Abstract
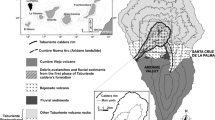
Carbon dioxide flux from the soil is regularly monitored in selected areas of Vesuvio and Solfatara (Campi Flegrei, Pozzuoli) with the twofold aim of i) monitoring spatial and temporal variations of the degassing process and ii) investigating if the surface phenomena could provide information about the processes occurring at depth. At present, the surveyed areas include 15 fixed points around the rim of Vesuvio and 71 fixed points in the floor of Solfatara crater. Soil CO2 flux has been measured since 1998, at least once a month, in both areas. In addition, two automatic permanent stations, located at Vesuvio and Solfatara, measure the CO2 flux and some environmental parameters that can potentially influence the CO2 diffuse degassing. Series acquired by continuous stations are characterized by an annual periodicity that is related to the typical periodicities of some meteorological parameters. Conversely, series of CO2 flux data arising from periodic measurements over the arrays of Vesuvio and Solfatara are less dependent on external factors such as meteorological parameters, local soil properties (porosity, hydraulic conductivity) and topographic effects (high or low ground). Therefore we argue that the long-term trend of this signal contains the “best” possible representation of the endogenous signal related to the upflow of deep hydrothermal fluids.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acocella V, Salvini F, Funiciello R, Faccenna C (1999) The role of transfer structures on volcanic activity at Campi Flegrei (Southern Italy). J Volcanol Geotherm Res 62:123–139
Allard P, Maiorani A, Tedesco D, Cortecci G, Turi B (1991) Isotopic study of the origin of sulfur and carbon in Solfatara fumaroles, Campi Flegrei caldera. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 48:139–159
Andronico D, Calderoni G, Cioni R, Sbrana A, Sulpizio R, Santacroce R (1995) Geological map of Somma-Vesuvius volcano. Per Mineral 64:77–78
Barberi F, Corrado G, Innocenti F, Luongo G (1984) Phlegrean fields 1982–1984: brief chronicle of a volcano emergency in a densely populated area. Bull Volcanol 47:175–185
Barberi F, Carapezza M, Innocenti F, Luongo G, Santacroce R (1989) The problem of volcanic unrest: the Phlegraean fields case history. Atti convegno Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei 80:387–405
Baubron JC, Allard P, Toutain JP (1990) Diffuse volcanic emissions of carbon dioxide from Vulcano Island, Italy. Nature 344:51–53
Bianco F, Del Pezzo E, Saccorotti G, Ventura G (2004) The role of hydrothermal fluids in triggering the July–August 2000 seismic swarm at Campi Flegrei, Italy: evidence from seismological and mesostructural data. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 133:229–246
Brombach T, Hunziker JC, Chiodini G, Cardellini C, Marini L (2001) Soil diffuse degassing and thermal energy fluxes from the southern Lakki plain, Nisyros (Greece). Geophys Res Lett 28:69–72
Carapezza ML, Granieri D (2004) CO2 soil flux at Vulcano (Italy): comparison of active and passive methods. Appl Geochem 19:73–88
Cardellini C, Chiodini G, Frondini F (2003) Application of stochastic simulation to CO2 flux from soil: mapping and quantification of gas release. J Geophys Res 108:2425. doi:10.1029/2002JB002165
Chiodini G, Frondini F, Raco B (1996) Diffuse emission of CO2 from the Fossa crater, Vulcano Island (Italy). Bull Volcanol 58:41–50
Chiodini G, Cioni R, Guidi M, Marini L, Raco B (1998) Soil CO2 measurements in volcanic and geothermal areas. Appl Geochem 13:543–552
