Abstract
Introduction
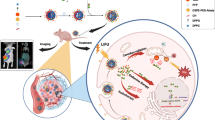
Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted nanoparticles can be used to deliver a therapeutic and imaging agent to EGFR-overexpressing tumor cells. 131I-labeled anti-EGFR nanoparticles derived from cetuximab were used as a tumor-targeting vehicle in radionuclide therapy.
Methods
This paper describes the construction of the anti-EGFR nanoparticle EGFR–BSA–PCL. This nanoparticle was characterized for EGFR-targeted binding and cellular uptake in EGFR-overexpressing cancer cells by using flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. Anti-EGFR and non-targeted nanoparticles were labeled with 131I using the chloramine-T method. Analyses of cytotoxicity and targeted cell killing with 131I were performed using the MTT assay. The time-dependent cellular uptake of 131I-labeled anti-EGFR nanoparticles proved the slow-release effects of nanoparticles. A radioiodine therapy study was also performed in mice.
Results
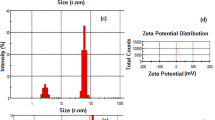
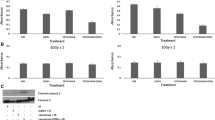
The EGFR-targeted nanoparticle EGFR–BSA–PCL and the non-targeted nanoparticle BSA–PCL were constructed; the effective diameters were approximately 100 nm. The results from flow cytometry and confocal microscopy revealed significant uptake of EGFR–BSA–PCL in EGFR-overexpressing tumor cells. Compared with EGFR–BSA–PCL, BSA–PCL could also bind to cells, but tumor cell retention was minimal and weak. In MTT assays, the EGFR-targeted radioactive nanoparticle 131I–EGFR–BSA–PCL showed greater cytotoxicity and targeted cell killing than the non-targeted nanoparticle 131I–BSA–PCL. The radioiodine uptake of both 131I-labeled nanoparticles, 131I–EGFR–BSA–PCL and 131I–BSA–PCL, was rapid and reached maximal levels 4 h after incubation, but the 131I uptake of 131I–EGFR–BSA–PCL was higher than that of 131I–BSA–PCL. On day 15, the average tumor volumes of the 131I–EGFR–BSA–PCL and 131I–BSA–PCL groups showed a slow growth relationship compared with that of the control group.
Conclusion
The EGFR-targeted nanoparticle EGFR–BSA–PCL demonstrated superior cellular binding and uptake compared with those of the control BSA–PCL. The EGFR-targeted radioactive nanoparticle 131I–EGFR–BSA–PCL exhibited favorable intracellular retention of 131I. Radionuclide therapy using 131I–EGFR–BSA–PCL, which showed excellent targeted cell killing, suppressed cancer cell growth caused by EGFR overexpression.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almutairi A, Rossin R, Shokeen M, Hagooly A, Ananth A, Capoccia B, Guillaudeu S, Abendschein D, Anderson CJ, Welch MJ, Frechet JM (2009) Biodegradable dendritic positron-emitting nanoprobes for the noninvasive imaging of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:685–690
Ang KK, Berkey BA, Tu X, Zhang HZ, Katz R, Hammond EH, Fu KK, Milas L (2002) Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor expression on survival and pattern of relapse in patients with advanced head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res 62:7350–7356
Bandekar A, Zhu C, Jindal R, Bruchertseifer F, Morgenstern A, Sofou S (2014) Anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen liposomes loaded with 225Ac for potential targeted antivascular alpha-particle therapy of cancer. J Nucl Med 55:107–114
Brand TM, Iida M, Li C, Wheeler DL (2011) The nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor signaling network and its role in cancer. Discov Med 12:419–432
Capelan M, Pugliano L, De Azambuja E, Bozovic I, Saini KS, Sotiriou C, Loi S, Piccart-Gebhart MJ (2013) Pertuzumab: new hope for patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. Ann Oncol 24:273–282
Carlsson J, Forssell Aronsson E, Hietala SO, Stigbrand T, Tennvall J (2003) Tumour therapy with radionuclides: assessment of progress and problems. Radiother Oncol 66:107–117
Chen K, Li ZB, Wang H, Cai W, Chen X (2008) Dual-modality optical and positron emission tomography imaging of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor on tumor vasculature using quantum dots. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35:2235–2244
Chen S, Zhao X, Chen J, Kuznetsova L, Wong SS, Ojima I (2010) Mechanism-based tumor-targeting drug delivery system. Validation of efficient vitamin receptor-mediated endocytosis and drug release. Bioconjug Chem 21:979–987
