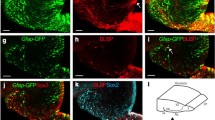
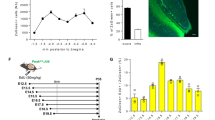
Abstract
The dentate gyrus (DG) principal cells are glutamatergic granule cells (GCs), and they are located in a compact cell layer. However, GCs are also present in the adjacent hilar region, but have been described in only a few studies. Therefore, we used the transcription factor prospero homeobox 1 (Prox1) to quantify GCs at postnatal day (PND) 16, 30, and 60 in a common mouse strain, C57BL/6J mice. At PND16, there was a large population of Prox1-immunoreactive (ir) hilar cells, with more in the septal than temporal hippocampus. At PND30 and 60, the size of the hilar Prox1-ir cell population was reduced. Similar numbers of hilar Prox1-expressing cells were observed in PND30 and 60 Swiss Webster mice. Prox1 is usually considered to be a marker of postmitotic GCs. However, many Prox1-ir hilar cells, especially at PND16, were not double-labeled with NeuN, a marker typically found in mature neurons. Most hilar Prox1-positive cells at PND16 co-expressed doublecortin (DCX) and calretinin, markers of immature GCs. Double-labeling with a marker of actively dividing cells, Ki67, was not detected. These results suggest that, surprisingly, a large population of cells in the hilus at PND16 are immature GCs (Type 2b and Type 3 cells). We also asked whether hilar Prox1-ir cell numbers are modifiable. To examine this issue, we conditionally deleted the proapoptotic gene BAX in Nestin-expressing cells at a time when there are numerous immature GCs in the hilus, PND2-8. When these mice were examined at PND60, the numbers of Prox1-ir hilar cells were significantly increased compared to control mice. However, deletion of BAX did not appear to change the proportion that co-expressed NeuN, suggesting that the size of the hilar Prox1-expressing population is modifiable. However, deleting BAX, a major developmental disruption, does not appear to change the proportion that ultimately becomes neurons.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J, Bayer SA (1990a) Mosaic organization of the hippocampal neuroepithelium and the multiple germinal sources of dentate granule cells. J Comp Neurol 301:325–342
Altman J, Bayer SA (1990b) Migration and distribution of two populations of hippocampal granule cell precursors during the perinatal and postnatal periods. J Comp Neurol 301:365–381
Altman J, Das GD (1965) Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol 124:319–335
Amaral DG (1978) A golgi study of cell types in the hilar region of the hippocampus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 182:851–914
Amaral DG, Dent JA (1981) Development of the mossy fibers of the dentate gyrus: I. A light and electron microscopic study of the mossy fibers and their expansions. J Comp Neurol 195:51–86
Attardo A, Fabel K, Krebs J, Haubensak W, Huttner WB, Kempermann G (2010) Tis21 expression marks not only populations of neurogenic precursor cells but also new postmitotic neurons in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Cereb Cortex 20:304–314
Bayer SA (1982) Changes in the total number of dentate granule cells in juvenile and adult rats: A correlated volumetric and 3h-thymidine autoradiographic study. Exp Brain Res 46:315–323
Bayer SA, Yackel JW, Puri PS (1982) Neurons in the rat dentate gyrus granular layer substantially increase during juvenile and adult life. Science 216:890–892
Brandt MD, Jessberger S, Steiner B, Kronenberg G, Reuter K, Bick-Sander A, von der Behrens W, Kempermann G (2003) Transient calretinin expression defines early postmitotic step of neuronal differentiation in adult hippocampal neurogenesis of mice. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:603–613
Brown JP, Couillard-Despres S, Cooper-Kuhn CM, Winkler J, Aigner L, Kuhn HG (2003) Transient expression of doublecortin during adult neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol 467:1–10
Choi YS, Cho KO, Kim SY (2007) Asymmetry in enhanced neurogenesis in the rostral dentate gyrus following kainic acid-induced status epilepticus in adult rats. Arch Pharm Res 30:646–652
Cowan WM, Stanfield BB, Kishi K (1980) The development of the dentate gyrus. Curr Top Dev Biol 15(Pt 1):103–157
Cowen DS, Takase LF, Fornal CA, Jacobs BL (2008) Age-dependent decline in hippocampal neurogenesis is not altered by chronic treatment with fluoxetine. Brain Res 1228:14–19
Cushman JD, Maldonado J, Kwon EE, Garcia AD, Fan G, Imura T, Sofroniew MV, Fanselow MS (2012) Juvenile neurogenesis makes essential contributions to adult brain structure and plays a sex-dependent role in fear memories. Front. Behav Neurosci 6:3
