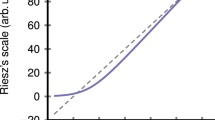
Abstract
The limits on maximum information that can be transferred by single neurons may help us to understand how sensory and other information is being processed in the brain. According to the efficient-coding hypothesis (Barlow, Sensory Comunication, MIT press, Cambridge, 1961), neurons are adapted to the statistical properties of the signals to which they are exposed. In this paper we employ methods of information theory to calculate, both exactly (numerically) and approximately, the ultimate limits on reliable information transmission for an empirical neuronal model. We couple information transfer with the metabolic cost of neuronal activity and determine the optimal information-to-metabolic cost ratios. We find that the optimal input distribution is discrete with only six points of support, both with and without a metabolic constraint. However, we also find that many different input distributions achieve mutual information close to capacity, which implies that the precise structure of the capacity-achieving input is of lesser importance than the value of capacity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Faycal IC, Trott MD, Shamai S (2001) The capacity of discrete-time memoryless Rayleigh-fading channels. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 47(4):1290–1301
Abramowitz M, Stegun IA (1965) Handbook of mathematical functions, with formulas, graphs, and mathematical tables. Dover, New York
Alexander RM (1996) Optima for animals. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Atick JJ (1992) Could information theory provide an ecological theory of sensory processing? Netw Comput Neural Syst 3(2):213–251
Attwell D, Laughlin SB (2001) An energy budget for signaling in the grey matter of the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21(10):1133–1145
Baddeley R, Abbott LF, Booth MCA, Sengpiel F, Freeman T, Wakeman EA, Rolls ET (1997) Responses of neurons in primary and inferior temporal visual cortices to natural scenes. Proc Roy Soc B 264:1775–1783
Balasubramanian V, Berry MJ (2002) A test of metabolically efficient coding in the retina. Netw Comput Neural Syst 13:531–552
Barlow HB (1961) Possible principles underlying the transformation of sensory messages. In: Rosenblith W (ed) Sensory Communication. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 217–234
Bernardo JM (1979) Reference posterior distributions for Bayesian inference. J Roy Stat Soc B 41:113–147
Blahut R (1972) Computation of channel capacity and rate-distortion functions. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 18(4):460–473
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L (2004) Convex optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Brunel N, Nadal JP (1998) Mutual information, Fisher information, and population coding. Neural Comput 10(7):1731–1757
Carandini M (2004) Amplification of trial-to-trial response variability by neurons in visual cortex. PLoS Biol 2(9):e264
Chan TH, Hranilovic S, Kschischang FR (2005) Capacity-achieving probability measure for conditionally Gaussian channels with bounded inputs. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 51:2073–2088
Chiang M, Boyd S (2004) Geometric programming duals of channel capacity and rate distortion. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 50:245–258
Clarke BS, Barron AR (1990) Information-theoretic asymptotics of Bayes methods. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 36(3):453–471
Cover TM, Thomas JA (1991) Elements of information theory. Wiley, New York
Dauwels J (2005) Numerical computation of the capacity of continuous memoryless channels. In: Cardinal J, Cerf N, Delgrange O (eds) Proceedings of the 26th symposium on information theory in the Benelux. WIC, Brussels, pp 221–228
Davis M (1980) Capacity and cutoff rate for Poisson-type channels. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 26(6):710–715
Dimitrov AG, Miller JP (2001) Neural coding and decoding: communication channels and quantization. Netw Comput Neural Syst 12(4):441–472
Fairhall AL, Lewen GD, Bialek W, de Ruyter van Steveninck RR (2001) Efficiency and ambiguity in an adaptive neural code. Nature 412:787–792
Farkhooi F, Müller E, Nawrot MP (2011) Adaptation reduces variability of the neuronal population code. Phys Rev E 83(050):905
Gallager RG (1968) Information theory and reliable communication. Wiley, New York
Gastpar M, Rimoldi B, Vetterli M (2003) To code, or not to code: Lossy source-channel communication revisited. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 49(5):1147–1158
Grant M, Boyd S (2009) Cvx: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming (web page and software). http://stanford.edu/boyd/cvx
Greenwood PE, Lansky P (2005) Optimal signal estimation in neuronal models. Neural Comput 17(10):2240–2257
Gremiaux A, Nowotny T, Martinez D, Lucas P, Rospars JP (2012) Modelling the signal delivered by a population of first-order neurons in a moth olfactory system. Brain Res 1434:123–135
Huang J, Meyn SP (2005) Characterization and computation of optimal distributions for channel coding. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 51(7):2336–2351
Ikeda S, Manton JH (2009) Capacity of a single spiking neuron channel. Neural Comput 21(6):1714–1748
Jacobson H (1950) The informational capacity of the human ear. Science 112(2901):143
Johnson DH, Goodman IN (2008) Inferring the capacity of the vector poisson channel with a bernoulli model. Netw Comput Neural Syst 19(1):13–33
Johnson N, Kotz S, Balakrishnan N (1994) Continuous univariate distributions, vol 1. Wiley, New York
Kelley JE (1960) The cutting-plane method for solving convex programs. J Soc Indus Appl Math 8(4):703–712
Komninakis C, Vandenberghe L, Wesel RD (2001) Capacity of the binomial channel or minimax redundancy for memoryless channels. In: Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on information theory, Washington, p 127
