Abstract
Purpose
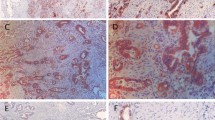
We investigated the relationships between biomarkers related to anaerobic glycolytic metabolism (GLUT1, LDH5, PDK1, and HIF-1α proteins), pathologic response, and prognosis.
Methods
All stage II and stage III rectal cancer patients had 50.4 Gy (1.8 Gy/day in 28 fractions) over 5.5 weeks, plus 5-fluorouracil (425 mg/m2/day) and leucovorin (20 mg/m2/day) bolus on days 1 to 5 and 29 to 33, and surgery was performed at 7 to 10 weeks after completion of all therapies. Expression of GLUT1, LDH5, PDK1, and HIF-1α proteins was determined by immunohistochemistry and was assessed in 104 patients with rectal cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.
Results
This study included stage II and III rectal cancer patients, and each stage accounted for each 50 % of the total cases. A high expression of GLUT1 protein was associated with a significantly lower rate of ypCR compared with low expression of GLUT1 protein (4.0 % vs. 27.8 %, respectively; p = 0.012). GLUT1 expression was also significantly higher in the poor response group (Grade 0, 1) than in the good response group (Grade 2, 3) (34.0 % vs. 14.8 %, respectively; p = 0.022). In recurrence analysis, the expression of GLUT1 protein demonstrated a significant correlation with time to recurrence, based on a log-rank method (p = 0.016). When analyzed by multiple Cox regression, the positive expression of GLUT1 was the most significant and independent unfavorable prognostic factor (p = 0.004).
Conclusions
GLUT1 expression is a predictive and prognostic factor for pathologic complete response and recurrence in rectal cancer patients treated with 5-flurouracil and leucovorin neo-adjuvant chemoradiotherapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kockerling F, Reymond MA, Altendorf-Hofmann A, Dworak O, Hohenberger W (1998) Influence of surgery on metachronous distant metastases and survival in rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 16(1):324–329
Gerard JP, Conroy T, Bonnetain F, Bouche O, Chapet O, Closon-Dejardin MT, Untereiner M, Leduc B, Francois E, Maurel J, Seitz JF, Buecher B, Mackiewicz R, Ducreux M, Bedenne L (2006) Preoperative radiotherapy with or without concurrent fluorouracil and leucovorin in T3-4 rectal cancers: results of FFCD 9203. J Clin Oncol 24(28):4620–4625. doi:24/28/462010.1200/JCO.2006.06.7629
Crane CH, Sargent DJ (2004) Substitution of oral fluoropyrimidines for infusional fluorouracil with radiotherapy: how much data do we need? J Clin Oncol 22(15):2978–2981. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.04.953 JCO.2004.04.953
Bosset JF, Collette L, Calais G, Mineur L, Maingon P, Radosevic-Jelic L, Daban A, Bardet E, Beny A, Ollier JC (2006) Chemotherapy with preoperative radiotherapy in rectal cancer. N Engl J Med 355(11):1114–1123. doi:355/11/111410.1056/NEJMoa060829
Capirci C, Valentini V, Cionini L, De Paoli A, Rodel C, Glynne-Jones R, Coco C, Romano M, Mantello G, Palazzi S, Mattia FO, Friso ML, Genovesi D, Vidali C, Gambacorta MA, Buffoli A, Lupattelli M, Favretto MS, La Torre G (2008) Prognostic value of pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer: long-term analysis of 566 ypCR patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72(1):99–107. doi:S0360-3016(07)04759-110.1016/j.ijrobp. 2007.12.019
Rodel C, Martus P, Papadoupolos T, Fuzesi L, Klimpfinger M, Fietkau R, Liersch T, Hohenberger W, Raab R, Sauer R, Wittekind C (2005) Prognostic significance of tumor regression after preoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(34):8688–8696. doi:JCO.2005.02.132910.1200/JCO.2005.02.1329
Kim BC (2011) Prognostic significance of tumor regression grade after preoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. J Korean Soc Coloproctol 27(1):1–2. doi:10.3393/jksc.2011.27.1.1
Suarez J, Vera R, Balen E, Gomez M, Arias F, Lera JM, Herrera J, Zazpe C (2008) Pathologic response assessed by Mandard grade is a better prognostic factor than down staging for disease-free survival after preoperative radiochemotherapy for advanced rectal cancer. Colorectal Dis 10(6):563–568. doi:CDI142410.1111/j.1463-1318.2007.01424.x
Theodoropoulos G, Wise WE, Padmanabhan A, Kerner BA, Taylor CW, Aguilar PS, Khanduja KS (2002) T-level downstaging and complete pathologic response after preoperative chemoradiation for advanced rectal cancer result in decreased recurrence and improved disease-free survival. Dis Colon Rectum 45(7):895–903