Dayer AG, Ford AA, Cleaver KM, Yassaee M, Cameron HA (2003) Short-term and long-term survival of new neurons in the rat dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol 460:563–572
Farrar CE, Huang CS, Clarke SG, Houser CR (2005) Increased cell proliferation and granule cell number in the dentate gyrus of protein repair-deficient mice. J Comp Neurol 493:524–537
Faulkner RL, Jang MH, Liu XB, Duan X, Sailor KA, Kim JY, Ge S, Jones EG, Ming GL, Song H, Cheng HJ (2008) Development of hippocampal mossy fiber synaptic outputs by new neurons in the adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:14157–14162
Ferland RJ, Gross RA, Applegate CD (2002) Differences in hippocampal mitotic activity within the dorsal and ventral hippocampus following flurothyl seizures in mice. Neurosci Lett 332:131–135
Gage FH, G. K, H. S (2015) Neurogenesis. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold spring Harbor
Galeeva A, Treuter E, Tomarev S, Pelto-Huikko M (2007) A prospero-related homeobox gene prox-1 is expressed during postnatal brain development as well as in the adult rodent brain. Neuroscience 146:604–616
Galichet C, Guillemot F, Parras CM (2008) Neurogenin 2 has an essential role in development of the dentate gyrus. Development 135:2031–2041.
Gerdes J, Li L, Schlueter C, Duchrow M, Wohlenberg C, Gerlach C, Stahmer I, Kloth S, Brandt E, Flad HD (1991) Immunobiochemical and molecular biologic characterization of the cell proliferation-associated nuclear antigen that is defined by monoclonal antibody ki-67. Am J Pathol 138:867–873
Gong C, Wang TW, Huang HS, Parent JM (2007) Reelin regulates neuronal progenitor migration in intact and epileptic hippocampus. J Neurosci 27:1803–1811
Gould E, Woolley CS, McEwen BS (1991) Naturally occurring cell death in the developing dentate gyrus of the rat. J Comp Neurol 304:408–418
Hayes NL, Nowakowski RS (2002) Dynamics of cell proliferation in the adult dentate gyrus of two inbred strains of mice. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 134:77–85.
He J, Crews FT (2007) Neurogenesis decreases during brain maturation from adolescence to adulthood. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86:327–333
Heine VM, Maslam S, Joels M, Lucassen PJ (2004) Prominent decline of newborn cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis in the aging dentate gyrus, in absence of an age-related hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis activation. Neurobiol Aging 25:361–375
Ho A, Villacis AJ, Svirsky SE, Foilb AR, Romeo RD (2012) The pubertal-related decline in cellular proliferation and neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of male rats is independent of the pubertal rise in gonadal hormones. Dev Neurobiol 72:743–752
Iwano T, Masuda A, Kiyonari H, Enomoto H, Matsuzaki F (2012) Prox1 postmitotically defines dentate gyrus cells by specifying granule cell identity over CA3 pyramidal cell fate in the hippocampus. Development 139:3051–3062.
Jinno S (2011a) Topographic differences in adult neurogenesis in the mouse hippocampus: a stereology-based study using endogenous markers. Hippocampus 21:467–480
Jinno S (2011b) Decline in adult neurogenesis during aging follows a topographic pattern in the mouse hippocampus. J Comp Neurol 519:451–466
Kempermann G, Kuhn HG, Gage FH (1997) Genetic influence on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:10409–10414
Kempermann G, Jessberger S, Steiner B, Kronenberg G (2004) Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus. Trends Neurosci 27:447–452
Key G, Meggetto F, Becker MH, al Saati T, Schluter C, Duchrow M, Delsol G, Gerdes J (1992) Immunobiochemical characterization of the antigen detected by monoclonal antibody ind.64. Evidence that ind.64 reacts with the cell proliferation associated nuclear antigen previously defined by ki-67. Virchows Archiv B. Cell Pathol Mol Pathol 62:259–262
Key G, Becker MH, Baron B, Duchrow M, Schluter C, Flad HD, Gerdes J (1993) New ki-67-equivalent murine monoclonal antibodies (mib 1–3) generated against bacterially expressed parts of the ki-67 cdna containing three 62 base pair repetitive elements encoding for the ki-67 epitope. Lab Invest 68:629–636
Kim JS, Jung J, Lee HJ, Kim JC, Wang H, Kim SH, Shin T, Moon C (2009) Differences in immunoreactivities of ki-67 and doublecortin in the adult hippocampus in three strains of mice. Acta Histochem 111:150–156
Koyama R, Tao K, Sasaki T, Ichikawa J, Miyamoto D, Muramatsu R, Matsuki N, Ikegaya Y (2012) GABAergic excitation after febrile seizures induces ectopic granule cells and adult epilepsy. Nat Med 18:1271–1278
Lavado A, Lagutin OV, Chow LM, Baker SJ, Oliver G (2010) Prox1 is required for granule cell maturation and intermediate progenitor maintenance during brain neurogenesis. PLoS Biol 8.
