Abstract
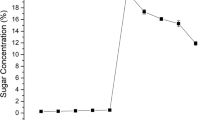
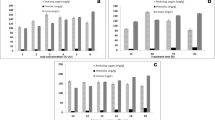
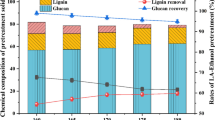
Rice straw is a lignocellulosic biomass that constitutes a renewable organic substance and alternative source of energy; however, its structure confounds the liberation of monosaccharides. Pretreating rice straw using a TiO2/UV system facilitated its hydrolysis with Accellerase 1000™, suggesting that hydroxyl radicals (OH·) from the TiO2/UV system could degrade lignin and carbohydrates. TiO2/UV pretreatment was an essential step for conversion of hemicellulose to xylose; optimal conditions for this conversion were a TiO2 concentration of 0.1% (w/v) and an irradiation time of 2 h with a UV-C lamp at 254 nm. After enzymatic hydrolysis, the sugar yields from rice straw pretreated with these parameters were 59.8 ± 0.7% of the theoretical for glucose (339 ± 13 mg/g rice straw) and 50.3 ± 2.8% for xylose (64 ± 3 mg/g rice straw). The fermentation of enzymatic hydrolysates containing 10.5 g glucose/L and 3.2 g xylose/L with Pichia stipitis produced 3.9 g ethanol/L with a corresponding yield of 0.39 g/g rice straw. The maximum possible ethanol conversion rate is 76.47%. TiO2/UV pretreatment can be performed at room temperature and atmospheric pressure and demonstrates potential in large-scale production of fermentable sugars.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saha BC (2003) Hemicellulose bioconversion. J Ind Microbiol Biot 30:279–291
Jorgensen H, Kristensen JB, Felby C (2007) Enzymatic conversion of lignocellulose into fermentable sugars: challenges and opportunities. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 1:119–134
Um BH, Karim M, Henk L (2003) Effect of sulfuric and phosphoric acid pretreatments on enzymatic hydrolysis of corn stover. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 105–108:115–125
Ballesteros I, Negro MJ, Oliva JM, Cabanas A, Manzanares P, Ballesteros M (2006) Ethanol production from steam-explosion pretreated wheat straw. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 129–132:496–508
Nguyen MT, Choi SP, Lee J, Lee JH, Sim SJ (2009) Hydrothermal acid pretreatment of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii biomass for ethanol production. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:161–166
Xu J, Thomsen MH, Thomsen AB (2009) Pretreatment on corn stover with low concentration of formic acid. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:845–850
Kim TH, Lee YY (2006) Fractionation of corn stover by hot-water and aqueous ammonia treatment. Bioresour Technol 97:224–232
Tanriseven A, Robyt JF (1993) Interpretation of dextransucrase inhibition at high sucrose concentrations. Carbohydr Res 245:97–104
Lu Y, Yang B, Gregg D, Saddler JN, Mansfield SD (2002) Cellulase adsorption and an evaluation of enzyme recycle during hydrolysis of steam-exploded softwood residues. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 98–100:641–654
Liu CG, Wyman CE (2005) Partial flow of compressed-hot water through corn stover to enhance hemicellulose sugar recovery and enzymatic digestibility of cellulose. Bioresour Technol 96:1978–1985
Karimi K, Emtiazi G, Taherzadeh MJ (2006) Ethanol production from dilute-acid pretreated rice straw by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation with Mucor indicus, Rhizopus oryzae, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Tech 40:138–144
Rabelo SC, Maciel R, Costa AC (2008) A comparison between lime and alkaline hydrogen peroxide pretreatments of sugarcane bagasse for ethanol production. Appl Biochem Biotech 148:45–58
Bjerre AB, Olesen AB, Fernqvist T, Ploger A, Schmidt AS (1996) Pretreatment of wheat straw using combined wet oxidation and alkaline hydrolysis resulting in convertible cellulose and hemicellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:568–577
Gollapalli LE, Dale BE, Rivers DM (2002) Predicting digestibility of ammonia fiber explosion (AFEX)-treated rice straw. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 98–100:23–35
Lee YJ, Chung CH, Day DF (2009) Sugarcane bagasse oxidation using a combination of hypochlorite and peroxide. Bioresour Technol 100:935–941
Mosier N, Wyman CE, Dale BE, Elander RT, Lee YY, Holtzapple M, Ladisch MR (2005) Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 96:673–686
Wyman CE, Dale BE, Elander RT, Holtzapple M, Ladisch MR, Lee YY (2005) Coordinated development of leading biomass pretreatment technologies. Bioresour Technol 96:1959–1966
Chen SF, Lie YZ (1996) Study on the photocatalytic degradation of glyphosate by TiO2 photocatalyst. Chemosphere 67:1010–1017
Fox MA, Dulay MT (1993) Heterogeneous photocatalysis. Chemosphere 67:1010–1017
Gierer J (2000) The interplay between oxygen-derived radical species in the delignification during oxygen and hydrogen peroxide bleaching. In: Scultz TP (ed) Lignin, properties and materials. American Chemical Society, Washington, USA (Chapter 21)
Ruiz R, Ehrman T (1996) Chemical analysis and testing task: LAP-002 (Determination of carbohydrates in biomass by high performance liquid chromatography). National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, USA
Templeton D, Ehrman T (1995) Chemical analysis and testing task: LAP-003 (Determination of acid-insoluble lignin in biomass). National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO. USA
Kang HK, Oh JS, Kim D (2009) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of the glucansucrase DSRWC from Weissella cibaria synthesizing a alpha(1→6) glucan. FEMS Microbiol Lett 292:33–41
Lee JH, Kim D, Baek JS, Park KH, Han NS, Robyt JF (1998) Modification of starch using dextransucrase and characterization of the modified starch. Kor J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 26:143–150
Brown L, Torget R (1996) Chemical analysis and testing task: LAP-009 (Enzymatic Saccharification of Lignocellulosic Biomass). National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, USA
Ma H, Liu WW, Chen X, Wu YJ, Yu ZL (2009) Enhanced enzymatic saccharification of rice straw by microwave pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 100:1279–1284
Hu ZH, Liu SY, Yue ZB, Yan LF, Yang MT, Yu HQ (2008) Micro-scale analysis of in vitro anaerobic degradation of lignocellulosic wastes by rumen microorganisms. Environ Sci Technol 42:276–281
Hideno A, Inoue H, Tsukahara K, Fujimoto S, Minowa T, Inoue S, Endo T, Sawayama S (2009) Wet disk milling pretreatment without sulfuric acid for enzymatic hydrolysis of rice straw. Bioresour Technol 100:2706–2711
Jeya M, Zhang YW, Kim IW, Lee JK (2009) Enhanced saccharification of alkali-treated rice straw by cellulase from Trametes hirsuta and statistical optimization of hydrolysis conditions by RSM. Bioresour Technol 100:5155–5161
Huang CF, Lin TH, Guo GL, Hwang WS (2009) Enhanced ethanol production by fermentation of rice straw hydrolysate without detoxification using a newly adapted strain of Pichia stipitis. Bioresour Technol 100:3914–3920
Zhong C, Lau MW, Balan V, Dale BE, Yuan YJ (2009) Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation from AFEX-treated rice straw. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:667–676
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Priority Research Centers Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2010-0029626).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, HK., Kim, D. Efficient bioconversion of rice straw to ethanol with TiO2/UV pretreatment. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35, 43–48 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0589-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0589-9