Chen CL, Hu GY, Mei Q, Qiu H, Long GX, Hu GQ (2012) Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted ultra-small superparamagnetic iron oxide particles for magnetic resonance molecular imaging of lung cancer cells in vitro. Chin Med J (Engl) 125:2322–2328
Chen Y, Peng J, Han M, Omar M, Hu D, Ke X, Lu N (2015) A low-molecular-weight heparin-coated doxorubicin-liposome for the prevention of melanoma metastasis. J Drug Target 23:335–346
Cho YS, Yoon TJ, Jang ES, Soo Hong K, Young Lee S, Ran Kim O, Park C, Kim YJ, Yi GC, Chang K (2010) Cetuximab-conjugated magneto-fluorescent silica nanoparticles for in vivo colon cancer targeting and imaging. Cancer Lett 299:63–71
Chung TH, Hsiao JK, Hsu SC, Yao M, Chen YC, Wang SW, Kuo MY, Yang CS, Huang DM (2011) Iron oxide nanoparticle-induced epidermal growth factor receptor expression in human stem cells for tumor therapy. ACS Nano 5:9807–9816
Du C, Deng D, Shan L, Wan S, Cao J, Tian J, Achilefu S, Gu Y (2013) A pH-sensitive doxorubicin prodrug based on folate-conjugated BSA for tumor-targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 34:3087–3097
Elbayoumi TA, Pabba S, Roby A, Torchilin VP (2007) Antinucleosome antibody-modified liposomes and lipid-core micelles for tumor-targeted delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic agents. J Liposome Res 17:1–14
Fondell A, Edwards K, Unga J, Kullberg E, Park JW, Gedda L (2011) In vitro evaluation and biodistribution of HER2-targeted liposomes loaded with an (125)I-labelled DNA-intercalator. J Drug Target 19:846–855
Giaccone G (2005) HER1/EGFR-targeted agents: predicting the future for patients with unpredictable outcomes to therapy. Ann Oncol 16:538–548
Gupta B, Torchilin VP (2007) Monoclonal antibody 2C5-modified doxorubicin-loaded liposomes with significantly enhanced therapeutic activity against intracranial human brain U-87 MG tumor xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56:1215–1223
Hu G, Lijowski M, Zhang H, Partlow KC, Caruthers SD, Kiefer G, Gulyas G, Athey P, Scott MJ, Wickline SA, Lanza GM (2007) Imaging of Vx-2 rabbit tumors with alpha(nu)beta3-integrin-targeted 111In nanoparticles. Int J Cancer 120:1951–1957
Hussain AF, Kruger HR, Kampmeier F, Weissbach T, Licha K, Kratz F, Haag R, Calderon M, Barth S (2013) Targeted delivery of dendritic polyglycerol–doxorubicin conjugates by scFv-SNAP fusion protein suppresses EGFR+ cancer cell growth. Biomacromolecules 14:2510–2520
Jung KH, Choe YS, Paik JY, Lee KH (2011) 99mTc-Hydrazinonicotinamide epidermal growth factor-polyethylene glycol-quantum dot imaging allows quantification of breast cancer epidermal growth factor receptor expression and monitors receptor downregulation in response to cetuximab therapy. J Nucl Med 52:1457–1464
Kao HW, Lin YY, Chen CC, Chi KH, Tien DC, Hsia CC, Lin MH, Wang HE (2013) Evaluation of EGFR-targeted radioimmuno-gold-nanoparticles as a theranostic agent in a tumor animal model. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:3180–3185
Kim YH, Jeon J, Hong SH, Rhim WK, Lee YS, Youn H, Chung JK, Lee MC, Lee DS, Kang KW, Nam JM (2011) Tumor targeting and imaging using cyclic RGD-PEGylated gold nanoparticle probes with directly conjugated iodine-125. Small 7:2052–2060
Lee HY, Li Z, Chen K, Hsu AR, Xu C, Xie J, Sun S, Chen X (2008) PET/MRI dual-modality tumor imaging using arginine-glycine-aspartic (RGD)-conjugated radiolabeled iron oxide nanoparticles. J Nucl Med 49:1371–1379
Li L, Wartchow CA, Danthi SN, Shen Z, Dechene N, Pease J, Choi HS, Doede T, Chu P, Ning S, Lee DY, Bednarski MD, Knox SJ (2004) A novel antiangiogenesis therapy using an integrin antagonist or anti-Flk-1 antibody coated 90Y-labeled nanoparticles. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:1215–1227
Liu Z, Dong C, Wang X, Wang H, Li W, Tan J, Chang J (2014) Self-assembled biodegradable protein-polymer vesicle as a tumor-targeted nanocarrier. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:2393–2400
Mamot C, Drummond DC, Greiser U, Hong K, Kirpotin DB, Marks JD, Park JW (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted immunoliposomes mediate specific and efficient drug delivery to EGFR- and EGFRvIII-overexpressing tumor cells. Cancer Res 63:3154–3161
Mamot C, Drummond DC, Noble CO, Kallab V, Guo Z, Hong K, Kirpotin DB, Park JW (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted immunoliposomes significantly enhance the efficacy of multiple anticancer drugs in vivo. Cancer Res 65:11631–11638
