Abstract
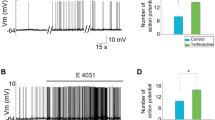
Different erg (ether-à-go-go-related gene; Kv11) K+ channel subunits are expressed throughout the brain. Especially mitral cells of the olfactory bulb are stained intensely by erg1a, erg1b, erg2, and erg3 antibodies. This led us to study the erg current in mitral/tufted (M/T) neurons from mouse olfactory bulb in primary culture. M/T neurons were identified by their morphology and presence of mGluR1 receptors, and RT-PCR demonstrated the expression of all erg subunits in cultured M/T neurons. Using an elevated external K+ concentration, a relatively uniform erg current was recorded in the majority of M/T cells and isolated with the erg channel blocker E-4031. With 4-s depolarizations, the erg current started to activate at −65 mV and exhibited half maximal activation at −51 mV. An increase in the external K+ concentration resulted in an increase in erg whole-cell conductance. The specific group 1 mGluR agonist, DHPG, which depolarizes mitral cells, reduced erg channel availability. DHPG accelerated erg current deactivation, reduced the maximum current amplitude, and shifted availability and activation curves to more depolarized potentials. A pharmacological block of erg channels depolarized the resting potential of M/T cells and clearly demonstrated the involvement of erg channels in the control of mitral cell excitability.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcangeli A, Becchetti A, Mannini A, Mugnai G, De Filippi P, Tarone G, Del Bene MR, Barletta E, Wanke E, Olivotto M (1993) Integrin-mediated neurite outgrowth in neuroblastoma cells depends on the activation of potassium channels. J Cell Biol 122:1131–1143
Barros F, Delgado LM, del Camino D, de la Peña P (1992) Characteristics and modulation by thyrotropin-releasing hormone of an inwardly rectifying K+ current in patch-perforated GH3 anterior pituitary cells. Pflugers Arch 422:31–39
Bauer CK (1998) The erg inwardly rectifying K+ current and its modulation by thyrotrophin-releasing hormone in giant clonal rat anterior pituitary cells. J Physiol 510:63–70
Bauer CK, Schwarz JR (2001) Physiology of EAG K+ channels. J Membr Biol 182:1–15
Bauer CK, Meyerhof W, Schwarz JR (1990) An inward-rectifying K+ current in clonal rat pituitary cells and its modulation by thyrotrophin-releasing hormone. J Physiol 429:169–189
Bauer CK, Schäfer R, Schiemann D, Reid G, Hanganu I, Schwarz JR (1999) A functional role of the erg-like inward-rectifying K+ current in prolactin secretion from rat lactotrophs. Mol Cell Endocrinol 148:37–45
Bian JS, McDonald TV (2007) Phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate interactions with the HERG K+ channel. Pflugers Arch 455:105–113
Bovolin P, Bovetti S, Fasolo A, Katarova Z, Szabo G, Shipley MT, Margolis FL, Puche AC (2009) Developmental regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 splice variants in olfactory bulb mitral cells. J Neurosci Res 87:369–379
Chiesa N, Rosati B, Arcangeli A, Olivotto M, Wanke E (1997) A novel role for HERG K+ channels: spike-frequency adaptation. J Physiol 501:313–318
Christie JM, Bark C, Hormuzdi SG, Helbig I, Monyer H, Westbrook GL (2005) Connexin36 mediates spike synchrony in olfactory bulb glomeruli. Neuron 46:761–772
Curran ME, Splawski I, Timothy KW, Vincent GM, Green ED, Keating MT (1995) A molecular basis for cardiac arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell 80:795–803
Esclapez M, Tillakaratne NJ, Tobin AJ, Houser CR (1993) Comparative localization of mRNAs encoding two forms of glutamic acid decarboxylase with nonradioactive in situ hybridization methods. J Comp Neurol 331:339–362
Furlan F, Guasti L, Avossa D, Becchetti A, Cilia E, Ballerini L, Arcangeli A (2005) Interneurons transiently express the ERG K+ channels during development of mouse spinal networks in vitro. Neuroscience 135:1179–1192
Furlan F, Taccola G, Grandolfo M, Guasti L, Arcangeli A, Nistri A, Ballerini L (2007) ERG conductance expression modulates the excitability of ventral horn GABAergic interneurons that control rhythmic oscillations in the developing mouse spinal cord. J Neurosci 27:919–928
