Abstract
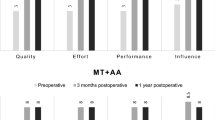
Spasmodic dysphonia (SD) remains one of the most difficult of laryngeal pathologies to treat. With limited role for speech therapy, various surgical modalities have been tried with various success rates. The objective of the study is to report the results of vocal outcome after thyroarytenoid myoneurectomy in patients of adductor spasmodic dysphonia (ASD). 15 patients of ASD were selected. GRBAS, and voice handicap index (VHI) were used for perceptual evaluation of voice. Thyroarytenoid myoneurectomy was performed by vaporizing the muscular layer of the vocal fold with CO2 laser, at an intensity of 6 W with 1.2 mm diameter in scanner mode. Voice analysis was repeated at 12, 24 and 48 months follow-up. Preoperative GRBAS scores and VHI score of all the patients were poor. At 12 months 12/15 (80 %) patients having strain score of 0. There was marked improvement in VHI scores at 6 months. 10/15 (67 %) patients have been followed up for 24 months. 5/10 (50 %) patients have strain (S) value of 0. VHI scoring of 5/10 (50 %) patients was <30. Two of the four patients completed 48 months follow-up had a strain (S) value of 0, one patient has strain value of 1 and one patient had strain value of 2. 2/4 patients had VHI score of <30; one patient had that of 40. Trans-oral CO2 laser thyroarytenoid myoneurectomy shows significant long-term improvement in voice quality in terms of reduced speech brakes, effort and strain in voice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isshiki N, Tsuji DH, Yamamoto Y, Iizuka Y (2000) Midline lateralization thyroplasty for adductor spasmodic dysphonia. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 109:187–193
Blitzer A, Lovelace RE, Brin MF, Fahn S, Fink ME (1985) Electromyographic findings in focal laryngeal dystonia (spastic dysphonia). Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 94:591–594
Erickson ML (2003) Effects of voicing and syntactic complexity on sign expression in adductor spasmodic dysphonia. Am J Speech Lang Pathol 12:416–424
Rodriquez AA, Ford CN, Bless DM, Harmon RL (1994) Electromyographic assessment of spasmodic dysphonia patients prior to botulinum toxin injection. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 34:403–407
Sercarz JA, Berke GS, Ming Y, Rothschiller J, Graves MC (1992) Bilateral thyroarytenoid denervation: a new treatment for laryngeal hyperadduction disorders studies in the canine. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 107:657–668
Bocchino JV, Tucker HM (1979) Recurrent laryngeal nerve pathology in spasmodic dysphonia. Laryngoscope 88:1274–1278
Kosaki H, Iwamura S, Yamazaki I (1999) Histologic study of the recurrent nerve in spasmodic dysphonia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 120:129–133
Chan SW, Baxter M, Oates J, Yorston A (2004) Long term results of Type II thyroplasty for adductor spasmodic dysphonia. Laryngoscope 14:1604–1608
Roy N, Mauszycki SC et al (2005) Task specific in adductor spasmodic dysphonia versus muscle tension dysphonia. Laryngoscope 115:311–316
Dedo HH (1976) Recurrent laryngeal section for spastic dysphonia. Ann Otol Rhinol laryngol 85:451–459
Tucker HM (1989) Laryngeal framework surgery in the management of spasmodic dysphonia: preliminary report. Ann Otol Rhinol laryngol 98:52–54
Blitzer A, Brin MF, Stewart CF (1998) Botulinum toxin management of spasmodic dysphonia (laryngeal dystonia): a 12 year experience in more than 900 patients. Laryngoscope 108:1435–1441
Domingos HT, Fernanda SC, Rui I, Luiz US, Adriana H (2006) Impact in vocal quality in partial myectomy and neurectomy endoscopic of thyroarytenoid muscle in patients with adductor spasmodic dysphonia. Rev Bras Otorhinolaryngol 72:261–266
Chih-Ying S, Hui-ching C, Shang-Shyue T, Jeng-Fen C (2007) Trans oral approach to laser thyroarytenoid myoneurectomy for treatment of adductory spasmodic dysphonia: short term results. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 116(1):11–18
Hussaina A, Shakeela M (2010) Selective lateral laser thyroarytenoid myotomy for adductor spasmodic dysphonia. J Laryngol Otol 124:886–891
Su CY, Lai CC, Wu PY, Huang HH (2010) Transoral laser ventricular fold resection and thyroarytenoid myoneurectomy for adductor spasmodic dysphonia: long-term outcome. Laryngoscope 120(2):313–318
Remacle M, Plouin-Gaudon I, Lawson G, Abitbol J (2005) Bipolar radiofrequency-induced thermotherapy (rfitt) for the treatment of spasmodic dysphonia. A report of three cases. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 262(10):871–874
Koufman JA, Rees CJ, Halum SL, Blalock D (2006) Treatment of adductor-type spasmodic dysphonia by surgical myectomy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 115:97–102
Jacobsen BH, Johnson A, Grywalki C, Silebergleit A, Jacobsen G, Benninger MS (1997) The Voice handicap index (VHI): determination and validation. Am J Speech Lang Pat 6:66–70
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gandhi, S., Remacle, M., Mishra, P. et al. Vocal outcome after endoscopic thyroarytenoid myoneurectomy in patients with adductor spasmodic dysphonia. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271, 3249–3254 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3129-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3129-9