Lazarov O, Mattson MP, Peterson DA, Pimplikar SW, van Praag H (2010) When neurogenesis encounters aging and disease. Trends Neurosci 33:569–579
Leung L, Andrews-Zwilling Y, Yoon SY, Jain S, Ring K, Dai J, Wang MM, Tong L, Walker D, Huang Y (2012) Apolipoprotein e4 causes age- and sex-dependent impairments of hilar GABAergic interneurons and learning and memory deficits in mice. PLoS ONE 7:e53569
Li G, Pleasure SJ (2007) Genetic regulation of dentate gyrus morphogenesis. Prog Brain Res 163:143–152
Li G, Kataoka H, Coughlin SR, Pleasure SJ (2009) Identification of a transient subpial neurogenic zone in the developing dentate gyrus and its regulation by cxcl12 and reelin signaling. Development 136:327–335.
Martin LA, Tan SS, Goldowitz D (2002) Clonal architecture of the mouse hippocampus. J Neurosci 22:3520–3530
Martinez A, Ruiz M, Soriano E (1999) Spiny calretinin-immunoreactive neurons in the hilus and CA3 region of the rat hippocampus: Local axon circuits, synaptic connections, and glutamic acid decarboxylase 65/67 mrna expression. J Comp Neurol 404:438–448
Marti-Subirana A, Soriano E, Garcia-Verdugo JM (1986) Morphological aspects of the ectopic granule-like cellular populations in the albino rat hippocampal formation: a golgi study. J Anat 144:31–47
Mathews EA, Morgenstern NA, Piatti VC, Zhao C, Jessberger S, Schinder AF, Gage FH (2010) A distinctive layering pattern of mouse dentate granule cells is generated by developmental and adult neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol 518:4479–4490
McCloskey DP, Hintz TM, Pierce JP, Scharfman HE (2006) Stereological methods reveal the robust size and stability of ectopic hilar granule cells after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in the adult rat. Eur J Neurosci 24:2203–2210
Mullen RJ, Buck CR, Smith AM (1992) Neun, a neuronal specific nuclear protein in vertebrates. Development 116:201–211.
Munster-Wandowski A, Gomez-Lira G, Gutierrez R (2013) Mixed neurotransmission in the hippocampal mossy fibers. Front Cell Neurosci 7:210
Muramatsu R, Ikegaya Y, Matsuki N, Koyama R (2008) Early-life status epilepticus induces ectopic granule cells in adult mice dentate gyrus. Exp Neurol 211:503–510
Myers CE, Bermudez-Hernandez K, Scharfman HE (2013) The influence of ectopic migration of granule cells into the hilus on dentate gyrus-CA3 function. PLoS ONE 8:e68208
Namba T, Mochizuki H, Onodera M, Mizuno Y, Namiki H, Seki T (2005) The fate of neural progenitor cells expressing astrocytic and radial glial markers in the postnatal rat dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci 22:1928–1941
Nicola Z, Fabel K, Kempermann G (2015) Development of the adult neurogenic niche in the hippocampus of mice. Front Neuroanat 9:53
Oliver G, Sosa-Pineda B, Geisendorf S, Spana EP, Doe CQ, Gruss P (1993) Prox 1, a prospero-related homeobox gene expressed during mouse development. Mech Dev 44:3–16
Parent JM (2007) Adult neurogenesis in the intact and epileptic dentate gyrus. Prog Brain Res 163:529–540
Parent JM, Yu TW, Leibowitz RT, Geschwind DH, Sloviter RS, Lowenstein DH (1997) Dentate granule cell neurogenesis is increased by seizures and contributes to aberrant network reorganization in the adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 17:3727–3738
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates.: Academic Press, Cambridge
Pierce JP, McCloskey DP, Scharfman HE (2011) Morphometry of hilar ectopic granule cells in the rat. J Comp Neurol 519:1196–1218
Pleasure SJ, Collins AE, Lowenstein DH (2000) Unique expression patterns of cell fate molecules delineate sequential stages of dentate gyrus development. J Neurosci 20:6095–6105
Pritchett KR, Taft RA (2007) Chap. 3—reproductive biology of the laboratory mouse. In: The mouse in biomedical research (second edition) (Fox JG, Davisson MT, Quimby FW, Barthold SW, Newcomer CE, Smith AL (eds)), Academic Press, Burlington, pp. 91–121.