Kostal L (2010) Information capacity in the weak-signal approximation. Phys Rev E 82(026):115
Kostal L (2012) Approximate information capacity of the perfect integrate-and-fire neuron using the temporal code. Brain Res 1434:136–141
Kostal L, Lansky P (2010) Information transfer with small-amplitude signals. Phys Rev E 81:050,901(R)
Kostal L, Lansky P (2013) Information transfer under metabolic constraints in a simple homogeneous population of olfactory neurons (manuscript submitted)
Kostal L, Lansky P, Rospars JP (2008) Efficient olfactory coding in the pheromone receptor neuron of a moth. PLoS Comp Biol 4:e1000,053
Lansky P, Sacerdote L (2001) The Ornstein-Uhlenbeck neuronal model with signal-dependent noise. Phys Lett A 285(3–4):132–140
Lansky P, Pokora O, Rospars JP (2008) Classification of stimuli based on stimulus-response curves and their variability. Brain Res 1225:57–66
Laughlin SB (1981) A simple coding procedure enhances a neuron’s information capacity. Z Naturforsch 36(9–10):910–912
Laughlin SB, de Ruyter van Steveninck RR, Anderson JC (1998) The metabolic cost of neural information. Nat Neurosci 1(1):36–41
Levy WB, Baxter RA (1996) Energy efficient neural codes. Neural Comput 8(3):531–543
Levy WB, Baxter RA (2002) Energy-efficient neuronal computation via quantal synaptic failures. J Neurosci 22(11):4746–4755
Machens CK, Gollisch T, Kolesnikova O, Herz AVM (2005) Testing the efficiency of sensory coding with optimal stimulus ensembles. Neuron 47(3):447–456
McDonnell MD, Flitney AP (2009) Signal acquisition via polarization modulation in single photon sources. Phys Rev E 80:060,102(R)
McDonnell MD, Stocks NG (2008) Maximally informative stimuli and tuning curves for sigmoidal rate-coding neurons and populations. Phys Rev Lett 101(5):058,103
McDonnell MD, Mohan A, Stricker C, Ward LM (2012) Input-rate modulation of gamma oscillations is sensitive to network topology, delays and short-term plasticity. Brain Res 1434:162–177
McEliece RJ (2002) The theory of information and coding. Cambridge University Press, Cambdridge
Moujahid A, d’Anjou A, Torrealdea FJ (2011) Energy and information in Hodgkin-Huxley neurons. Phys Rev E 83(031):912
Mountcastle VB, Poggio GF, Werner G (1963) The relation of thalamic cell response to peripheral stimuli varied over an intensive continuum. J Neurophysiol 26(5):807–834
Nadal JP, Bonnasse-Gahot L (2012) Perception of categories: from coding efficiency to reaction times. Brain Res 1434:47–61
Nikitin AP, Stocks NG, Morse RP, McDonnell MD (2009) Neural population coding is optimized by discrete tuning curves. Phys Rev Lett 103(138):101
Pawlas Z, Klebanov LB, Prokop M, Lansky P (2008) Parameters of spike trains observed in a short time window. Neural Comput 20(5):1325–1343
Quastler H (1953) Essays on the use of information theory in biology. University of Illinois Press, Champaign
Quiroga RQ, Panzeri S (2009) Extracting information from neuronal populations: information theory and decoding approaches. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:173–185
Rieke F, de Ruyter van Steveninck RR, Warland D, Bialek W (1997) Spikes: exploring the neural code. MIT Press, Cambridge
Rissanen JJ (1996) Fisher information and stochastic complexity. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 42(1):40–47
Sadeghi P, Vontobel PO, Shams R (2009) Optimization of information rate upper and lower bounds for channels with memory. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 55(2):663–688
Schreiber S, Machens CK, Herz AVM, Laughlin SB (2002) Energy-efficient coding with discrete stochastic events. Neural Comput 14:1323–1346
Schroeder DJ (1999) Astronomical optics. Academic Press, San Diego
Shadlen MN, Newsome WT (1998) The variable discharge of cortical neurons: implications for connectivity, computation, and information coding. J Neurosci 18(10):3870–3896
Smith JG (1971) The information capacity of amplitude-and variance-constrained sclar gaussian channels. Inform Control 18(3):203–219
Stein RB (1967) The information capacity of nerve cells using a frequency code. Biophys J 7(6):797–826
Stein RB, Gossen ER, Jones KE (2005) Neuronal variability: noise or part of the signal? Nat Rev Neurosci 6(5):389–397
de Ruyter van Steveninck RR, Laughlin SB (1996) The rate of information transfer at graded-potential synapses. Nature 379(6566):642–644
Suksompong P, Berger T (2010) Capacity analysis for integrate-and-fire neurons with descending action potential thresholds. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 56(2):838–851
Tchamkerten A (2004) On the discreteness of capacity-achieving distributions. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 50(11):2773–2778
Tuckwell HC (1988) Introduction to theoretical neurobiology, vol 2. Cambridge University Press, New York
Verdu S (1990) On channel capacity per unit cost. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 36(5):1019–1030
Wainrib G, Thieullen M, Pakdaman K (2010) Intrinsic variability of latency to first-spike. Biol Cyb 103:43–56
Weinstock R (1974) Calculus of variations. Dover, New York
Wiener MC, Richmond BJ (1999) Using response models to estimate channel capacity for neuronal classification of stationary visual stimuli using temporal coding. J Neurophysiol 82(6):2861–2875
Acknowledgments
L. Kostal and P. Lansky were supported by the Institute of Physiology RVO: 67985823, Centre for Neuroscience P304/12/G069 and the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic projects P103/11/0282 and P103/12/P558. M. D. McDonnell’s contribution was supported by the Australian Research Council under ARC grant DP1093425 (including an Australian Research Fellowship).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostal, L., Lansky, P. & McDonnell, M.D. Metabolic cost of neuronal information in an empirical stimulus-response model. Biol Cybern 107, 355–365 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-013-0554-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-013-0554-6