Abstract
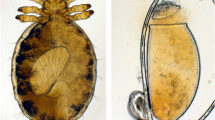
Infestation with the chewing louse (Werneckiella (Damalinia) equi) can be found on horses world-wide. Louse infestations, including clinical signs of louse-derived dermatitis, are known from Icelandic horses. A clinical field investigation was conducted in Iceland using horses with natural louse infestations to evaluate the efficacy of imidacloprid in a 10% solution in comparison with phoxim in a 0.05% solution. A total of 27 horses received a single imidacloprid treatment using 16 ml of the 10% solution along the mane and on the dorso-lateral trunk. A further 43 horses were treated twice, 14 days apart, with phoxim, using 2×50 ml solution applied along the mane and the dorso-lateral trunk. At the final evaluation on day 28, complete control of the lice was obtained for the imidacloprid treated horses and only a single moribund louse was found on two horses treated with phoxim.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (1992) Bayer Animal Health, Sebacil product information. Bayer Animal Health, Leverkusen
Arundel JH (1985) Parasitic diseases of the horse. Vet Rev 28:92–93
Egri B, Sarkozy P, Banhidy G (1995) Prevalence of botfly larvae and lice in studs of north Caucasus (Stawropol County, Russia). Acta Vet Hung 43:287–28
George JB, Otobo S, Ogunleye J, Adediminiyi B (1992) Louse and mite infestation in domestic animals in northern Nigeria. Trop Anim Health Prod 24:121–124
Hanssen I, Mencke N, Asskildt H, Ewald-Hamm D, Dorn H (1999) Field study on the insecticidal efficacy of Advantage against natural infestations of dogs with lice. Parasitol Res 85:347–348
Liebisch A, Rahman MS, Awad Hassan A (1980) Beitrag zur Therapie der Psoroptes- und Sarkoptesräude verschiedener Haustierarten mit dem Phosphorsäureester Sebacil. Vet Med Nachr 1:3-16
Mehlhorn H (ed) (2000) Encylopedic reference of parasitology, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 339–343
Moreby C (1978) The biting louse genus Werneckiella (Phthiraptera: Trichodectidae) ectoparasitic on the horse family Equidae (Mammalia: Perissodactyla). J Nat Hist 12:395–412
Perris EE (1995) Louse infestations. In: Turner AS (ed) Dermatology, the vet clinics of North America. Equine Pract 11:20–28
Polozowski A, Czeszcyszyn T, Pytloch P (2001) Efficacy of fipronil against Werneckiella equi in horses. In: Proceedings of the WAAVP, Stresa, Italy 2001, p 133
Rommel M (ed) (2000) Parasitosen der Einhufer (Pferd, Esel). In: Rommel M. Eckert J, Kutzer E, Körting W, Schneider T (eds) Veterinärmedizinische Parasitologie, 5th edn. Parey, Berlin, pp 421–422
Wright R (1999) Lice on horses. Can Vet J 40:590–591
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mencke, N., Larsen, K.S., Eydal, M. et al. Natural infestation of the chewing lice (Werneckiella equi) on horses and treatment with imidacloprid and phoxim. Parasitol Res 94, 367–370 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1227-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-004-1227-0