Rao MS, Hattiangady B, Shetty AK (2006) The window and mechanisms of major age-related decline in the production of new neurons within the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. Aging Cell 5:545–558
Sahay A, Scobie KN, Hill AS, O’Carroll CM, Kheirbek MA, Burghardt NS, Fenton AA, Dranovsky A, Hen R (2011) Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve pattern separation. Nature 472:466–470
Sandler R, Smith AD (1991) Coexistence of GABA and glutamate in mossy fiber terminals of the primate hippocampus: An ultrastructural study. J Comp Neurol 303:177–192
Scharfman HE, McCloskey DP (2009) Postnatal neurogenesis as a therapeutic target in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 85:150–161
Scharfman HE, Goodman JH, Sollas AL (2000) Granule-like neurons at the hilar/CA3 border after status epilepticus and their synchrony with area CA3 pyramidal cells: functional implications of seizure-induced neurogenesis. J Neurosci 20:6144–6158
Scharfman HE, Sollas AE, Berger RE, Goodman JH, Pierce JP (2003) Perforant path activation of ectopic granule cells that are born after pilocarpine-induced seizures. Neuroscience 121:1017–1029
Scharfman H, Goodman J, McCloskey D (2007) Ectopic granule cells of the rat dentate gyrus. Dev Neurosci 29:14–27
Schauwecker PE (2006) Genetic influence on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of two strains of adult mice. Brain Res 1120:83–92
Schlessinger AR, Cowan WM, Gottlieb DI (1975) An autoradiographic study of the time of origin and the pattern of granule cell migration in the dentate gyrus of the rat. J Comp Neurol 159:149–175
Seki T, Arai Y (1995) Age-related production of new granule cells in the adult dentate gyrus. Neuroreport 6:2479–2482
Snyder JS, Radik R, Wojtowicz JM, Cameron HA (2009) Anatomical gradients of adult neurogenesis and activity: Young neurons in the ventral dentate gyrus are activated by water maze training. Hippocampus 19:360–370
Soriano E, Frotscher M (1993) Spiny nonpyramidal neurons in the CA3 region of the rat hippocampus are glutamate-like immunoreactive and receive convergent mossy fiber input. J Comp Neurol 333:435–448
Steiner B, Zurborg S, Horster H, Fabel K, Kempermann G (2008) Differential 24 h responsiveness of prox1-expressing precursor cells in adult hippocampal neurogenesis to physical activity, environmental enrichment, and kainic acid-induced seizures. Neuroscience 154:521–529
Sun W, Winseck A, Vinsant S, Park OH, Kim H, Oppenheim RW (2004) Programmed cell death of adult-generated hippocampal neurons is mediated by the proapoptotic gene bax. J Neurosci 24:11205–11213
Szabadics J, Varga C, Brunner J, Chen K, Soltesz I (2010) Granule cells in the CA3 area. J Neurosci 30:8296–8307
Und Halbach OVB (2007) Immunohistological markers for staging neurogenesis in adult hippocampus. Cell Tissue Res 329:409–420.
Urban N, Guillemot F (2014) Neurogenesis in the embryonic and adult brain: Same regulators, different roles. Front Cell Neurosci 8:396
Volz F, Bock HH, Gierthmuehlen M, Zentner J, Haas CA, Freiman TM (2011) Stereologic estimation of hippocampal GluR2/3- and calretinin-immunoreactive hilar neurons (presumptive mossy cells) in two mouse models of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 52:1579–1589
Zhang J, Jiao J (2015) Molecular biomarkers for embryonic and adult neural stem cell and neurogenesis. Biomed Res Int 2015:727542.
Acknowledgements
Supported by NIH MH-090606, NS-081203, and the New York State Office of Mental Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bermudez-Hernandez, K., Lu, YL., Moretto, J. et al. Hilar granule cells of the mouse dentate gyrus: effects of age, septotemporal location, strain, and selective deletion of the proapoptotic gene BAX . Brain Struct Funct 222, 3147–3161 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1391-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1391-5