55(5), 779–786, doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4379-2.
Acknowledgements
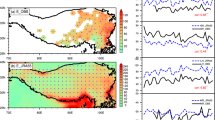
Thanks to Dr. WANG Meirong for plotting Fig. 1, and to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments. This study was supported by the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Major Research Plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 91637312, 91437219, 91637208, and 41530426), and the Special Program for Applied Research on Super Computation of the NSFC–Guangdong Joint Fund (second phase) (Grant No. U1501501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, G., He, B., Duan, A. et al. Formation and variation of the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau and its climate effects. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 34, 1169–1184 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-017-7014-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-017-7014-5