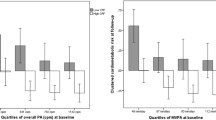
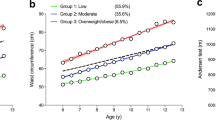
Abstract
The link between aerobic fitness and physical activity in children has been studied in a number of earlier studies and the results have generally shown weak to moderate correlations. This overall finding has been widely questioned partly because of the difficulty in obtaining valid estimates of physical activity. This study investigated the cross-sectional and longitudinal relationship between aerobic fitness and physical activity in a representative sample of 9 and 15-year-old children (n = 1260 cross-sectional, n = 153 longitudinal). The specific goal was to improve past studies using an objective method of activity assessment and taking into account a number of major sources of error. Data came from the Danish part of the European youth heart study, 1997–2003. The cross-sectional results generally showed a weak to moderate association between aerobic fitness and physical activity with standardized regression coefficients ranging from 0.14 to 0.33. The longitudinal results revealed a tendency towards an interaction effect of baseline physical activity on the relationship between changes in physical activity and aerobic fitness. Moderate to moderately strong regression effect sizes were observed in the lower quadrant of baseline physical activity compared to weak effect sizes in the remaining quadrants. In conclusion, the present study confirms earlier findings of a weak to moderate association between aerobic fitness and physical activity in total population of children. However, the study also indicates that inactive children can achieve notable increase in aerobic fitness by increasing their habitual physical activity level. A potential physiological explanation for these results is highlighted.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth BE, Leon AS, Richardson MT, Jacobs DR, Paffenbarger RS Jr (1993) Accuracy of the college alumnus physical activity questionnaire. J Clin Epidemiol 46:1403–1411
Armstrong N, Balding J, Gentle P, Williams J, Kirby B (1990) Peak oxygen uptake and physical activity in 11- to16-year-olds. Pediatr Exer Sci 2:349–358
Baquet G, Twisk JW, Kemper HC, Van Praagh E, Berthoin S (2006) Longitudinal follow-up of fitness during childhood: interaction with physical activity. Am J Hum Biol 18:51–58
Berg A, Kim SS, Keul J (1986) Skeletal muscle enzyme activities in healthy young subjects. Int J Sports Med 7:236–239
Berthouze SE, Minaire PM, Castells J, Busso T, Vico L, Lacour JR (1995) Relationship between mean habitual daily energy expenditure and maximal oxygen uptake. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27:1170–1179
Bland JM, Altman DG (1996) Measurement error. BMJ 312:1654
Boreham CA, Twisk J, Savage MJ, Cran GW, Strain JJ (1997) Physical activity, sports participation, and risk factors in adolescents. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29:788–793
Boreham C, Twisk J, van Mechelen W, Savage M, Strain J, Cran G (1999) Relationships between the development of biological risk factors for coronary heart disease and lifestyle parameters during adolescence: the Northern Ireland Young Hearts Project. Public Health 113:7–12
Brage S (2000) Measurement of physical activity by accelerometry—usability of the computer science and applications (CSA) Model 7164 accelerometer in epidemiology. Thesis/Dissertation, Institute of Sports Science and Clinical Biomechanics, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Southern Denmark
Carroll RJ (1998) Measurement error in epidemiologic studies, chap 3. In: Armitage P, Theodore C (eds) Encyclopedia of biostatistics. Wiley, New York, pp 2491–2519
Dencker M, Thorsson O, Karlsson MK, Linden C, Svensson J, Wollmer P, Andersen LB (2006) Daily physical activity and its relation to aerobic fitness in children aged 8–11 years. Eur J Appl Physiol 96:587–592