Ganetzky B, Robertson GA, Wilson GF, Trudeau MC, Titus SA (1999) The eag family of K+ channels in Drosophila and mammals. Ann NY Acad Sci 868:356–369
Guasti L, Cilia E, Crociani O, Hofmann G, Polvani S, Becchetti A, Wanke E, Tempia F, Arcangeli A (2005) Expression pattern of the ether-a-go-go-related (ERG) family proteins in the adult mouse central nervous system: evidence for coassembly of different subunits. J Comp Neurol 491:157–174
Hagendorf S, Fluegge D, Engelhardt C, Spehr M (2009) Homeostatic control of sensory output in basal vomeronasal neurons: activity-dependent expression of ether-à-go-go-related gene potassium channels. J Neurosci 29:206–221
Hayar A, Heyward PM, Heinbockel T, Shipley MT, Ennis M (2001) Direct excitation of mitral cells via activation of alpha1-noradrenergic receptors in rat olfactory bulb slices. J Neurophysiol 86:2173–2182
Heinbockel T, Heyward P, Conquet F, Ennis M (2004) Regulation of main olfactory bulb mitral cell excitability by metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR1. J Neurophysiol 92:3085–3096
Hirdes W, Horowitz LF, Hille B (2004) Muscarinic modulation of erg potassium current. J Physiol 559:67–84
Hirdes W, Schweizer M, Schuricht KS, Guddat SS, Wulfsen I, Bauer CK, Schwarz JR (2005) Fast erg K+ currents in rat embryonic serotonergic neurones. J Physiol 564:33–49
Hurley KM, Gaboyard S, Zhong M, Price SD, Wooltorton JR, Lysakowski A, Eatock RA (2006) M-like K+ currents in type I hair cells and calyx afferent endings of the developing rat utricle. J Neurosci 26:10253–10269
Khayari A, Math F, Davrainville JL (1988) Electrical stimulation of primary olfactory nerve induces two types of variations in the extracellular potassium activity within the glomerulus of the rat olfactory bulb in vivo. Brain Res 457:188–191
Kiehn J, Lacerda AE, Wible B, Brown AM (1996) Molecular physiology and pharmacology of HERG. Single-channel currents and block by dofetilide. Circulation 94:2572–2579
Kirchberger NM, Wulfsen I, Schwarz JR, Bauer CK (2006) Effects of TRH on heteromeric rat erg1a/erg1b K+ channels are dominated by the erg1b subunit. J Physiol 571:27–42
Lecchi M, Redaelli E, Rosati B, Gurrola G, Florio T, Crociani O et al (2002) Isolation of a long-lasting eag-related gene-type K+ current in MMQ lactotrophs and its accommodating role during slow firing and prolactin release. J Neurosci 22:3414–3425
Monyer H, Jonas P (1995) Polymerase chain reaction analysis of ion channel expression in single neurons of brain slices. In: Sakmann B, Neher E (eds) Single-channel recording, 2nd edn. Plenum, New York, pp 357–373
Mugnaini E, Wouterlood FG, Dahl AL, Oertel WH (1984) Immunocytochemical identification of GABAergic neurons in the main olfactory bulb of the rat. Arch Ital Biol 122:83–113
Muramoto K, Kato M, Matsuoka M, Kuroda Y, Ichikawa M (2001) A primary culture system of rat olfactory bulb forming many synapses similar to intact ones and spontaneously generating synchronous intracellular calcium oscillations. Anat Embryol 203:9–21
Nie L, Gratton MA, Mu KJ, Dinglasan JN, Feng W, Yamoah EN (2005) Expression and functional phenotype of mouse ERG K+ channels in the inner ear: potential role in K+ regulation in the inner ear. J Neurosci 25:8671–8679
Ohya S, Horowitz B, Greenwood IA (2002) Functional and molecular identification of ERG channels in murine portal vein myocytes. Am J Physiol 283:C866–C877
Papa M, Boscia F, Canitano A, Castaldo P, Sellitti S, Annunziato L, Taglialatela M (2003) Expression pattern of the ether-a-gogo-related (ERG) K + channel-encoding genes ERG1, ERG2, and ERG3 in the adult rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 466:119–135
Pessia M, Servettini I, Panichi R, Guasti L, Grassi S, Arcangeli A, Wanke E, Pettorossi VE (2008) ERG voltage-gated K+ channels regulate excitability and discharge dynamics of the medial vestibular nucleus neurones. J Physiol 586:4877–4890
Sacco T, Bruno A, Wanke E, Tempia F (2003) Functional roles of an ERG current isolated in cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Neurophysiol 90:1817–1828
Saganich MJ, Machado E, Rudy B (2001) Differential expression of genes encoding subthreshold-operating voltage-gated K+ channels in brain. J Neurosci 21:4609–4624