Chiodini G, Frondini F, Cardellini C, Granieri D, Marini L, Ventura G (2001a) CO2 degassing and energy release at Solfatara Volcano, Campi Flegrei, Italy. J Geophys Res 106:16213–16221
Chiodini G, Marini L, Russo M (2001b) Geochemical evidences of high temperature hydrothermal brines at Vesuvio volcano (Italy). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:2129–2147
Chiodini G, Todesco M, Caliro S, Del Gaudio C, Macedonio G, Russo M (2003) Magma degassing as a trigger of bradyseismic events: the case of Phlegrean Fields (Italy). Geophys Res Lett 30:1434. doi:10.1029/2002GL016790
Chiodini G, Granieri D, Avino R, Caliro S, Costa A, Werner C (2005) Carbon dioxide diffuse degassing and estimation of heat release from volcanic and hydrothermal systems. J Geophys Res 110:B08204. doi:10.1029/2004JB003542
Chiodini G, Caliro S, Cardellini C, Avino R, Granieri D, Schmidt A (2008) Carbon isotopic composition of soil CO2 efflux, a powerful method to discriminate different sources feeding soil CO2 degassing in volcanic-hydrothermal areas. Earth Planet Sci Lett 274:372–379
Cioni R, Santacroce R, Sbrana A (1999) Pyroclastic deposits as a guide for reconstructing the multi-stage evolution of the Somma-Vesuvius caldera. Bull Volcanol 61:207–222
De Natale G, Troise C, Pingue F, Mastrolorenzo G, Pappalardo L, Battaglia M, Boschi E (2006) The Campi Flegrei caldera: Unrest mechanisms and hazards. In: Troise C, De Natale G, Kilburn CRJ (eds) Mechanisms of activity and unrest at large calderas. Geol Soc London Spec Pub 269:25–45
De Vivo B, Rolandi G, Gans PB, Calvert A, Bohrson WA, Spera FJ, Belkin HE (2001) New constraints on the pyroclastic eruptive history of the Campanian Volcanic Plain (Italy). Mineral Petrol 73:47–65
Deino AL, Orsi G, De Vita S, Piochi M (2004) The age of the Neapolitan Yellow Tuff caldera forming eruption (Campi Flegrei caldera Italy) assessed by 40Ar/39Ar dating method. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 133:157–170
Deutsch CV, Journel AG (1998) GSLIB: geostatistical software library and users guide. Oxford Univ Press, New York
Di Renzo V, Di Vito MA, Arienzo I, Civetta L, D’Antonio M, Giordano F, Orsi G, Tonarini S (2007) Magmatic history of Somma-Vesuvius on the basis of new geochemical and isotopic data from a deep borehole (Camaldoli della Torre). J Petrol 48:753–784
Di Vito MA, Lirer L, Mastrolorenzo G, Rolandi G (1987) The 1538 Monte Nuovo eruption (Campi Flegrei, Italy). Bull Volcanol 49:608–615
Frondini F, Chiodini G, Caliro S, Cardellini C, Granieri D, Ventura G (2004) Diffuse CO2 degassing at Vesuvio, Italy. Bull Volcanol 66:642–651. doi:10.1007/s00445-004-0346-x
Garside MJ (1971) Best subset search. Appl Stat 20:112–115
Gilbert RO (1987) Statistical methods for environmental pollution monitoring. Van Nostrand-Reinhold, New York
Granieri D, Chiodini G, Marzocchi W, Avino R (2003) Continuous monitoring of CO2 soil diffuse degassing at Phlegraean Fields (Italy): influence of environmental and volcanic parameters. Earth Planet Sci Lett 212:167–179
Orsi G, Di Vito MA, de Vita S (1996) The restless, resurgent Campi Flegrei Nested Caldera (Italy): constraints on its evolution and configuration. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 74:179–214
Rogie JD, Kerrick DM, Sorey ML, Chiodini G, Galloway DL (2001) Dynamic of carbon dioxide emission at Mammoth Mountain, California. Earth Planet Sci Lett 188:535–541
Rosi M, Sbrana A (eds) (1987) Phlegraean fields. Quaderni de “La Ricerca Scientifica” 114(9) CNR, Roma
Saccorotti G, Bianco F, Castellano M, Del Pezzo E (2001) The July-August 2000 seismic swarms at Campi Flegrei volcanic complex, Italy. Geophys Res Lett 28:2525–2528
