Abstract
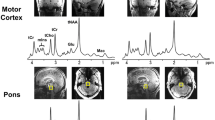
Biomarkers beyond clinical assessment are needed in patients who suffer from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Here, single-voxel proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS) of the gray matter of the motor cortex and the white matter including the pyramidal tracts was used to investigate concentrations of N-acetylaspartate (NAA), creatine (Cr), choline (Cho), myoinositol, glutamate, and glutamine in patients with definite ALS in a longitudinal design (three measurements at study inclusion, after 3 and 6 months). A volume-corrected analysis of gray and white matter fractions within the volumes of interest (VOI) was performed for the identification of the absolute metabolite concentrations. The patient group showed a significant decline of the compound NAA over time in the motor cortex areas both of the clinically more and less affected hemisphere between first measurement and month 6 and for the less affected side additionally between first measurement and month 3. For the NAA/(Cr + Cho) ratio, significant decline in the less affected hemisphere was observed from the first measurement to month 3 and to month 6 as well as from month 3 to month 6. In contrast, neither NAA nor the NAA/(Cr + Cho) ratios in the white matter areas showed any significant alterations. All other compounds showed no significant changes over time. In summary, the longitudinal changes of cortical metabolite concentrations in the course of ALS could be assessed by optimized 1H MRS techniques at group level, so that 1H MRS parameters, in particular volume-corrected values of NAA in the clinically less affected hemisphere, seem to have the potential to serve as a surrogate marker for monitoring ALS disease progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karitzky J, Ludolph AC (2001) Imaging and neurochemical markers for diagnosis and disease progression in ALS. J Neurol Sci 191:35–1
Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL (2000) El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1:293–99
Chan S, Kaufmann P, Shungu DC, Mitsumoto H (2003) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and primary lateral sclerosis: evidence-based diagnostic evaluation of the upper motor neuron. Neuroimag Clin N Am 13:307–26
Cheung G, Gawel MJ, Cooper PW, Farb RI, Ang LC, Gawal MJ (1995) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: correlation of clinical and MR imaging findings. Radiology 194:263–70
Comi G, Rovaris M, Leocani L (1999) Neuroimaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 6:629–37
Hofmann E, Ochs G, Pelzl A, Warmuth-Metz M (1998) The corticospinal tract in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an MRI study. Neuroradiology 40:71–5
Goodin DS, Rowley HA, Olney RK (1988) Magnetic resonance imaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 23:418–20
Terao S, Sobue G, Yasuda T, Kachi T, Takahashi M, Mitsuma T (1995) Magnetic resonance imaging of the corticospinal tracts in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 133:66–2
Thorpe JW, Moseley IF, Hawkes CH, MacManus DG, McDonald WI, Miller DH (1996) Brain and spinal cord MRI in motor neuron disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 61:314–17
Waragai M, Shinotoh H, Hayashi M, Hattori T (1997) High signal intensity on T1 weighted MRI of the anterolateral column of the spinal cord in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 62:88–1
Sobel DF, Gallen CC, Schwartz BJ, Waltz TA, Copeland B, Yamada S, Hirschkoff EC, Bloom FE (1993) Locating the central sulcus: comparison of MR anatomic and magnetoencephalographic functional methods. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:915–25
Miller BL (1991) A review of chemical issues in 1H NMR spectroscopy: N-acetyl-L-aspartate, creatine and choline. NMR Biomed 4:47–2
Bowen BC, Pattany PM, Bradley WG, Murdoch JB, Rotta F, Younis AA, Duncan RC, Quencer RM (2000) MR imaging and localized proton spectroscopy of the precentral gyrus in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:647–58
Gredal O, Rosenbaum S, Topp S, Karlsborg M, Strange P, Werdelin L (1997) Quantification of brain metabolites in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by localized proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurology 48:878–81
Jones AP, Gunawardena WJ, Coutinho CM, Gatt JA, Shaw IC, Mitchell JD (1995) Preliminary results of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in motor neurone disease (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). J Neurol Sci 129(Suppl):85–9
Kalra S, Arnold DL (2004) ALS surrogate markers. MRS. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord Suppl 1:111–14. Review
Pioro EP, Antel JP, Cashman NR, Arnold DL (1994) Detection of cortical neuron loss in motor neuron disease by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in vivo. Neurology 44:1933–938
Chan S, Shungu DC, Douglas-Akinwande A, Lange DJ, Rowland LP (1999) Motor neuron diseases: comparison of single-voxel proton MR spectroscopy of the motor cortex with MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 212:763–69
Block W, Karitzky J, Traber F, Pohl C, Keller E, Mundegar RR, Lamerichs R, Rink H, Ries F, Schild HH, Jerusalem F (1998) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the primary motor cortex in patients with motor neuron disease: subgroup analysis an follow-up measures. Arch Neurology 55:931–36
Ellis CM, Simmons A, Andrews C, Dawson JM, Williams SCR, Leigh PN (1998) A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study in ALS. Neurology 51:1104–109
Kalra S, Cashman NR, Caramanos Z, Genge A, Arnold DL (2003) Gabapentin therapy for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: lack of improvement in neuronal integrity shown by MR spectroscopy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:476–80
Suhy J, Miller RG, Rule R, Schuff N, Licht J, Dronsky V, Gelinas D, Maudsley AA, Weiner MW (2002) Early detection and longitudinal changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by (1)H MRSI. Neurology 58:773–79
Rule RR, Suhy J, Schuff N, Gelinas DF, Miller RG, Weiner MW (2004) Reduced NAA in motor and non-motor brain regions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 5:141–49
The ALS CNTF treatment study (ACTS) Phase I-II study group (1996) The amyotrophic lateral sclerosis functional rating scale. Assessment of activities of daily living in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol 53:141–47
Klose U (1990) In vivo proton spectroscopy in the presence of eddy currents. Magn Reson Med 14:26–0
Provencher SW (1993) Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magn Reson Med 30:672–79
Ethofer T, Seeger U, Klose U, Erb M, Kardatzki B, Kraft E, Landwehrmeyer GB, Grodd W, Storch A (2004) Proton MR spectroscopy in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Neurology 62:1016–018
Pioro EP, Majors AW, Mitsumoto H, Nelson DR, Ng TC (1999) 1H-MRS evidence of neurodegeneration and excess glutamate + glutamine in ALS medulla. Neurology 53:71–9
Urenjak J, Williams SR, Gadian DG, Noble M (1993) Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy unambiguously identifies different neural cell types. J Neurosci 13:981–89
Williams SCR (1992) In vivo proton spectroscopy. In: NMR basic principles and progress, vol. 28. Berlin, Springer, pp 55–0
Kassubek J, Unrath A, Huppertz HJ, Lule D, Ethofer T, Sperfeld AD, Ludolph AC (2005) Global brain atrophy and corticospinal tract alterations in ALS, as investigated by voxel-based morphometry of 3-D MRI. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 6:213–20
Kalra S, Hanstock CF, Martin WRW (2006) Detection of cerebral degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using high-field magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Neurol 63:1144–148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Unrath, A., Ludolph, A.C. & Kassubek, J. Brain metabolites in definite amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol 254, 1099–1106 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0495-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0495-2