Sahara Y, Kobuta T, Ichikawa M (2001) Cellular localization of metabotropic glutamate receptors mGluR1, 2/3, 5 and 7 in the main and accessory olfactory bulb of the rat. Neurosci Lett 312:59–62
Sanguinetti MC, Jiang C, Curran ME, Keating MT (1995) A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell 81:299–307
Schäfer R, Wulfsen I, Behrens S, Weinsberg F, Bauer CK, Schwarz JR (1999) The erg-like potassium current in rat lactotrophs. J Physiol 518:401–416
Schledermann W, Wulfsen I, Schwarz JR, Bauer CK (2001) Modulation of rat erg1, erg2, erg3 and HERG K+ currents by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in anterior pituitary cells via the native signal cascade. J Physiol 532:143–163
Schönherr R, Rosati B, Hehl S, Rao VG, Arcangeli A, Olivotto M, Heinemann SH, Wanke E (1999) Functional role of the slow activation property of ERG K+ channels. Eur J Neurosci 11:753–760
Shi W, Wymore RS, Wang HS, Pan Z, Cohen IS, McKinnon D, Dixon JE (1997) Identification of two nervous system-specific members of the erg potassium channel gene family. Neurosci 17:9423–9432
Shibasaki T (1987) Conductance and kinetics of delayed rectifier potassium channels in nodal cells of the rabbit heart. J Physiol 387:227–250
Shigemoto R, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N (1992) Distribution of the mRNA for a metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1) in the central nervous system: an in situ hybridization study in adult and developing rat. J Comp Neurol 322:121–135
Spector PS, Curran ME, Keating MT, Sanguinetti MC (1996) Class III antiarrhythmic drugs block HERG, a human cardiac delayed rectifier K+ channel. Open-channel block by methanesulfonanilides. Circ Res 78:499–503
Sturm P, Wimmers S, Schwarz JR, Bauer CK (2005) Extracellular potassium effects are conserved within the rat erg K+ channel family. J Physiol 564:329–345
Titus SA, Warmke JW, Ganetzky B (1997) The Drosophila erg K + channel polypeptide is encoded by the seizure locus. J Neurosci 17:2906–2918
Trombley PQ, Westbrook GL (1990) Excitatory synaptic transmission in cultures of rat olfactory bulb. J Neurophysiol 64:598–606
Van den Pol AN (1995) Presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptors in adult and developing neurons: autoexcitation in the olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 359:253–271
Walz W (2000) Role of astrocytes in the clearance of excess extracellular potassium. Neurochem Int 36:291–300
Wang S, Liu S, Morales MJ, Strauss HC, Rasmusson RL (1997) A quantitative analysis of the activation and inactivation kinetics of HERG expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol 502:45–60
Warmke JW, Ganetzky B (1994) A family of potassium channel genes related to eag in Drosophila and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:3438–3442
Weinsberg F, Bauer CK, Schwarz JR (1997) The class III antiarrhythmic agent E-4031 selectively blocks the inactivating inward-rectifying potassium current in rat anterior pituitary tumor cells (GH3/B6 cells). Pflugers Arch 434:1–10
Wimmers S, Bauer CK, Schwarz JR (2002) Biophysical properties of heteromultimeric erg K+ channels. Pflugers Arch 445:423–430
Wimmers S, Wulfsen I, Bauer CK, Schwarz JR (2001) Erg1, erg2 and erg3 K channel subunits are able to form heteromultimers. Pflugers Arch 441:450–455
Zhou Z, Gong Q, Ye B, Fan Z, Makielski JC, Robertson GA, January CT (1998) Properties of HERG channels stably expressed in HEK 293 cells studied at physiological temperature. Biophys J 74:230–241
Acknowledgements
We thank Saskia Siegel, Barbara Merz, Telse Kock, Annett Hasse and Dr. Susanne Fehr for their help. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 444, A3; SCHW 292/14-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wiebke Hirdes and Nora Napp contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirdes, W., Napp, N., Wulfsen, I. et al. Erg K+ currents modulate excitability in mouse mitral/tufted neurons. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 459, 55–70 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-009-0709-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-009-0709-4