Abstract
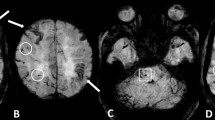
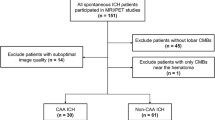
The pathogenesis of cortical microinfarcts (CMIs) is considered to be heterogeneous including cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) such as hypertensive vasculopathy (HV) and cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA). Recent advances in MRI have enabled the detection of CMIs in vivo. To investigate the characteristics of CMIs in advanced cerebral SVD, we performed a retrospective analysis of 85 patients with cognitive impairment who had multiple lobar cerebral microbleeds (CMBs) on 3 T MRI. Among them, 41 (48.2%) patients were classified into the strictly lobar CMB group (i.e. probable-CAA group), and 44 (51.8%) patients were classified into the non-lobar with lobar CMBs group (i.e. mix-CMBs group). The relationship between CMIs and CMBs, cortical superficial siderosis (cSS) and white matter hyperintensity was evaluated. Nine of the 41 (22.0%) patients with probable-CAA had a total of 19 CMIs, while 12 of the 44 (27.3%) patients with mix-CMBs had a total of 38 CMIs. In the probable-CAA group, the presence of CMIs was significantly associated with the presence of cSS (p < 0.001). In addition, a close spatial association between CMIs and cSS was observed. On the contrary, in the mix-CMB group, the presence of CMIs was significantly associated with the number of lobar CMBs in the frontal lobe (p = 0.034). Our results suggest that CMIs in the probable-CAA may be attributable to more severe CAA, while CMIs in the mix-CMBs indicate an advanced HV, especially when observed with more numerous lobar CMBs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brundel M, de Bresser J, van Dillen JJ, Kappelle LJ, Biessels GJ (2012) Cerebral microinfarcts: a systematic review of neuropathological studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:425–436
van Veluw SJ, Shih AY, Smith EE, Chen C, Schneider JA, Wardlaw JM, Greenberg SM, Biessels GJ (2017) Detection, risk factors, and functional consequences of cerebral microinfarcts. Lancet Neurol 16:730–740
Deramecourt V, Slade JY, Oakley AE, Perry RH, Ince PG, Maurage CA, Kalaria RN (2012) Staging and natural history of cerebrovascular pathology in dementia. Neurology 78:1043–1050
Charidimou A, Boulouis G, Gurol ME, Ayata C, Bacskai BJ, Frosch MP, Viswanathan A, Greenberg SM (2017) Emerging concepts in sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Brain 140:1829–1850
Linn J, Halpin A, Demaerel P, Ruhland J, Giese AD, Dichgans M, van Buchem MA, Bruckmann H, Greenberg SM (2010) Prevalence of superficial siderosis in patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 74:1346–1350
Martinez-Ramirez S, Romero JR, Shoamanesh A, McKee AC, Van Etten E, Pontes-Neto O, Macklin EA, Ayres A, Auriel E, Himalli JJ et al (2015) Diagnostic value of lobar microbleeds in individuals without intracerebral hemorrhage. Alzheimers Dement 11:1480–1488
Greenberg SM, Charidimou A (2018) Diagnosis of cerebral amyloid angiopathy: evolution of the Boston criteria. Stroke 49:491–497
Gouw AA, Seewann A, van der Flier WM, Barkhof F, Rosemller AM, Scheltens P, Geurts JJ (2011) Heterogeneity of small vessel disease: a systematic review of MRI and histopathology correlations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82:126–135
Park JH, Seo SW, Kim C, Kim GH, Noh HJ, Kim ST, Kwak KC, Yoon U et al (2013) Pathogenesis of cerebral microbleeds: in vivo imaging of amyloid and subcortical ischemic small vessel disease in 226 individuals with cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol 73:584–593
Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Park JH, Kim S, Woo SY, Kwak KC, Lee JM, Jung NY et al (2016) Synergistic effects of longitudinal amyloid and vascular changes on lobar microbleeds. Neurology 87:1575–1582
Ii Y, Maeda M, Kida H, Matsuo K, Shindo A, Taniguchi A, Tomimoto H (2013) In vivo detection of cortical microinfarcts on ultrahigh-field MRI. J Neuroimaging 23:28–32
Niwa A, Ii Y, Shindo A, Matsuo K, Ishikawa H, Taniguchi A, Takase S, Maeda M, Sakuma H, Akatsu H, Hashizume Y, Tomimoto H (2017) Comparative analysis of cortical microinfarcts and microbleeds using 3.0-Tesla postmortem magnetic resonance images and histopathology. J Alzheimers Dis 59:951–959
