Abstract
Rationale
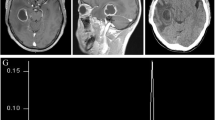
We report on a cerebral infection by Pseudallescheria boydii in a 21-month-old boy after a near-drowning episode. MRI revealed multiple (>60) intracerebral abscesses.
Methods
The surgical therapy included CSF drainage and microsurgical resection of one abscess for microbiological diagnosis. Antimycotic therapy included terbinafine and intraventricular caspofungin in addition to voriconazole.
Results
Systemic side effects of chemotherapy were not observed. After placement of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt, the boy was transferred to a rehabilitation clinic and improved neurologically. After 20 months, MRI documented a continuing remission of the disease.
Conclusion
Our case proves that an aggressive treatment should be undertaken and can be successful in CNS pseudallescheriasis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RL, Carroll TF, Harvey JT, Myers MG (1984) Petriellidium (Allescheria) boydii orbital and brain abscess treated with intravenous miconazole. Am J Ophthalmol 97:771–775
Cornely OA, Schmitz K, Aisenbrey S (2002) The first echinocandin: caspofungin. Mycoses 45(Suppl 3):6–60
Dworzack DL, Clark RB, Borkowski WJ Jr, Smith DL, Dykstra M, Pugsley MP, Horowitz EA, Connolly TL, McKinney DL, Hostetler MK (1989) Pseudallescheria boydii brain abscess: association with near-drowning and efficacy of high-dose, prolonged miconazole therapy in patients with multiple abscesses. Medicine (Baltimore) 68:218–224
Fisher JF, Shadomy S, Teabeaut JR, Woodward J, Michaels GE, Newman MA, White E, Cook P, Seagraves A, Yaghmai F, Rissing JP (1982) Near-drowning complicated by brain abscess due to Petriellidium boydii. Arch Neurol 39:511–513
Garcia JA, Ingram CW, Granger D (1990) Persistent neutrophilic meningitis due to Pseudallescheria boydii [letter]. Rev Infect Dis 12:959–960
Girmenia C, Luzi G, Monaco Mmartino P (1998) Use of voriconazole in treatment of Scedosporium apiospermum infection: case report. J Clin Microbiol 36:1436–1438
Kershaw P, Freeman R, Templeton D, DeGirolami PC, DeGirolami U, Tarsy D, Hoffmann S, Eliopoulos G, Karchmer AW (1990) Pseudallescheria boydii infection of the central nervous system. Arch Neurol 47:468–472
Meletiadis J, Mouton JW, Rodriguez-Tudela JL, Meis JF, Verweij PE (2000) In vitro interaction of terbinafine with itraconazole against clinical isolates of Scedosporium prolificans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:470–472
Nesky MA, McDougal EC, Peacock JE Jr (2000) Pseudallescheria boydii brain abscess successfully treated with voriconazole and surgical drainage: case report and literature review of central nervous system pseudallescheriasis. Clin Infect Dis 31:673–677
Pacetti SA, Gelone SP (2003) Caspofungin acetate for treatment of invasive fungal infections. Ann Pharmacother 37:90–98
Pérez RE, Smith M, McClendon J, Kim J, Eugenio N (1988) Pseudallescheria boydii brain abscess: complication of an intravenous catheter. Am J Med 84:359–362
Pfaller MA, Marco F, Messer SA, Jones RN (1998) In vitro activity of two echinocanin derivatives, LY303366 and MK-0991 (L-743,792), against clinical isolates of Aspergillus, Fusarium, Rhizopus, and other filamentous fungi. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 30:251–255
Ryder NS (1999) Activity of terbinafine against serious fungal pathogens. Mycoses 42:115–119
Rüchel R, Wilichowski E (1995) Cerebral Pseudallescheria mycosis after near-drowning. Mycoses 38:473–475
Safdar A, Papadopoulos EB, Young JW (2002) Breakthrough Scedosporium apiospermum (Pseudallescheria boydii) brain abscess during therapy for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis following high-risk allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Scedosporiosis and recent advances in antifungal therapy. Transplant Infect Dis 4:212–217
Sheehan DJ, Hitchcock CA, Sibley CM (1999) Current and emerging azole antifungal agents. Clin Microbiol Rev 12:40–79
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Professor R. Rüchel, Universität Göttingen, Germany, and Professor K. Tintelnot, Robert-Koch Institute Berlin, Germany, for their helpful comments during the discussion of therapeutic options.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mursch, K., Trnovec, S., Ratz, H. et al. Successful treatment of multiple Pseudallescheria boydii brain abscesses and ventriculitis/ependymitis in a 2-year-old child after a near-drowning episode. Childs Nerv Syst 22, 189–192 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-1151-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-1151-3