Abstract
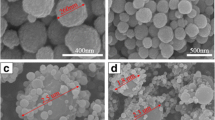
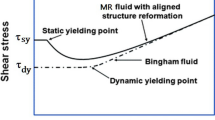
The hydrothermal fabrication of crystalline manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) nanoparticles and their application as a magnetorheological (MR) fluid dispersed in an insulating oil are described herein. The morphology and crystal structure of the MnFe2O4 nanoparticles are revealed by transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and X-ray diffraction. In addition, with a relatively high saturation magnetization of the MnFe2O4 particles, their typical MR behavior is demonstrated by rheometric steady shear and dynamic oscillation tests under an applied magnetic field. Moreover, the flow and yield stress curves for the MnFe2O4 nanoparticle-based MR fluid are shown to conform to the Herschel–Bulkley model with a slope of 1.5. Finally, under the same magnetic field strength, the dynamic yield stress is shown to be higher than the elastic yield stress.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thakur S, Karak N (2014) Multi-stimuli responsive smart elastomeric hyperbranched polyurethane/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. J Mater Chem A 2:14867–14875
Plachy T, Masar M, Mrlik M, Machovsky M, Machovska Z, Kutalkova E, Kuritka I (2019) Switching between negative and positive electrorheological effect of g-C3N4 by copper ions doping. Adv Powder Technol 30:714–723
Fameau A-L, Salonen A (2014) Effect of particles and aggregated structures on the foam stability and aging. C R Phys 15:748–760
Sun Y, Huang Y, Wang M, Wu J, Yuan S, Ding J, Peng Y, Pu H, Xie S, Luo J (2020) Design, testing and modelling of a tuneable GER fluid damper under shear mode. Smart Mater Struct 29:085011
Bica I, Anitas EM, Chirigiu L, Daniela C, Chirigiu LME (2018) Hybrid magnetorheological suspension: effects of magnetic field on the relative dielectric permittivity and viscosity. Colloid Polym Sci 296:1373–1378
Cheng HB, Zuo L, Song JH, Zhang QJ, Wereley NM (2010) Magnetorheology and sedimentation behavior of an aqueous suspension of surface modified carbonyl iron particles. J Appl Phys 107:09B507
Kim JW, Kim SG, Choi HJ, Suh MS, Shin MJ, Jhon MS (2001) Synthesis and electrorheological characterization of polyaniline and Na+-montmorillonite clay nanocomposite. Int J Mod Phys B 15:657–664
Sutrisno J, Purwanto A, Mazlan SA (2015) Recent progress on magnetorheological solids: materials, fabrication, testing, and applications. Adv Eng Mater 17:563–597
Ahamed R, Ferdaus MM, Li Y (2016) Advancement in energy harvesting magneto-rheological fluid damper: a review. Korea-Aust Rheol J 28:355–379
Ginder JM, Davis LC, Elie LD (1966) Rheology of magnetorheological fluids: models and measurements. Int J Mod Phys B 10:3293–3303
Anupama AV, Kumaran V, Sahoo B (2018) Magneto-mechanical response of additive-free Fe-based magnetorheological fluids: role of particle shape and magnetic properties. Mater Res Express 5:1–11
Rwei S, Lee H, Yoo S, Wang L, Lin J (2005) Magnetorheological characteristics of aqueous suspensions that contain Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Colloid Polym Sci 283:1253–1258
Agustín-Serrano R, Donado F, Rubio-Rosas E (2013) Magnetorheological fluid based on submicrometric silica-coated magnetite particles under an oscillatory magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater 335:149–158
Zhou T, Zhang T, Zeng Y, Zhang R, Lou Z, Deng J, Wang L (2018) Structure-driven efficient NiFe2O4 materials for ultra-fast response electronic sensing platform. Sensors Actuators B Chem 255:1436–1444
Cao Y, Qin H, Niu X, Jia D (2016) Simple solid-state chemical synthesis and gas-sensing properties of spinel ferrite materials with different morphologies. Ceram Int 42:10697–10703
Yadav RS, Kuřitka I, Havlica J, Hnatko M, Alexander C, Masilko J, Kalina L, Hajdúchová M, Rusnak J, Enev V (2018) Structural, magnetic, elastic, dielectric and electrical properties of hot-press sintered Co1−xZnxFe2O4 (x= 0.0, 0.5) spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 447:48–57
Anupama AV, Kumaran V, Sahoo B (2019) Effect of magnetic dipolar interactions and size dispersity on the origin of steady state magnetomechanical response in bidisperse Mn–Zn ferrite spherical particle based magnetorheological fluids. New J Chem 43:9969–9979
Anupama AV, Kumaran V, Sahoo B (2018) Magnetorheological fluids containing rod-shaped lithium–zinc ferrite particles: the steady-state shear response. Soft Matter 14:5407–5419
Anupama AV, Kumaran V, Sahoo B (2018) Steady-shear magnetorheological response of fluids containing solution-combustion-synthesized Ni-Zn ferrite powder. Adv Powder Technol 29:2188–2193
Anupama AV, Kumaran V, Sahoo B (2018) Application of Ni-Zn ferrite powders with polydisperse spherical particles in magnetorheological fluids. Powder Technol 338:190–196