Dencker M, Thorsson O, Karlsson MK, Linden C, Wollmer P, Andersen LB (2008) Daily physical activity related to aerobic fitness and body fat in an urban sample of children. Scand J Med Sci Sports 18:728–735
Ekelund U, Poortvliet E, Nilsson A, Yngve A, Holmberg A, Sjostrom M (2001) Physical activity in relation to aerobic fitness and body fat in 14- to 15-year-old boys and girls. Eur J Appl Physiol 85:195–201
Elosua R, Garcia M, Aguilar A, Molina L, Covas MI, Marrugat J (2000) Validation of the Minnesota leisure time physical activity questionnaire in Spanish women. Investigators of the MARATDON group. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:1431–1437
Hands B, Larkin D, Parker H, Straker L, Perry M (2009) The relationship among physical activity, motor competence and health-related fitness in 14-year-old adolescents. Scand J Med Sci Sports 19:655–663
Hopkins WG, Wilson NC, Russell DG (1991) Validation of the physical activity instrument for the life in New Zealand national survey. Am J Epidemiol 133:73–82
Hoppeler H, Howald H, Conley K, Lindstedt SL, Claassen H, Vock P, Weibel ER (1985) Endurance training in humans: aerobic capacity and structure of skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 59:320–327
Ignico AA, Mahon AD (1995) The effects of a physical fitness program on low-fit children. Res Q Exerc Sport 66:85–90
Jerusalem F, Engel AG, Peterson HA (1975) Human muscle fiber fine structure: morphometric data on controls. Neurology 25:127–134
Katzmarzyk PT, Malina RM, Song TM, Bouchard C (1998) Physical activity and health-related fitness in youth: a multivariate analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc 30:709–714
Klissouras V (1971) Heritability of adaptive variation. J Appl Physiol 31:338–344
Klissouras V (1997) Heritability of adaptive variation: an old problem revisited. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 37:1–6
Kohl HW, Fulton J, Caspersen CJ (2000) Assessment of physical activity among children and adolescents: a review and synthesis. Prev Med 31:S54–S76
Kristensen PL, Korsholm L, Moller NC, Wedderkopp N, Andersen LB, Froberg K (2008a) Sources of variation in habitual physical activity of children and adolescents: the European youth heart study. Scand J Med Sci Sports 18:298–308
Kristensen PL, Moller NC, Korsholm L, Wedderkopp N, Andersen LB, Froberg K (2008b) Tracking of objectively measured physical activity from childhood to adolescence: the European youth heart study. Scand J Med Sci Sports 18:171–178
Lamb KL, Brodie DA (1991) Leisure-time physical activity as an estimate of physical fitness: a validation study. J Clin Epidemiol 44:41–52
Malina RM, Katzmarzyk PT (2006) Physical activity and fitness in an international growth standard for preadolescent and adolescent children. Food Nutr Bull 27:S295–S313
Mandigout S, Lecoq AM, Courteix D, Guenon P, Obert P (2001) Effect of gender in response to an aerobic training programme in prepubertal children. Acta Paediatr 90:9–15
Martinez-Vizcaino V, Sanchez-Lopez M (2008) Relationship between physical activity and physical fitness in children and adolescents. Rev Esp Cardiol 61:108–111
Mobert J, Koch G, Humplik O, Oyen EM (1997) Cardio-vascular adjustment to supine and seated postures: Effect of physical training. pp 429–433
Morrow JR, Freedson PS (1994) Relationship between habitual physical activity and aerobic fitness in adolescents. Pediatr Exer Sci 6:315–329
Paffenbarger RS Jr, Blair SN, Lee IM, Hyde RT (1993) Measurement of physical activity to assess health effects in free-living populations. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25:60–70
Pate RR, Dowda M, Ross JG (1990) Associations between physical activity and physical fitness in American children. Am J Dis Child 144:1123–1129
Raboud JM (1998) Errors in variables, chap 2. In: Armitage P, Theodore C (eds) Encyclopedia of biostatistics. Wiley, New York, pp 1373–1375
Rennie KL, Wareham NJ (1998) The validation of physical activity instruments for measuring energy expenditure: problems and pitfalls. Public Health Nutr 1:265–271
