Abstract
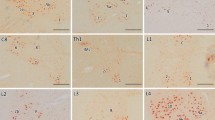
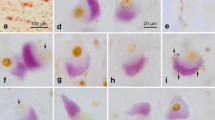
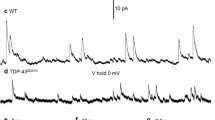
Skein-like and spherical inclusions within the somatodendritic compartment of a few types of susceptible neurons in the human nervous system are the currently acknowledged pathological hallmarks of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). These inclusions consist chiefly of an aggregated, phosphorylated, and ultimately ubiquitinated intranuclear protein, TDP-43. To investigate the development of these inclusions, a single neuronal type that is susceptible to the ALS-associated pathological process, i.e., the class of large multipolar somatomotor neurons in the lower brainstem and spinal cord, was studied in four cases of sporadic ALS and four age-matched controls using immunoreactions against phosphorylated TDP-43 (pTDP-43), p62, and ubiquitin. In these neurons, the protein TDP-43, after its displacement outside of the cell nucleus and abnormal phosphorylation, forms light microscopically visible dash-like aggregates which were dispersed throughout their entire somatodendritic domain and even extended into the proximal portions of the axon. Many motor neurons contained these lesions, which were not detectable with anti-TDP-43 and anti-p62. In an additional step, a small number of the neurons that contain the dash-like lesions displayed a clustering of the aggregated material, which forms thick net-like (potential precursors of the skein-like inclusions) and spherical inclusions. This material, in turn, was ubiquitinated and p62-immunopositive. Thus, dash-like pTDP-43 aggregates are regularly seen in motor neurons in ALS and may represent the initial cellular lesion in this disease. Because these aggregates were not stained with antibodies against p62 and non-phosphorylated TDP-43, it is possible that phosphorylation of TDP-43 is required for its aggregation in sporadic ALS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H et al (2006) TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351:602–611
Braak E, Braak H, Mandelkow EM (1994) A sequence of cytoskeleton changes related to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles and neuropil threads. Acta Neuropathol 87:554–567
Braak E, Sandmann-Keil D, Rüb U et al (2001) Alpha-synuclein immunopositive Parkinson’s disease-related inclusion bodies in lower brainstem nuclei. Acta Neuropathol 101:195–201
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Demonstration of amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary changes in whole brain sections. Brain Pathol 1:213–216
Braak H, Del Tredici K (2009) Neuroanatomy and pathology of sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 201:1–119
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–210
Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rüb U, Bratzke H, Del Tredici K (2004) Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res 318:121–134
Brandmeir NJ, Geser F, Kwong LK et al (2008) Severe subcortical TDP-43 pathology in sporadic frontotemporal lobar degeneration with motor neuron disease. Acta Neuropathol 115:123–131
Davidson Y, Kelley T, Mackenzie IR et al (2007) Ubiquitinated pathological lesions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration contain the TAR DNA-binding protein, TDP-43. Acta Neuropathol 113:521–533
Dickson DW, Josephs KA, Amador-Ortiz C (2007) TDP-43 in differential diagnosis of motor neuron disorders. Acta Neuropathol 114:71–79
Fujita Y, Mizuno Y, Takatama M, Okamoto K (2008) Anterior horn cells with abnormal TDP-43 immunoreactivities show fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus in ALS. J Neurol Sci 269:30–34
Geser F, Brandmeir NJ, Kwong LK et al (2008) Evidence of multisystem disorder in whole-brain map of pathological TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol 65:636–641
Geser F, Martinez-Lage M, Kwong LK, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2009) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, frontotemporal dementia and beyond: the TDP-43 diseases. J Neurol 256:1205–1214
Geser F, Martinez-Lage M, Robinson J et al (2009) Clinical and pathological continuum of multisystem TDP-43 proteinopathies. Arch Neurol 66:180–189
Hasegawa M, Arai T, Nonaka T et al (2008) Phosphorylated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 64:60–70
Kato S, Shaw P, Wood-Allum C, Leigh PN, Shaw CE (2003) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In: Dickson DW (ed) Neurodegeneration: the molecular pathology of dementia and movement disorders. ISN Neuropathologica Press, Basel, pp 350–371
Kuusisto E, Parkkinen L, Alafuzoff I (2003) Morphogenesis of Lewy bodies: dissimilar incorporation of α-synuclein, ubiquitin, and p62. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:1241–1253
Leigh PN, Anderton BH, Dodson A et al (1988) Ubiquitin deposits in anterior horn cells in motor neurone disease. Neurosci Lett 93:197–203
Lin WL, Dickson DW (2008) Ultrastructural localization of TDP-43 in filamentous neuronal inclusions in various neurodegenerative disease. Acta Neuropathol 116:205–213
Lowe J, Lennox G, Jefferson D et al (1988) A filamentous inclusion body within anterior horn neurones in motor neurone disease defined by immunocytochemical localisation of ubiquitin. Neurosci Lett 94:203–210
Mackenzie IR, Bigio EH, Ince PG et al (2007) Pathological TDP-43 distinguishes sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with SOD1 mutations. Ann Neurol 61:427–434
Mizuno Y, Amari M, Takatama M et al (2006) Immunoreactivities of p62, an ubiquitin-binding protein, in the spinal anterior horn cells of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 249:13–18
Mori F, Tanji K, Zhang HX et al (2008) Maturation process of TDP-43-positive neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with and without dementia. Acta Neuropathol 116:193–204
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK et al (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314:130–133
Neumann M, Kwong LK, Sampathu DM, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2007) TDP-43 proteinopathy in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: protein misfolding diseases without amyloidosis. Arch Neurol 64:1388–1394
Neumann M, Kwong LK, Lee EB et al (2009) Phosphorylation of S409/410 of TDP is a consistent feature in all sporadic and familial forms of TDP-43 proteinopathies. Acta Neuropathol 117:137–149
Piao YS, Wakabayashi K, Kakita A et al (2003) Neuropathology with clinical correlations of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: 102 autopsy cases examined between 1962 and 2000. Brain Pathol 13:10–22
Tan CF, Eguchi H, Tagawa A et al (2007) TDP-43 immunoreactivity in neuronal inclusions in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with or without SOD1 gene mutation. Acta Neuropathol 113:535–542
Thal DR, Rüb U, Schultz C et al (2000) Sequence of Aβ protein deposition in the human medial temporal lobe. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 59:733–748
Thal DR, Rüb U, Orantes M, Braak H (2002) Phases of Abeta-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology 58:1791–1800
Zatloukai K, Stumptner C, Fuchsbichler A et al (2002) p62 is a common component of cytoplasmic inclusions in protein aggregation diseases. Am J Pathol 160:255–263
Acknowledgments
This study was made possible in part by funding from the German Research Council (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft). They also wish to thank Ms. Corinna Hendrich, M.D. (Department of Neurology, University of Ulm) for help with clinical protocols, as well as Ms. Siegrid Baumann, Ms. Gabrielle Ehmke, Ms. Verena Hofmann, Ms. Irina Lungrin (immunohistochemistry), and Mr. Stephan Mayer (graphics) for their technical expertise.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braak, H., Ludolph, A., Thal, D.R. et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: dash-like accumulation of phosphorylated TDP-43 in somatodendritic and axonal compartments of somatomotor neurons of the lower brainstem and spinal cord. Acta Neuropathol 120, 67–74 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0683-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0683-0