Kumar R, Anupama AV, Kumaran V, Sahoo B (2018) Effect of solvents on the structure and magnetic properties of pyrolysis derived carbon globules embedded with iron/iron carbide nanoparticles and their applications in magnetorheological fluids. Nano-Struct Nano-Objects 16:167–173
Gao CY, Kim MW, Bae DH, Dong YZ, Piao SH, Choi HJ (2017) Fe3O4 nanoparticle-embedded polystyrene composite particles fabricated via a Shirasu porous glass membrane technique and their magnetorheology. Polymer 125:21–29
Anupama AV, Kumaran V, Sahoo B (2018) Application of monodisperse Fe3O4 submicrospheres in magnetorheological fluids. J Ind Eng Chem 67:347–357
Anupama AV, Khopka VB, Kumaran V, Sahoo B (2018) Magnetic field dependent steady-state shear response of Fe3O4 micro-octahedron based magnetorheological fluids. Phys Chem Chem Phys 20:20247–20256
Kuncser V, Schinteie G, Sahoo B, Keune W, Bica D, Vekas L, Filoti G (2006) Magnetic interactions in water based ferrofluids studied by Mossbauer spectroscopy. J Phys Condens Matter 19:016205
Kurtinaitienė M, Mažeika K, Ramanavičius S, Pakštas V, Jagminas A (2016) Effect of additives on the hydrothermal synthesis of manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Adv Nano Res 4:1–14
Akhtar MJ, Younas M (2012) Structural and transport properties of nanocrystalline MnFe2O4 synthesized by co-precipitation method. Solid State Sci 14:1536–1542
Iranmanesh P, Saeednia S, Mehran M, Dafeh SR (2017) Modified structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline MnFe2O4 by pH in capping agent free co-precipitation method. J Magn Magn Mater 425:31–36
Bhandare SV, Kumar R, Anupama AV, Choudhary HK, Jali VM, Sahoo B (2017) Annealing temperature dependent structural and magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles grown by sol-gel auto-combustion method. J Magn Magn Mater 433:29–34
Anupama AV, Kumar R, Choudhary HK, Jagadeesha Angadi V, Somashekarappa HM, Rudraswamy B, Sahoo B (2020) Gamma-irradiation induced modifications in structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Mn0.5Zn0.5 SmxFe2-xO4 ceramics. Radiat Phys Chem 166:108506
Angadi VJ, Anupama AV, Kumar R, Choudhary HK, Matteppanavar S, Somashekarappa HM, Rudraswamy B, Sahoo B (2017) Composition dependent structural and morphological modifications in nanocrystalline Mn-Zn ferrites induced by high energy γ-irradiation. Mater Chem Phys 199:313–321
Khilari S, Pandit S, Varanasi JL, Das D, Pradhan D (2015) Bifunctional manganese ferrite/polyaniline hybrid as electrode material for enhanced energy recovery in microbial fuel cell. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:20657–20666
Ma J, Hou Y, Ji T, Zhao J, Zhang S (2016) Preparation of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles via a facile water-glycol solvothermal approach. Synth React Inorg M 46:1513–1518
Hosseini SH, Moghimi A, Moloudi M (2014) Magnetic, conductive, and microwave absorption properties of polythiophene nanofibers layered on MnFe2O4/Fe3O4 core–shell structures. Mater Sci Semicond Process 24:272–277
Ruíz-Baltazar A, Esparza R, Rosas G, Ramiro Perez-Campos R (2015) Effect of the surfactant on the growth and oxidation of iron nanoparticles. J Nanomater 2015:240948
Gandha K, Mohapatra J, Hossain MK, Elkins K, Poudyal N, Rajeshwarb K, Liu JP (2016) Mesoporous iron oxide nanowires: synthesis, magnetic and photocatalytic properties. RSC Adv 66:90537–90546
Kuncser V, Schinteie G, Sahoo B, Keune W, Bica D, Vekas L, Filoti G (2006) Magnetic interactions in water based ferrofluids studied by Mo ̈ssbauer spectroscopy. J Phys Condens Matter 19:016205
Holzwarth U, Gibson N (2011) The Scherrer equation versus the ‘Debye-Scherrer equation’. Nat Nanotechnol 6:534
Mrlík M, Sedlacik M, Pavlínek V, Peer P, Filip P, Sáha P (2013) Magnetorheology of carbonyl iron particles coated with polypyrrole ribbons: the steady shear study. J Phys Conf Ser 412:012016
Chand M, Shankar A, Jain K, Pant R (2014) Improved properties of bidispersed magnetorheological fluids. RSC Adv 4:53960–53966
Kwon SH, Na SM, Flatau AB, Choi HJ (2020) Fe-Ga alloy based magnetorheological fluid and its viscoelastic characteristics. J Ind Eng Chem 82:433–438
Chotpattananont D, Sirivat A, Jamieson AM (2006) Creep and recovery behaviors of a polythiophene-based electrorheological fluid. Polymer 47:3568–3575
Funding
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (2018R1A4A1025169).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, C.Y., Baek, E., You, C.Y. et al. Magnetic-stimuli rheological response of soft-magnetic manganese ferrite nanoparticle suspension. Colloid Polym Sci 299, 865–872 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-021-04808-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-021-04808-7