Ishikawa H, Ii Y, Niwa A, Shindo A, Ito A, Matsuura K, Sasaki R, Uno K, Maeda M, Tomimoto H (2018) Comparison of premortem magnetic resonance imaging and postmortem autopsy findings of a cortical microinfarct. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 27:2623–2626
van Dalen JW, Scuric EE, van Veluw SJ, Caan MW, Nederveen AJ, Biessels GJ, van Gool WA, Richard E (2015) Cortical microinfarcts detected in vivo on 3 Tesla MRI: clinical and radiological correlates. Stroke 46:255–257
van Veluw SJ, Hilal S, Kuijf HJ, Ikram MK, Xin X, Yeow TB, Venketasubramanian N, Biessels GJ, Chen C (2015) Cortical microinfarcts on 3 T MRI: clinical correlates in memory-clinic patients. Alzheimers Dement 11:1500–1509
Ueda Y, Satoh M, Tabei K, Kida H, Ii Y, Asahi M, Maeda M, Sakuma H, Tomimoto H (2016) Neuropsychological features of microbleeds and cortical microinfarct detected by high resolution magnetic resonance imaging. J Alzheimers Dis 53:315–325
Hilal S, Sikking E, Shaik MA, Chan QL, van Veluw SJ, Vrooman H, Cheng CY, Sabanayagam C et al (2016) Cortical cerebral microinfarcts on 3 T MRI: a novel marker of cerebrovascular disease. Neurology 87:1583–1590
van den Brink H, Zwiers A, Switzer AR, Charlton A, MaCreary CR, Goodyear BG, Frayne R, Biessels GJ, Smith EE (2018) Cortical microinfarcts on 3 T magnetic resonance imaging in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Stroke 49:1899–1905
Xiong L, van Veluw SJ, Bounemia N, Charidimou A, Pasi M, Boulouis G, Reijmer YD, Giese AK et al (2018) Cerebral cortical microinfarcts on magnetic resonance imaging and their association with cognition in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Stroke 49:2330–2336
van Rooden S, Goos JD, van Opstal AM, Versluis MJ, Webb AG, Blauw GJ, van der Flier WM, Scheltens P et al (2014) Increased number of microinfarcts in Alzheimer disease at 7-T MR imaging. Radiology 270:205–211
van Veluw SJ, Heringa SM, Kuijf HJ, Koek HL, Luijten PR, Biessels GJ (2014) Cerebral cortical microinfarcts at 7 Tesla MRI in patients with early Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 39:163–167
Fazekas F, Kleinert R, Roob G, Kleinert G, Kapeller P, Schmidt R, Hartung HP (1999) Histopathologic analysis of foci of signal loss on gradient-echo T2*-weighted MR images in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: evidence of microangiopathy-related microbleeds. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:637–642
MaKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of department of health and human services task force of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Bruandet A, Richard F, Bombois S, Mauraqe CA, Deramecourt V, Lebett F, Amouyel P, Pasqueir F (2009) Alzheimer’s disease with cerebrovascular disease and vascular dementia: clinical features and course compared with Alzheimer’s diease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80:133–139
Winblad B, Palmer K, Kivipelto M, Jelic V, Fratiglioni L, Wahlund LO, Nordberg A, Bäckman L, Albert M, Almkvist O et al (2004) Mild cognitive impairment—beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. J Intern Med 256:240–246
Román GC, Tatemichi TK, Erkinjuntti T, Cummings JL, Masdeu JC, Garcia JH, Amaducci L, Orgogozo JM, Brun A, Hofman A et al (1993) Vascular dementia: diagnostic criteria for research studies. Report of the NINDS-AIREN International Workshop. Neurology 43:250–260
Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, Cordonnier C, Fazekas F, Frayne R, Lindlei RI, O’Brien JT, Barkhof F, Benavente OR et al (2013) Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol 12:822–838
Gregoire SM, Chaudhary UJ, Brown MM, Yousry TA, Kallis C, Jäger HR, Werring DJ (2009) The microbleed anatomical rating scale (MARS): reliability of a tool to map brain microbleeds. Neurology 73:1759–1766
Wahlund LO, Barkhof F, Fazekas F, Bronge L, Augustin M, Sjögren M, Wallin A, Ader H, Leys D, Pantoni L et al (2001) A new rating scale for aging-related white matter changes applicable to MRI and CT. Stroke 32:1318–1322
Charidimou A, Linn J, Vernooij MW, Opherkr HR, Akoudad S, Baron JC, Greenberg SM, Jäger HR, Werring DJ (2015) Cortical superficial siderosis: detection and clinical significance in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and related conditions. Brain 138:2126–2139
Okamoto Y, Yamamoto T, Kalaria RN, Senzaki H, Maki T, Hase Y, Kitamura A, Washida K, Yamada M, Ito H, Tomimoto H, Takahashi R, Ihara M (2012) Cerebral hypoperfusion accelerates cerebral amyloid angiopathy and promotes cortical microinfarcts. Acta Neuropathol 123:381–394