Richardson MT, Leon AS, Jacobs DR Jr, Ainsworth BE, Serfass R (1994) Comprehensive evaluation of the Minnesota leisure time physical activity questionnaire. J Clin Epidemiol 47:271–281
Richardson MT, Ainsworth BE, Jacobs DR, Leon AS (2001) Validation of the Stanford 7-day recall to assess habitual physical activity. Ann Epidemiol 11:145–153
Riddoch C, Edwards D, Page A, Froberg K, Anderssen SA, Wedderkopp N, Brage S, Cooper AR, Sardinha LB, Harro M, Heggebø LK, Mechelen WV, Boreham C, Ekelund U, Andersen LB (2005) The European youth heart study—cardiovascular disease risk factors in children: rationale, aims, design and validation of methods. J Physical Activity Health 2:115–129
Rowland, TW (2005) Children’s exercise physiology. Human Kinetics
Rowland T (2009) Aerobic (un)trainability of children: mitochondrial biogenesis and the “crowded cell” hypothesis. Pediatr Exerc Sci 21:1–9
Rowland TW, Boyajian A (1995) Aerobic response to endurance exercise training in children. Pediatrics 96:654–658
Rowland TW, Martel L, Vanderburgh P, Manos T, Charkoudian N (1996) The influence of short-term aerobic training on blood lipids in healthy 10–12 year old children. Int J Sports Med 17:487–492
Rowlands AV, Eston RG, Ingledew DK (1999) Relationship between activity levels, aerobic fitness, and body fat in 8- to 10-yr-old children. J Appl Physiol 86:1428–1435
Sallis JF, Patterson TL, Buono MJ, Nader PR (1988) Relation of cardiovascular fitness and physical activity to cardiovascular disease risk factors in children and adults. Am J Epidemiol 127:933–941
Sallis JF, McKenzie TL, Alcaraz JE (1993) Habitual physical activity and health-related physical fitness in fourth-grade children. Am J Dis Child 147:890–896
Shore S, Shephard RJ (1998) Immune responses to exercise and training: a comparison of children and young adults. Pediatr Exerc Sci 10:210–226
Sunnegardh J, Bratteby LE (1987) Maximal oxygen uptake, anthropometry and physical activity in a randomly selected sample of 8 and 13 year old children in Sweden. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 56:266–272
Tanner JM (1981) Growth and maturation during adolescence. Nutr Rev 39:43–55
Tolfrey K, Campbell IG, Batterham AM (1998) Aerobic trainability of prepubertal boys and girls. Pediatr Exerc Sci 10:248–263
Trost SG et al (2002) Age and gender differences in objectively measured physical activity in youth. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34(2):350–355
Tuero C, De Paz JA, Marquez S (2001) Relationship of measures of leisure time physical activity to physical fitness indicators in Spanish adults. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 41:62–67
Vanderburgh PM (1998) Two important cautions in the use of allometric scaling: the common exponent and group difference principles. Meas Phys Education Exerc Sci 2:153–163
Welsman JR, Armstrong N, Withers S (1997) Responses of young girls to two modes of aerobic training. Br J Sports Med 31:139–142
Williams CA, Armstrong N, Powell J (2000) Aerobic responses of prepubertal boys to two modes of training. Br J Sports Med 34:168–173
Williford HN, Blessing DL, Duey WJ, Barksdale JM, Wang N, Olson MS, Teel S (1996) Exercise training in black adolescents: changes in blood lipids and Vo2max. Ethn Dis 6:279–285
Yoshizawa S, Honda H, Nakamura N, Itoh K, Watanabe N (1997) Effects of an 18-month endurance run training program on maximal aerobic power in 4- to 6-year-old girls. Pediatr Exerc Sci 9:33–43
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Klaas Westerterp.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kristensen, P.L., Moeller, N.C., Korsholm, L. et al. The association between aerobic fitness and physical activity in children and adolescents: the European youth heart study. Eur J Appl Physiol 110, 267–275 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1491-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1491-x