Salazar JML, Hernandez PA, Perez NM, Melian G, Alvarez J, Notsu K (2001) Diffuse emission of carbon dioxide from Cerro Negro volcano, Nicaragua, Central America. Geophys Res Lett 28:4275–4278
Santacroce R (ed) (1987) Somma-Vesuvius. Quaderni de “La Ricerca Scientifica” 114(8) CNR, Roma
Santacroce R, Cioni R, Marianelli P, Sbrana A (2005) Understanding Vesuvius and preparing for its next eruption. In: Balmuth MS, Chester DK, Johnston PA (eds) Cultural responses to the volcanic landscape; the Mediterranean and beyond. Archaeological Institute of America, pp 27–55
Todesco M, Chiodini G, Macedonio G (2003) Monitoring and modelling hydrothermal fluid emission at La Solfatara (Phlegrean Fields, Italy). An interdisciplinary approach to the study of diffuse degassing. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 125:57–79
Troise C, De Natale G, Pingue F, Obrizzo F, De Martino P, Tammaro U, Boschi E (2007) Renewed ground uplift at Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy): new insight on magmatic processes and forecast. Geophys Res Lett 34:L03301. doi:10.1029/2006GL028545
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank C. Werner and J.P. Toutain for their helpful criticism, corrections and suggestions, which greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: P. Delmelle
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
445_2009_304_MOESM1_ESM.txt
Supplementary Material 1. 7030_meteo_station.txt; Data relative to automatic meteorological station (7030) at Vesuvio crater. 5 columns: Date (dd/mm/yy); Tair Ta (°C); Air Relative Humidity Ha (%); Atmospheric Pressure Pa (mbar); Rainfall Rain (mm). (TXT 16 kb)
445_2009_304_MOESM2_ESM.txt
Supplementary Material 2. FCO2_Solfatara_array.txt; Data relative to CO2 soil flux at the array of Solfatara. 72 columns: Date (dd/mm/yyyy) and 71 fixed points (from #1 to #73, skipping #53 and #54); unit for CO2 flux is g m-2-d-1 (grams per square meter per day). (TXT 34 kb)
445_2009_304_MOESM3_ESM.txt
Supplementary Material 3. FCO2_Vesuvio_array.txt; Data relative to CO2 soil flux at the array of Vesuvio. 16 columns: Date (dd/mm/yyyy) and 15 fixed points (from #1 to #15); unit for CO2 flux is g m-2-d-1 (grams per square meter per day). (TXT 8 kb)
445_2009_304_MOESM4_ESM.txt
Supplementary Material 4. FLXOV1_station.txt; Data relative to automatic CO2 soil flux station (FLXOV1) at Solfatara 7 columns: Date (dd/mm/yy); CO2 soil flux FCO2 (g m-2 d-1); Air Relative Humidity Ha (%); Air temperature Ta (°C);Atmospheric Pressure Pa (mbar); Soil Humidity Hs(%); Wind Speed Vw (m/s). (TXT 551 kb)
445_2009_304_MOESM5_ESM.txt
Supplementary Material 5. FLXOV4_station.txt; Data relative to automatic CO2 soil flux station (FLXOV4) at Vesuvio 2 columns: Date (dd/mm/yy); CO2 soil flux FCO2 (g m-2 d-1). (TXT 16 kb)
445_2009_304_MOESM6_ESM.txt
Supplementary Material 6. Ts_Solfatara_array.txt; Data relative to soil temperature at the array of Solfatara. 72 columns: Date (dd/mm/yyyy) and 71 fixed points (from #1 to #73, skipping #53 and #54); unit for soil temperature is °C. (TXT 35 kb)
445_2009_304_MOESM7_ESM.txt
Supplementary Material 7. Ts_Vesuvio_array.txt; Data relative to soil temperature at the array of Vesuvio. 16 columns: Date (dd/mm/yyyy) and 15 fixed points (from #1 to #15); unit for soil temperature is °C. (TXT 9 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Granieri, D., Avino, R. & Chiodini, G. Carbon dioxide diffuse emission from the soil: ten years of observations at Vesuvio and Campi Flegrei (Pozzuoli), and linkages with volcanic activity. Bull Volcanol 72, 103–118 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-009-0304-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-009-0304-8