Abstract
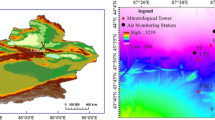
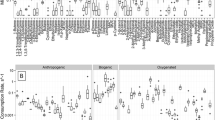
The vertical observation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) is an important means to clarify the mechanisms of ozone formation. To explore the vertical evolution of VOCs in summer, a field campaign using a tethered balloon during summer photochemical pollution was conducted in Shijiazhuang from 8 June to 3 July 2019. A total of 192 samples were collected, 23 vertical profiles were obtained, and the concentrations of 87 VOCs were measured. The range of the total VOC concentration was 41–48 ppbv below 600 m. It then slightly increased above 600 m, and rose to 58 ± 52 ppbv at 1000 m. The proportion of alkanes increased with height, while the proportions of alkenes, halohydrocarbons and acetylene decreased. The proportion of aromatics remained almost unchanged. A comparison with the results of a winter field campaign during 8–16 January 2019 showed that the concentrations of all VOCs in winter except for halohydrocarbons were more than twice those in summer. Alkanes accounted for the same proportion in winter and summer. Alkenes, aromatics, and acetylene accounted for higher proportions in winter, while halohydrocarbons accounted for a higher proportion in summer. There were five VOC sources in the vertical direction. The proportions of gasoline vehicular emissions + industrial sources and coal burning were higher in winter. The proportions of biogenic sources + long-range transport, solvent usage, and diesel vehicular emissions were higher in summer. From the surface to 1000 m, the proportion of gasoline vehicular emissions + industrial sources gradually increased.
摘要
挥发性有机物(VOCs)的垂直观测是阐明臭氧形成机理的重要手段。为探讨夏季VOCs的垂直演变,本文作者于2019年6月8日至7月3日夏季光化学污染期间,在石家庄市使用系留气艇进行了外场垂直观测实验。实验期间共采集192个样品,获取23条垂直廓线,测定了87种VOCs的浓度。TVOCs浓度在0–600 m为41–48 ppbv,至1000 m浓度逐渐升高至58 ± 52 ppbv。烷烃占比随高度升高,烯烃、卤代烃和乙炔占比随高度下降,芳香烃占比基本不变。与2019年1月8日至16日冬季实验结果对比,冬夏季VOCs浓度垂直分布具有差异。除卤代烃外,其他VOCs在各高度冬季浓度均为夏季的2倍以上。烷烃在冬夏季的占比相同,烯烃、芳香烃和乙炔的占比在冬季高于夏季,卤代烃在夏季的占比高于冬季。垂直方向VOCs来源包括5类。汽油车尾气排放+工业源、燃煤占比在冬季较高。生物源+长距离传输、溶剂使用、柴油车尾气排放占比在夏季较高。从近地面至1000 m,汽油车尾气排放+工业源占比逐渐升高。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimoto, H., 2003: Global air quality and pollution. Science, 302, 1716–1719, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1092666.
Atkinson, R., and J. Arey, 2003: Atmospheric degradation of volatile organic compounds. Chemical Reviews, 103, 4605–4638, https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0206420.
Bonsang, B., D. Martin, G. Lambert, M. Kanakidou, J. C. Le Roulley, and G. Sennequier, 1991: Vertical distribution of non methane hydrocarbons in the remote marine boundary layer. J. Geophys. Res., 96, 7313–7324, https://doi.org/10.1029/90JD02539.
Cai, C. J., F. H. Geng, X. X. Tie, Q. Yu, and J. L. An, 2010: Characteristics and source apportionment of VOCs measured in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Environ., 44, 5005–5014, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.07.059.
Carter, W. P. L., 2010: Development of the SAPRC-07 chemical mechanism. Atmos. Environ., 44, 5324–5335, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.01.026.
Carter, W. P. L., and G. Heo, 2013: Development of revised SAPRC aromatics mechanisms. Atmos. Environ., 77, 404–414, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.05.021.
Chen, P., J. N. Quan, Q. Zhang, X. X. Tie, Y. Gao, X. Li, and M. Y. Huang, 2013: Measurements of vertical and horizontal distributions of ozone over Beijing from 2007 to 2010. Atmos. Environ., 74, 37–44, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosnvv.2013.03.026.
Chen, W. T., M. Shao, S. H. Lu, M. Wang, L. M. Zeng, B. Yuan, and Y. Liu, 2014: Understanding primary and secondary sources of ambient carbonyl compounds in Beijing using the PMF model. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 74, 3047–3062, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-3047-2014.
Chen, X. Y., and Coauthors, 2018: Factors dominating 3-dimensional ozone distribution during high tropospheric ozone period. Environmental Pollution, 232, 55–64, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.017.