Mamot C, Ritschard R, Kung W, Park JW, Herrmann R, Rochlitz CF (2006) EGFR-targeted immunoliposomes derived from the monoclonal antibody EMD72000 mediate specific and efficient drug delivery to a variety of colorectal cancer cells. J Drug Target 14:215–223
McDevitt MR, Chattopadhyay D, Kappel BJ, Jaggi JS, Schiffman SR, Antczak C, Njardarson JT, Brentjens R, Scheinberg DA (2007) Tumor targeting with antibody-functionalized, radiolabeled carbon nanotubes. J Nucl Med 48:1180–1189
Milenic DE, Brady ED, Brechbiel MW (2004) Antibody-targeted radiation cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:488–499
Mitra A, Nan A, Line BR, Ghandehari H (2006) Nanocarriers for nuclear imaging and radiotherapy of cancer. Curr Pharm Des 12:4729–4749
Nagaria TS, Williams JL, Leduc C, Squire JA, Greer PA, Sangrar W (2013) Flavopiridol synergizes with sorafenib to induce cytotoxicity and potentiate antitumorigenic activity in EGFR/HER-2 and mutant RAS/RAF breast cancer model systems. Neoplasia 15:939–951
Neff CP, Zhou J, Remling L, Kuruvilla J, Zhang J, Li H, Smith DD, Swiderski P, Rossi JJ, Akkina R (2011) An aptamer-siRNA chimera suppresses HIV-1 viral loads and protects from helper CD4(+) T cell decline in humanized mice. Sci Transl Med 3:66ra66
Nordberg E, Friedman M, Gostring L, Adams GP, Brismar H, Nilsson FY, Stahl S, Glimelius B, Carlsson J (2007) Cellular studies of binding, internalization and retention of a radiolabeled EGFR-binding affibody molecule. Nucl Med Biol 34:609–618
Normanno N, Tejpar S, Morgillo F, De Luca A, Van Cutsem E, Ciardiello F (2009) Implications for KRAS status and EGFR-targeted therapies in metastatic CRC. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6:519–527
Pastorino F, Brignole C, Marimpietri D, Sapra P, Moase EH, Allen TM, Ponzoni M (2003) Doxorubicin-loaded Fab’ fragments of anti-disialoganglioside immunoliposomes selectively inhibit the growth and dissemination of human neuroblastoma in nude mice. Cancer Res 63:86–92
Pinhassi RI, Assaraf YG, Farber S, Stark M, Ickowicz D, Drori S, Domb AJ, Livney YD (2010) Arabinogalactan-folic acid-drug conjugate for targeted delivery and target-activated release of anticancer drugs to folate receptor-overexpressing cells. Biomacromolecules 11:294–303
Saha RN, Vasanthakumar S, Bende G, Snehalatha M (2010) Nanoparticulate drug delivery systems for cancer chemotherapy. Mol Membr Biol 27:215–231
Su W, Wang H, Wang S, Liao Z, Kang S, Peng Y, Han L, Chang J (2012) PEG/RGD-modified magnetic polymeric liposomes for controlled drug release and tumor cell targeting. Int J Pharm 426:170–181
Ting G, Chang CH, Wang HE, Lee TW (2010) Nanotargeted radionuclides for cancer nuclear imaging and internal radiotherapy. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:1–17. doi:10.1155/2010/953537
Yang FY, Wang HE, Liu RS, Teng MC, Li JJ, Lu M, Wei MC, Wong TT (2012) Pharmacokinetic analysis of 111 in-labeled liposomal Doxorubicin in murine glioblastoma after blood-brain barrier disruption by focused ultrasound. PLoS ONE 7:e45468
Zhou X, Qiu J, Wang Z, Huang N, Li X, Li Q, Zhang Y, Zhao C, Luo C, Zhang N, Teng X, Chen Z, Liu X, Yu X, Wu W, Wei YQ, Li J (2012) In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activities of anti-EGFR single-chain variable fragment fused with recombinant gelonin toxin. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138:1081–1090
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (to Jian TAN) (No. 81171372) (to Wei LI) (No. 81301244), Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology (to Tong LIU) (No. 11JCYBJC11700) and the National Key Clinical Specialty Project of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This paper is our own work; we have no specific disclaimers or conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health and China Regulations For the Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals. The protocol was approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of the Tianjin Medical University General Hospital. All surgery was performed under sodium pentobarbital anesthesia, and all efforts were made to minimize suffering.
Additional information
Wei Li and Zhongyun Liu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Liu, Z., Li, C. et al. Radionuclide therapy using 131I-labeled anti-epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted nanoparticles suppresses cancer cell growth caused by EGFR overexpression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 619–632 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2067-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2067-2