Abstract
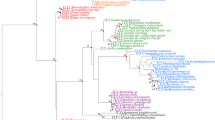
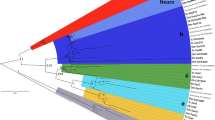
Homeobox genes are a large family of genes that encode helix–turn–helix transcription factors that play fundamental roles in such developmental processes including body axis formation and cell specification. They have been found in a wide variety of organisms, from fungi to plants and animals, with some classes being specific to the Metazoa. While it was once thought that organismal complexity was tied to gene complexity, sequencing of genomes from a cnidarian, poriferan, and placozoan have shown no clear correlation. However, little attention has been paid to ctenophores, another early branching taxon. Ctenophores are mostly pelagic marine animals, with complex morphological features, so understanding the gene content and expression of this nonbilaterian phylum is of key interest to evolutionary biology. Expression information from developmental genes in ctenophores is sparse. In this study, we isolated seven homeobox genes from the ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi and examined their expression through development. Phylogenetic analyses of these genes placed four in the ANTP class and three in the PRD class. These are the first reported full-length PRD class genes, although our analyses could not place them into specific families. We have found that most of these homeobox genes begin expression at gastrulation, and their expression patterns suggest a possible role in patterning of the tentacle apparati and pharynx.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ax P (1996) Multicellular animals: a new approach to the phylogenetic order in nature. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Banerjee-Basu S, Baxevanis AD (2001) Molecular evolution of the homeodomain family of transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res 29:3258–3269
Bumann D, Puls G (1997) The ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi has a flow-through system for digestion with three consecutive phases of extracellular digestion. Physiol Zool 70:1–6
Chun C (1880) Die Ctenophoren des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte. In: Fauna und Flora des Golfes Neapel, vol 1. Engelmann, Leipzig, pp 1–311
Cremona M, Colombo E, Andreazzoli M, Cossu G, Broccoli V (2004) Bsx, an evolutionary conserved Brain Specific homeoboX gene expressed in the septum, epiphysis, mammillary bodies and arcuate nucleus. Gene Expr Patterns 4:47–51
Derelle R, Manuel M (2007) Ancient connection between NKL genes and the mesoderm? Insights from Tlx expression in a ctenophore. Dev Genes Evol 217:253–261
Derelle R, Lopez P, Le Guyader H, Manuel M (2007) Homeodomain proteins belong to the ancestral molecular toolkit of eukaryotes. Evol Dev 9:212–219
Dunn CW, Hejnol A, Matus DQ, Pang K, Browne WE, Smith SA, Seaver E, Rouse GW, Obst M, Edgecombe GD, Sorensen MV, Haddock SHD, Schmidt-Rhaesa A, Okusu A, Kristensen RM, Wheeler WC, Martindale MQ, Giribet G (2008) Broad phylogenomic sampling improves resolution of the animal tree of life. Nature 452:745–749
Galliot B, de Vargas C, Miller D (1999) Evolution of homeobox genes: Q50 paired-like genes founded the paired class. Dev Genes Evol 209:186–197
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Hernandez-Nicaise M-L (1991) Ctenophora. In: Harrison FW, Westfall JA (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates: Placozoa, Porifera, Cnidaria and Ctenophora. vol. 2. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 359–418
Higashijima S, Kojima T, Michiue T, Ishimaru S, Emori Y, Saigo K (1992a) Dual Bar homeobox genes of Drosophila are required in two photoreceptor cells, R1 and R6, and primary pigment cells for normal eye development. Genes Dev 6:50–60
Higashijima S, Michiue T, Emori Y, Saigo K (1992b) Subtype determination of Drosophila embryonic external sensory organs by redundant homeobox genes BarH1 and BarH2. Genes Dev 6:1005–1018
Hoshiyama D, Iwabe N, Miyata T (2007) Evolution of the gene families forming the Pax/Six regulatory network: isolation of genes from primitive animals and molecular phylogenetic analyses. FEBS Lett 581:1639–1643
Hyman LH (1940) The invertebrates: protozoa through Ctenophora. McGraw-Hill, New York
Jager M, Queinnec E, Houliston E, Manuel M (2006) Expansion of the SOX gene family predate the emergence of the Bilateria. Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:842–854
Jakob W, Sagasser S, Dellaporta S, Holland P, Kuhn K, Schierwater B (2004) The Trox-2 Hox/ParaHox gene of the Trichoplax (Placozoa) marks an epithelial boundary. Dev Genes Evol 214:170–175
Jones B, McGinnis W (1993) A new Drosophila homeobox gene, bsh, is expressed in a subset of brain cells during embryogenesis. Development 117:793–806
Jones FS, Kioussi C, Copertino DW, Kallunki P, Holst BD, Edelman GM (1997) Barx2, a new homeobox gene of the Bar class, is expressed in neural and craniofacial structures during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2632–2637
Kusserow A, Pang K, Sturm C, Hrouda M, Lentfer J, Schmidt HA, Technau U, von Haeseler A, Hobmayer B, Martindale MQ, Holstein TW (2005) Unexpected complexity of the Wnt gene family in a sea anemone. Nature 433:156–160
Larroux C, Fahey B, Liubicich D, Hinman VF, Gauthier M, Gongora M, Green K, Wörheide G, Leys SP, Degnan B (2006) Developmental expression of transcription factor genes in a demosponge: insights into the origin of metazoan multicellularity. Evol Dev 8:150–173