Gao, W., X. X. Tie, J. M. Xu, R. J. Huang, X. Q. Mao, G. Q. Zhou, and L. Y. Chang, 2017: Long-term trend of O3 in a mega City (Shanghai), China: Characteristics, causes, and interactions with precursors. Science of the Total Environment, 603–604, 425–433, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.099.
Han, T. T., Z. Q. Ma, W. Y. Xu, L. Qiao, Y. R. Li, D. He, and Y. Wang, 2020: Characteristics and source implications of aromatic hydrocarbons at urban and background areas in Beijing, China. Science of the Total Environment, 707, 136083, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136083.
Islam, M. R., and Coauthors, 2020: Ambient air quality in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal, during the pre-monsoon: Concentrations and sources of particulate matter and trace gases. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 20, 2927–2951, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-20-2927-2020.
Koβmann, M., H. Vogel, B. Vogel, R. Vögtlin, U. Corsmeier, F. Fiedler, O. Klemm, and H. Schlager, 1996: The composition and vertical distribution of volatile organic compounds in southwestern Germany, eastern France and northern Switzerland during the TRACT Campaign in September 1992. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 21, 429–433, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-1946(97)81137-8.
Liu, C. T., Z. B. Ma, Y. J. Mu, J. F. Liu, C. L. Zhang, Y. Y. Zhang, P. F. Liu, and H. X. Zhang, 2017: The levels, variation characteristics, and sources of atmospheric non-methane hydrocarbon compounds during wintertime in Beijing, China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 10633–10649, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-10633-2017.
Liu, Y., M. Shao, L. L. Fu, S. H. Lu, L. M. Zeng, and D. G. Tang, 2008: Source profiles of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) measured in China: Part I. Atmos. Environ., 42, 6247–6260, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.01.070.
Liu, Y. F., and Coauthors, 2020: Characterization and sources of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and their related changes during ozone pollution days in 2016 in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution, 257, 113599, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113599.
Ma, Z. Q., H. H. Xu, W. Meng, X. L. Zhang, J. Xu, Q. Liu, and Y. S. Wang, 2013: Vertical ozone characteristics in urban boundary layer in Beijing. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 5449–5460, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2958-5.
Ma, Z. Q., J. Xu, W. J. Quan, Z. Y. Zhang, W. L. Lin, and X. B. Xu, 2016: Significant increase of surface ozone at a rural site, north of eastern China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 16, 3969–3977, https://doi.org/10.5144/acp-16-3969-2016.
Mao, T., Y. S. Wang, J. Jiang, F. K. Wu, and M. X. Wang, 2008: The vertical distributions of VOCs in the atmosphere of Beijing in autumn. Science of the Total Environment, 390, 97–108, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.08.035.
Paatero, P., 1997: Least squares formulation of robust non-negative factor analysis. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 37, 23–35, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7439(96)00044-5.
Paatero, P., and U. Tapper, 1994: Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Envionnmetrics, 5, 111–126, https://doi.org/10.1002/env.3170050203.
Richard, A., and Coauthors, 2011: Source apportionment of size and time resolved trace elements and organic aerosols from an urban courtyard site in Switzerland. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11, 8945–8963, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-8945-2011.
Sangiorgi, G., L. Ferrero, M. G. Perrone, E. Bolzacchini, M. Duane, and B. R. Larsen, 2011: Vertical distribution of hydrocarbons in the low troposphere below and above the mixing height: Tethered balloon measurements in Milan, Italy. Environmental Pollution, 159, 3545–3552, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.08.012.
Schnitzhofer, R., and Coauthors, 2009: A multimethodological approach to study the spatial distribution of air pollution in an Alpine valley during wintertime. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 9, 3385–3396, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-3385-2009.
Seinfeld, J. H., and S. N. Pandis, 2016: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change. 3rd ed., John Wiley & Sons.
Spirig, C., A. Neftel, L. I. Kleinman, and J. Hjorth, 2002: NOx versus VOC limitation of O3 production in the Po valley: Local and integrated view based on observations. J. Geophys. Res., 107, 8191, https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JD000561.
Sun, J., F. K. Wu, B. Hu, G. Q. Tang, J. K. Zhang, and Y. S. Wang, 2016: VOC characteristics, emissions and contributions to SOA formation during hazy episodes. Atmos. Environ., 141, 560–570, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.06.060.
Sun, J., Y. S. Wang, F. K. Wu, G. Q. Tang, L. L. Wang, Y. H. Wang, and Y. Yang, 2018: Vertical characteristics of VOCs in the lower troposphere over the North China Plain during pollution periods. Environmental Pollution, 236, 907–915, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.051.
