Abstract
Introduction
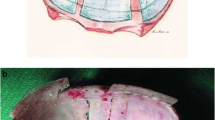
Trigonocephaly secondary to the premature fusion of the metopic synostosis is associated to a risk of cerebral compression and several craniofacial morphological alterations. Numerous surgical techniques have been proposed. They all carry a risk of secondary temporal hollowing
Purpose
The aim of this paper is to describe the surgical technique used for trigonocephaly at the craniofacial unit of Hopital Necker Enfants Malades (French National Referral Center for Faciocraniosynostosis) focusing on its advantages and limitations. Resorbable osteosynthesis should be part of the current techniques.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaud E, Marchac D, Renier D (2006) The treatment of craniosynostosis: indications and techniques. Neurochirurgie 52(2–3 Pt 2):264–291
Bottero L, Lajeunie E, Arnaud E, Marchac D, Renier D (1998) Functional outcome after surgery for trigonocephaly. Plast Reconstr Surg 102(4):952–958
Di Rocco C, Velardi F, Ferrario A, Marchese E (1996) Metopic synostosis: in favour of a "simplified" surgical treatment. Childs Nerv Syst 12(11):654–663
Di Rocco F, Arnaud E, Renier D (2009) Evolution in the frequency of nonsyndromic craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr 4(1):21–25
Di Rocco F, Arnaud E, Meyer P, Sainte-Rose C, Renier D (2009) Focus session on the changing "epidemiology" of craniosynostosis (comparing two quinquennia: 1985–1989 and 2003–2007) and its impact on the daily clinical practice: a review from Necker Enfants Malades. Childs Nerv Syst 25(7):807–811
Hayward R, Jones B, Evans R (1999) Functional outcome after surgery for trigonocephaly. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:582–583
Hilling DE, Mathijssen IM, Vaandrager JM (2006) Aesthetic results of fronto-orbital correction in trigonocephaly. J Craniofac Surg 17:1167–1174
Hinojosa J, Esparza J, Muñoz MJ, Salván R, Romance A, Alén JF, Muñoz A (2002) Surgical treatment of trigonocephalies and associated hypoteleorbitism. Neurocirugia (Astur) 13:437–445
Marchac D (1978) Radical forehead remodeling for craniostenosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 61:823–835
Marchac D, Renier D (1982) Chirurgie craniofaciale des craniosténoses. Mesdi, Paris, pp 1–173
Marchac D, Renier D (1982) Craniofacial surgery for craniosynostosis. Little Brown, Boston
Marchac D, Renier D, Broumand S (1994) Timing of treatment for craniosynostosis and facio-craniosynostosis: a 20-year experience. Br J Plast Surg 47:211–222
Renier D, Arnaud E, Marchac D (2006) Craniosynostosis: functional and morphologic postoperative results. Neurochirurgie 52(2–3 Pt 2):302–310
Renier D, Lajeunie E, Arnaud E, Marchac D (2000) Management of craniosynostoses. Childs Nerv Syst 16(10–11):645–658
Valentin M, Ducarme G, Yver C, Vuillard E, Belarbi N, Renier D, Luton D (2008) Trigonocephaly and valproate: a case report and review of literature. Prenat Diagn 28(3):259–261
van der Meulen JJ, Nazir PR, Mathijssen IM, van Adrichem LN, Ongkosuwito E, Stolk-Liefferink SA, Vaandrager MJ (2008) Bitemporal depressions after cranioplasty for trigonocephaly: a long-term evaluation of (supra) orbital growth in 92 patients. J Craniofac Surg 19(1):72–79
van der Meulen JJ, Willemsen J, van der Vlugt J, Nazir PR, Hilling D, Mathijssen IM, Ongkosuwito E, van Adrichem LN, Vaandrager MJ, Hovius SE, Unit DC (2009) On the origin of bitemporal hollowing. J Craniofac Surg 20(3):752–756
van der Meulen J, van der Hulst R, van Adrichem L, Arnaud E, Chin-Shong D, Duncan C, Habets E, Hinojosa J, Mathijssen I, May P, Morritt D, Nishikawa H, Noons P, Richardson D, Wall S, van der Vlugt J, Renier D (2009) The increase of metopic synostosis: a pan-European observation. J Craniofac Surg 20(2):283–286
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Rocco, F., Arnaud, E., Marchac, D. et al. Anterior fronto-orbital remodeling for trigonocephay. Childs Nerv Syst 28, 1369–1373 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1841-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1841-6