Larroux C, Fahey B, Degnan SM, Adamski M, Rohksar DS, Degnan BM (2007) The NK homeobox gene cluster predates the origin of Hox genes. Curr Biol 17:706–710
Larroux C, Luke GN, Koopman P, Rokhsar DS, Shimeld SM, Degnan BM (2008) Genesis and expansion of metazoan transcription factor gene classes. Mol Biol Evol 25:980–996
Magie CR, Pang K, Martindale MQ (2005) Genomic inventory and expression of Sox and Fox genes in the cnidarian Nematostella vectensis. Dev Genes Evol 215:618–630
Martindale MQ, Henry JQ (1999) Intracellular fate mapping in a basal metazoan, the ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi, reveals the origins of mesoderm and the existence of indeterminate cell lineages. Dev Biol 214:243–257
Martinelli C, Spring J (2005) T-box and homeobox genes from the ctenophore Pleurobrachia pileus: comparison of Brachyury, Tbx2/3 and Tlx in basal metazoans and bilaterians. FEBS Lett 579:5024–5028
Metschnikoff E (1885) Vergleichend-embryologische Studien. IV. Ueber die gastrulation und mesodermbildung der Ctenophoren. Z Wiss Zool 42:648–656
Monteiro AS, Schierwater B, Dellaporta SL, Holland PWH (2006) A low diversity of ANTP class homeobox genes in Placozoa. Evol Dev 8:779–794
Panganiban G, Rubenstein JLF (2002) Developmental functions of the Distal-less/Dlx homeobox genes. Development 129:4371–4386
Patterson KD, Cleaver O, Gerber WV, White FG, Krieg PA (2000) Distinct expression patterns for two Xenopus Bar homeobox genes. Dev Genes Evol 210:140–144
Peterson KJ, Eernisse DJ (2001) Animal phylogeny and the ancestry of bilaterians: inferences from morphology and 18S rDNA gene sequences. Evol Dev 3:170–205
Peterson KJ, Sperling EA (2007) Poriferan ANTP genes: primitively simple or secondarily reduced? Evol Dev 9:405–408
Podar M, Haddock SHD, Sogin ML, Harbison GR (2001) A molecular phylogenetic framework for the phylum Ctenophora using 18S rRNA genes. Mol Phylogenet Evol 21:218–230
Putnam NH, Srivastava M, Hellsten U, Dirks B, Chapman J, Salamov A, Terry A, Shapiro H, Lindquist E, Kapitonov VV, Jurka J, Genikhovich G, Grigoriev IV, Lucas SM, Steele RE, Finnerty JR, Technau U, Martindale MQ, Rokhsar DS (2007) Sea anemone genome reveals ancestral eumetazoan gene repertoire and genomic organization. Science 317:86–94
Reig G, Cabrejos ME, Concha ML (2007) Functions of BarH transcription factors during embryonic development. Dev Biol 302:367–375
Reverberi G, Ortolani G (1965) The development of the ctenophores egg. Riv Biol 58:113–137
Rohnquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Ryan JF, Burton PM, Mazza ME, Kwong GK, Mullikan JC, Finnerty JR (2006) The Cnidarian–Bilaterian ancestor possessed at least 56 homeoboxes. Evidence from the starlet sea anemone, Nematostella vectensis. Genome Biol 7:R54
Ryan JF, Mazza ME, Pang K, Matus DQ, Baxevanis AD, Martindale MQ, Finnerty JR (2007) Pre-bilaterian origins of the Hox cluster and the Hox code: evidence from the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis. PloS ONE 2:e153
Shu D-G, Morris SC, Han J, Li Y, Zhang X-L, Hua H, Zhang Z-F, Liu J-N, Guo J-F, Yao Y, Yasui K (2006) Lower Cambrian vendobionts from China and early diploblast evolution. Science 312:731–734
Siminionato E, Ledent V, Richards G, Thomas-Chollier M, Kerner P, Coornaert D, Degnan BM, Vervoort M (2007) Origin and diversification of the basic helix–loop–helix gene family in metazoans: insights from comparative genomics. BMC Evol Biol 7:33
Tamm SL, Tamm S (2002) Novel bridge of axon-like processes of epithelial cells in the aboral sense organ of ctenophores. J Morphol 254:99–120
Tissier-Seta J-P, Mucchielli M-L, Mark M, Mattei M-G, Goridis C, Brunet J-F (1995) Barx1, a new mouse homeodomain transcription factor expressed in cranio-facial ectomesenchyme and the stomach. Mech Dev 51:3–15
Wallberg A, Thollesson M, Farris JS, Jondelius U (2004) The phylogenetic position of the comb jellies (Ctenophora) and the importance of taxonomic sampling. Cladistics 20:558–578
Yamada A, Martindale MQ (2002) Expression of the ctenophore Brain Factor 1 forkhead gene ortholog (ctenoBF-1) mRNA is restricted to the presumptive mouth and feeding apparatus: implications for axial organization in the Metazoa. Dev Genes Evol 212:338–348
Yamada A, Pang K, Martindale MQ, Tochinai S (2007) Surprisingly complex T-box gene complement in diploblastic metazoans. Evol Dev 9:220–230
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Andreas Hejnol, Eric Röttinger, and two anonymous reviewers for comments that greatly improved this manuscript. We also thank David Q. Matus for assistance in phylogenetic analyses and Atsuko Yamada and students from the Embryology course for helping to collect animals. Without the support of the Marine Biological Laboratory (Woods Hole, MA, USA), this work could not have been done. This work was supported by the NSF Graduate Research Fellowship Program to K.P. and grants from NASA and NSF to M.Q.M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D.A. Weisblat
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, K., Martindale, M.Q. Developmental expression of homeobox genes in the ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi . Dev Genes Evol 218, 307–319 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-008-0222-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-008-0222-3