Tang, G., X. Li, Y. Wang, J. Xin, and X. Ren, 2009: Surface ozone trend details and interpretations in Beijing, 2001–2006. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 9, 8813–8823, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-8813-2009.
Tang, G., Y. Wang, X. Li, D. Ji, S. Hsu, and X. Gao, 2012: Spatial-temporal variations in surface ozone in Northern China as observed during 2009–2010 and possible implications for future air quality control strategies. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12, 2757–2776, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-2757-2012.
Tang, G., X. Zhu, B. Hu, J. Xin, L. Wang, C. Münkel, G. Mao, and Y. Wang, 2015: Impact of emission controls on air quality in Beijing during APEC 2014: Lidar ceilometer observations. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15, 12667–12680, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-12667-2015.
Tang, G. Q., N. Chao, Y. S. Wang, and J. S. Chen, 2016: Vehicular emissions in China in 2006 and 2010. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 48, 179–192, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.01.031.
Tang, G. Q., and Coauthors, 2017: Modelling study of boundary-layer ozone over northern China — Part I: Ozone budget in summer. Atmospheric Research, 187, 128–137, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.10.017.
Tang, G. Q., and Coauthors, 2021: Bypassing the NOx titration trap in ozone pollution control in Beijing. Atmospheric Research, 249, 105333, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105333.
Wöhrnschimmel, H., C. Márquez, V. Mugica, W. A. Stahel, J. Staehelin, B. Cárdenas, and S. Blanco, 2006: Vertical profiles and receptor modeling of volatile organic compounds over Southeastern Mexico City. Atmos. Environ., 40, 5125–5136, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.03.008.
Wu, S., and Coauthors, 2020: Vertically decreased VOC concentration and reactivity in the planetary boundary layer in winter over the North China Plain. Atmospheric Research, 240, 104930, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.104930.
Yang, X. Y., and Coauthors, 2020: Summertime ozone pollution in Sichuan Basin, China: Meteorological conditions, sources and process analysis. Atmos. Environ., 226, 117392, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117392.
Yang, Y., and Coauthors, 2019: Ambient volatile organic compounds in a suburban site between Beijing and Tianjin: Concentration levels, source apportionment and health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 695, 133889, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133889.
Yue, X., and Coauthors, 2017: Ozone and haze pollution weakens net primary productivity in China. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 6073–6089, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-6073-2017.
Yurdakul, S., M. Civan, Ö. Kuntasal, G. Doğan, H. Pekey, and G. Tuncel, 2018: Temporal variations of VOC concentrations in Bursa atmosphere. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 9, 189–206, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2017.09.004.
Zhang, C. X., and Coauthors, 2019: Satellite UV-Vis spectroscopy: Implications for air quality trends and their driving forces in China during 2005–2017. Light: Science & Applications, 8, 100, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-019-0210-6.
Zhang, K., G. L. Xiu, L. Zhou, Q. G. Bian, Y. S. Duan, D. N. Fei, D. F. Wang, and Q. Y. Fu, 2018: Vertical distribution of volatile organic compounds within the lower troposphere in late spring of Shanghai. Atmos. Environ., 186, 150–157, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.03.044.
Zhang, Q., and Coauthors, 2014: Variations of ground-level O3 and its precursors in Beijing in summertime between 2005 and 2011. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 14, 6089–6101, https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-6089-2014.
Zhao, W., and Coauthors, 2019: Evolution of boundary layer ozone in Shijiazhuang, a suburban site on the North China plain. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 83, 152–160, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.02.016.
Zheng, X., G. Ding, Y. U. Haiqing, Y. Liu, and X. U. Xiangde, 2005: Vertical distribution of ozone in the planetary boundary layer at the Ming Tombs, Beijing. Science in China Series D Earth Sciences, 48, 55–63.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFC021 0000), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41705113 and 41877312), the Young Talent Project of the Center for Excellence in Regional Atmospheric Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. CERAE20 1802), and a Beijing Major Science and Technology Project (Grant No. Z181100005418014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Article Highlights
• The VOC concentration slightly increased with height in the boundary layer in summer.
• The VOC concentration in summer was significantly lower than that in winter.
• The source contribution of gasoline vehicular emissions + industrial sources increased with height.
Electronic Supplementary Material to
376_2020_254_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Vertical Evolution of Boundary Layer Volatile Organic Compounds in Summer over the North China Plain and the Differences with Winter
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Tang, G., Wang, Y. et al. Vertical Evolution of Boundary Layer Volatile Organic Compounds in Summer over the North China Plain and the Differences with Winter. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 38, 1165–1176 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-020-0254-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-020-0254-9