Olichney JM, Ellis RJ, Katzman R, Sabbagh MN, Hansen L (1997) Types of cerebrovascular lesions associated with severe cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 826:493–497
Soontornniyomkij V, Lynch MD, Mermash S, Pomakian J, Badkoobehi H, Clare R, Vinters HV (2010) Cerebral microinfarcts associated with severe cerebral beta-amyloid angiopathy. Brain Pathol 20:459–467
Arvanitakis Z, Capuano AW, Leurgans SE, Buchman AS, Bennett DA, Schneider JA (2017) The relationship of cerebral vessel pathology to brain microinfarcts. Brain Pathol 27:77–85
Lauer A, van Veluw SJ, William CM, Charidimou A, Roongpiboonsopit D, Vashkevich A, Ayres A, Martinez-Ramirez S, Gurol EM, Biessels GJ et al (2016) Microbleeds on MRI are associated with microinfarcts on autopsy in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 87:1488–1492
van Veluw SJ, Biessels GJ, Klijn CJ, Rozemuller AJ (2016) Heterogeneous histopathology of cortical microbleeds in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 86:867–871
De Reuck J, Deramecourt V, Cordonnier C, Auger F, Durieux N, Pasquier F, Bordet R, Defebvre L, Caparros-Lefebvre D, Maurage CA, Leys D (2013) Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: a post-mortem 7.0-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging study with neuropathological correlates. Cerebrovasc Dis 36:412–417
De Reuck J, Deramecourt V, Auger F, Durieux N, Cordonnier C, Devos D, Defebvre L, Moreau C, Caparros-Lefebvre D, Bordet R, Maurage CA, Pasquier F, Leys D (2014) Post-mortem 7.0-tesla magnetic resonance study of cortical microinfarcts in neurodegenerative disease and vascular dementia with neuropathological correlates. J Neurol Sci 346:85–89
Pasi M, Charidimou A, Boulouis G, Auriel E, Ayres A, Schwab KM, Goldstein JN, Rosand J, Viswanasan A, Pantoni L, Greenberg SM, Gurol ME (2018) Mixed-location cerebral hemorrhage/microbleeds: underlying microangiopathy and recurrence risk. Neurology 90:e119–e126
Thal DR, Ghebremedhin E, Orantes M, Wiestler OD (2003) Vascular pathology in Alzheimer disease: correlation of cerebral amyloid angiopathy and arteriosclerosis/lipohyalinosis with cognitive decline. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:1287–1301
Kövari E, Herrmann FR, Gold G, Hof PR, Charidimou A (2017) Association of cortical microinfarcts and cerebral small vessel pathology in the ageing brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 43:505–513
Thomas T, Miners S, Love S (2015) Post-mortem assessment of hypoperfusion of cerebral cortex in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Brain 138:1059–1069
Westover MB, Bianchi MT, Yang C, Schneider JA, Greenberg SM (2013) Estimating cerebral microinfarct burden from autopsy samples. Neurology 80:1365–1369
Charidimou A, Farid K, Baron JC (2017) Amyloid-PET in sporadic amyloid angiopathy: a diagnostic accuracy meta-analysis. Neurology 89:1490–1498
Renard D, Castelnovo G, Wacongne A, Le Floch A, Thouvenot E, Mas J, Gabelle A, Labauge P, Lehmann S (2012) Interest of CSF biomarker analysis in possible cerebral amyloid angiopathy cases defined by the modified Boston criteria. J Neurol 259:2429–2433
Landi D, Maggio P, Lupoi P, Palazzo P, Altamura C, Falato E, Altavilla R, Vollaro S, Coniglio AD, Tibuzzi F et al (2015) Cortical ischemic lesion burden measured by DIR is related to carotid artery disease severity. Cerebrovasc Dis 39:23–30
Takasugi J, Miwa K, Watanabe Y, Okazaki S, Todo K, Sasaki T, Sakaguchi M, Mochizuki H (2019) Cortical cerebral microinfarcts on 3 T magnetic resonance imaging in patients with carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 50:639–644
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical standards
This study was approved by the ethical review board of Mie University Hospital and the requirement for written informed consent was waived because of the retrospective study design. This study was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards established in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its subsequent amendments.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ii, Y., Maeda, M., Ishikawa, H. et al. Cortical microinfarcts in patients with multiple lobar microbleeds on 3 T MRI. J Neurol 266, 1887–1896 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09350-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09350-9