Yeo SG, Kim DY, Kim TH, Chang HJ, Oh JH, Park W, Choi DH, Nam H, Kim JS, Cho MJ, Kim JH, Park JH, Kang MK, Koom WS, Nam TK, Chie EK, Lee KJ (2010) Pathologic complete response of primary tumor following preoperative chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: long-term outcomes and prognostic significance of pathologic nodal status (KROG 09-01). Ann Surg 252(6):998–1004. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181f3f1b100000658-201012000-00015
Warburg O (1956) On the origin of cancer cells. Science 123(3191):309–314
Semenza GL, Roth PH, Fang HM, Wang GL (1994) Transcriptional regulation of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. The Journal of biological chemistry 269(38):23757–23763
Semenza GL (2007) HIF-1 mediates the Warburg effect in clear cell renal carcinoma. Journal of bioenergetics and biomembranes 39(3):231–234. doi:10.1007/s10863-007-9081-2
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Gatter KC, Harris AL (2006) Lactate dehydrogenase 5 expression in operable colorectal cancer: strong association with survival and activated vascular endothelial growth factor pathway—a report of the Tumour Angiogenesis Research Group. J Clin Oncol 24(26):4301–4308. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.05.9501
Wigfield SM, Winter SC, Giatromanolaki A, Taylor J, Koukourakis ML, Harris AL (2008) PDK-1 regulates lactate production in hypoxia and is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cancer. Br J Cancer 98(12):1975–1984. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604356
Macheda ML, Rogers S, Best JD (2005) Molecular and cellular regulation of glucose transporter (GLUT) proteins in cancer. J Cell Physiol 202(3):654–662. doi:10.1002/jcp. 20166
Tredan O, Galmarini CM, Patel K, Tannock IF (2007) Drug resistance and the solid tumor microenvironment. J Natl Cancer Inst 99(19):1441–1454. doi:djm13510.1093/jnci/djm135
Coleman CN (1996) Modulating the radiation response. Oncologist 1(4):227–231
Janssen HL, Haustermans KM, Balm AJ, Begg AC (2005) Hypoxia in head and neck cancer: how much, how important? Head Neck 27(7):622–638. doi:10.1002/hed.20223
Nordsmark M, Alsner J, Keller J, Nielsen OS, Jensen OM, Horsman MR, Overgaard J (2001) Hypoxia in human soft tissue sarcomas: adverse impact on survival and no association with p53 mutations. Br J Cancer 84(8):1070–1075. doi:10.1054/bjoc.2001.1728S0007092001917288
Nordsmark M, Loncaster J, Chou SC, Havsteen H, Lindegaard JC, Davidson SE, Varia M, West C, Hunter R, Overgaard J, Raleigh JA (2001) Invasive oxygen measurements and pimonidazole labeling in human cervix carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 49(2):581–586. doi:S0360-3016(00)01493-0
Nordsmark M, Overgaard J (2000) A confirmatory prognostic study on oxygenation status and loco-regional control in advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated by radiation therapy. Radiother Oncol 57(1):39–43
Hong SH, Roh SY, Ko YH, Won HS, Lee MA, Woo IS, Byun JH, Kang JH, Hong YS, Jung CK (2010) Prognostic significance of glycolytic metabolic change related to HIF-1α in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Korean J Pathol 44(4):360–369
Chung FY, Huang MY, Yeh CS, Chang HJ, Cheng TL, Yen LC, Wang JY, Lin SR (2009) GLUT1 gene is a potential hypoxic marker in colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer 9:241. doi:1471-2407-9-24110.1186/1471-2407-9-241
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Simopoulos C, Polychronidis A, Sivridis E (2005) Lactate dehydrogenase 5 (LDH5) relates to up-regulated hypoxia inducible factor pathway and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 22(1):25–30. doi:10.1007/s10585-005-2343-7
Brown JM (2000) Exploiting the hypoxic cancer cell: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Mol Med Today 6(4):157–162. doi:S1357-4310(00)01677-4
Hockel M, Schlenger K, Aral B, Mitze M, Schaffer U, Vaupel P (1996) Association between tumor hypoxia and malignant progression in advanced cancer of the uterine cervix. Cancer Res 56(19):4509–4515
Knocke TH, Weitmann HD, Feldmann HJ, Selzer E, Potter R (1999) Intratumoral pO2-measurements as predictive assay in the treatment of carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Radiother Oncol 53(2):99–104
Yeung JM, Kalff V, Hicks RJ, Drummond E, Link E, Taouk Y, Michael M, Ngan S, Lynch AC, Heriot AG (2011) Metabolic response of rectal cancer assessed by 18-FDG PET following chemoradiotherapy is prognostic for patient outcome. Dis Colon Rectum 54(5):518–525. doi:10.1007/DCR.0b013e31820b36f000003453-201105000-00002
