Abstract
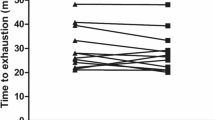
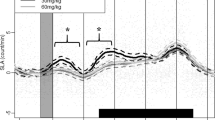
The combination of acute dopamine/noradrenaline reuptake inhibition (bupropion; BUP) and heat stress (30°C) significantly improves performance (9%). Furthermore the maintenance of a higher power output resulted in the attainment of significantly higher heart rates and rectal temperatures—above 40°C—in the BUP trial compared to the placebo trial. Since BUP is an aid to cease smoking that is taken for longer periods, question remains if similar performance and thermoregulatory effects are found following administration of BUP over several days (10 days). The purpose of the present study was to examine the effects of chronic BUP on exercise performance, thermoregulation and hormonal variables in the heat. Eight trained male cyclists participated in the study. Subjects completed two trials consisting of 60 min fixed intensity exercise (55% W max) followed by a time trial (TT) in a double-blind randomized crossover design. Exercise was performed in 30°C. Subjects took either placebo (PLAC) or BUP (Zyban™) for 3 days (150 mg), followed by 300 mg for 7 days. Chronic BUP did not influence TT performance (BUP 40′42″ ± 4′18″; PLAC 41′36″ ± 5′12″), but significantly increased core temperature (P = 0.030). BUP significantly increased circulating growth hormone levels (PLAC: 9.8 ± 5.8 ng L−1; BUP: 13 ± 6.8 ng L−1; P < 0.008). Discussion/conclusion: Chronic BUP did not influence TT performance in 30°C and subjects did not reach core temperature values as high as observed during the acute BUP study. It seems that chronic administration results in an adaptation of central neurotransmitter homeostasis, resulting in a different response to the drug.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borg GA (1982) Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc 14:377–381
Burgess ML, Davis JM, Borg TK, Buggy J (1991) Intracranial self-stimulation motivates treadmill running in rats. J Appl Physiol 71(4):1593–1597
Chekeley SE (1980) Neuroendocrine tests of monoamine function in man: a review of basic theory and its application to the study of depressive illness. Psychol Med 10:35–53
Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products (2002) Bupropion hydrochloride, international non-proprietary name (INN): Bupropion. Euopean Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products; CPMP/27610/02
George T, O’Malley S (2004) Current pharmacological treatments for nicotine dependence. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:42–48. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2003.11.003
Hasegawa H, Meeusen R, Sarre S, Diltoer M, Piacentini MF, Michotte Y (2005) Acute dopamine/noradrenaline reuptake inhibition increases brain and core temperature in rats. J Appl Physiol 99(4):1397–1401. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00435.2005
Hasegawa H, Piacentini MF, Sarre S, Michotte Y, Ishiwata T, Meeusen R (2008) Influence of brain catecholamines on the development of fatigue in exercising rats in the heat. J Physiol 586(1):141–149. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2007.142190
Holm KJ, Spencer CM (2000) Bupropion: a review of its use in the management of smoking cessation. Drugs 59:1007–1024. doi:10.2165/00003495-200059040-00019
Jefferson JW, Pradko JF, Muir KT (2005) Bupropion for major depressive disorder: Pharmacokinetic and formulation considerations. Clin Ther 27(11):1685–1695. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.11.011
Jeukendrup A, Saris WH, Brouns F, Kester AD (1996) A new validated endurance performance test. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:266–270. doi:10.1097/00005768-199602000-00017
Learned-Coughlin SM, Bergström M, Savitcheva I, Ascher J, Schmidt VD, Langstrom B (2003) In vivo activity of bupropion at the human dopamine transporter as measured by possitron emission tomography. Biol Psychiatry 54:800–805. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(02)01834-6
Liu YL, Connoley IP, Harrison J, Heal DJ, Stock MJ (2002) Comparison of the thermogenic and hypophagic effects of sibutramine’s metabolite 2 and other monoamine reuptake inhibitors. Eur J Pharmacol 452:49–56. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(02)02226-4
Meeusen R, Watson P, Hasegawa H, Roelands B, Piacentini MF (2006) Central Fatigue: the serotonine hypothesis and beyond. Sports Med 36(10):881–909. doi:10.2165/00007256-200636100-00006
Modell JG, Boyce S, Taylor E, Katholi C (2002) Treatment of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris with bupropion SR: A pilot study. Psychosom Med 64:835–840. doi:10.1097/01.PSY.0000021954.59258.9B
Nestler EJ, Hyman SE, Malenka RC (2001) Molecular neuropharmacology: a foundation for clinical neuroscience. McGraw-Hill, New York
Paterson NE, Balfour DJ, Markou A (2007) Chronic bupropion attenuated the anhedonic component of nicotine withdrawal in rats via inhibition of dopamine reuptake in the nucleus accumbens shell. Eur J Neurosci 25(10):3099–3108. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05546.x
Piacentini MF, Meeusen R, Buyse L, De Schutter G, Kempenaers F, Van Nijvel J, De Meirleir K (2002) No effect of a noradrenergic reuptake inhibitor on performance in trained cyclists. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34(7):1189–1193. doi:10.1097/00005768-200207000-00021
Piacentini MF, Clinckers R, Meeusen R, Sarre S, Ebinger G, Michotte Y (2003) Effect of bupropion on hippocampal neurotransmitters and on peripheral hormonal concentrations in the rat. J Appl Physiol 95(2):652–656
Piacentini MF, Meeusen R, Buyse L, De Schutter G, De Meirleir K (2004) Hormonal responses during prolonged exercise are influenced by a selective DA/NA reuptake inhibitor. Br J Sports Med 38:129–133. doi:10.1136/bjsm.2002.000760
Ramanathan LM (1964) A new weighting system for mean surface temperature of the human body. J Appl Physiol 19:531–532
Roelands B, Hasegawa H, Watson P, Buyse L, De Schutter G, Piacentini MF, Meeusen R (2008a) Acute DA reuptake inhibition enhances performance in warm but not temperate conditions. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40(5):858–879. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181659c4d
Roelands B, Goekint M, Heyman E, Piacentini MF, Watson P, Hasegawa H, Buyse L, Pauwels F, De Schutter G, Meeusen R (2008b) Acute noradrenaline reuptake inhibition decreases performance in normal and high ambient temperature. J Appl Physiol 105:206–212. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.90509.2008
Tella SR, Ladenheim B, Cadet JL (1997) Differential regulation of dopamine transporter after chronic self-administration of bupropion and nomifensine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281(1):508–513
Watson P, Hasegawa H, Roelands B, Piacentini MF, Loovrie R, Meeusen R (2005) Acute dopamine/noradrenaline reuptake inhibition enhances human exercise performance in warm, but not temperate conditions. J Physiol 565(3):873–883. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2004.079202
Yoshimura R, Yanagihara N, Hara K, Nakamura J, Toyohira Y, Ueno S, Izumi F (2001) Dual phases of functional change in norepinephrine transporter in cultured bovine adrenal medullary cells by long-term treatment with clozapine. J Neurochem 77:1018–1026. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00316.x
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research funding from the Vrije Universiteit Brussel (OZR 607, 990, 1236). Further we want to acknowledge the assistance of Prof. Dr. Ilse Smolders for the preparation of the treatments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roelands, B., Hasegawa, H., Watson, P. et al. Performance and thermoregulatory effects of chronic bupropion administration in the heat. Eur J Appl Physiol 105, 493–498 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0929-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0929-x