Martoni AA, Di Fabio F, Pinto C, Castellucci P, Pini S, Ceccarelli C, Cuicchi D, Iacopino B, Di Tullio P, Giaquinta S, Tardio L, Lombardi R, Fanti S, Cola B (2011) Prospective study on the FDG-PET/CT predictive and prognostic values in patients treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy and radical surgery for locally advanced rectal cancer. Ann Oncol 22(3):650–656. doi:mdq43310.1093/annonc/mdq433
Chapman JD, Engelhardt EL, Stobbe CC, Schneider RF, Hanks GE (1998) Measuring hypoxia and predicting tumor radioresistance with nuclear medicine assays. Radiother Oncol 46(3):229–237. doi:S0167814097001862
Jang NY, Kang SB, Kim DW, Kim JH, Lee KW, Kim IA, Kim JS (2011) The role of carcinoembryonic antigen after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 54(2):245–252. doi:10.1007/DCR.0b013e3181fcee6800003453-201102000-00020
Greijer AE, Delis-van Diemen PM, Fijneman RJ, Giles RH, Voest EE, van Hinsbergh VW, Meijer GA (2008) Presence of HIF-1 and related genes in normal mucosa, adenomas and carcinomas of the colorectum. Virchows Arch 452(5):535–544. doi:10.1007/s00428-008-0578-9
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Polychronidis A, Simopoulos C, Gatter KC, Harris AL, Sivridis E (2006) Endogenous markers of hypoxia/anaerobic metabolism and anemia in primary colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci 97(7):582–588. doi:CAS22010.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00220.x
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL, Dang CV (2006) HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab 3(3):177–185. doi:S1550-4131(06)00062-310.1016/j.cmet.2006.02.002
Papandreou I, Cairns RA, Fontana L, Lim AL, Denko NC (2006) HIF-1 mediates adaptation to hypoxia by actively downregulating mitochondrial oxygen consumption. Cell Metab 3(3):187–197. doi:S1550-4131(06)00060-X10.1016/j.cmet.2006.01.012
Sakashita M, Aoyama N, Minami R, Maekawa S, Kuroda K, Shirasaka D, Ichihara T, Kuroda Y, Maeda S, Kasuga M (2001) Glut1 expression in T1 and T2 stage colorectal carcinomas: its relationship to clinicopathological features. Eur J Cancer 37(2):204–209. doi:S0959804900003713
Haber RS, Rathan A, Weiser KR, Pritsker A, Itzkowitz SH, Bodian C, Slater G, Weiss A, Burstein DE (1998) GLUT1 glucose transporter expression in colorectal carcinoma: a marker for poor prognosis. Cancer 83(1):34–40. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19980701)83:1<34::AID-CNCR5>3.0.CO;2-E
Chang HJ, Jung KH, Kim DY, Jeong SY, Choi HS, Kim YH, Sohn DK, Yoo BC, Lim SB, Kim DH, Ahn JB, Kim IJ, Kim JM, Yoon WH, Park JG (2005) Bax, a predictive marker for therapeutic response to preoperative chemoradiotherapy in patients with rectal carcinoma. Hum Pathol 36(4):364–371. doi:S004681770500046810.1016/j.humpath.2005.01.018
Bengala C, Bettelli S, Bertolini F, Sartori G, Fontana A, Malavasi N, Depenni R, Zironi S, Del Giovane C, Luppi G, Conte PF (2010) Prognostic role of EGFR gene copy number and KRAS mutation in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer treated with preoperative chemoradiotherapy. Br J Cancer 103(7):1019–1024. doi:660585310.1038/sj.bjc.6605853
Toiyama Y, Inoue Y, Saigusa S, Okugawa Y, Yokoe T, Tanaka K, Miki C, Kusunoki M (2010) Gene expression profiles of epidermal growth factor receptor, vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 with special reference to local responsiveness to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and disease recurrence after rectal cancer surgery. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 22(4):272–280. doi:S0936-6555(10)00002-610.1016/j.clon.2010.01.001
Saigusa S, Toiyama Y, Tanaka K, Okugawa Y, Fujikawa H, Matsushita K, Uchida K, Inoue Y, Kusunoki M (2012) Prognostic significance of glucose transporter-1 (GLUT1) gene expression in rectal cancer after preoperative chemoradiotherapy. Surg Today 42(5):460–469. doi:10.1007/s00595-011-0027-2
Acknowledgments
The present work has been supported by grants from the clinical research fund of St. Vincent’s Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shim, B.Y., Jung, JH., Lee, KM. et al. Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) of anaerobic glycolysis as predictive and prognostic values in neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and laparoscopic surgery for locally advanced rectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 28, 375–383 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-012-1542-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-012-1542-3