Abstract
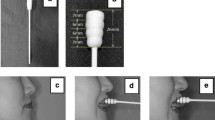
The tongue plays important roles in mastication, swallowing, and speech, but its sensorimotor function might be affected by endotracheal intubation. The objective of this pilot study was to describe disturbances in the sensorimotor functions of the tongue over 14 days following oral endotracheal extubation. We examined 30 post-extubated patients who had prolonged (≥48 h) oral endotracheal intubation from six medical intensive care units. Another 36 patients were recruited and examined from dental and geriatric outpatient clinics served as a comparison group. Tongue strength was measured by the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument. Sensory disturbance of the tongue was measured by evaluating light touch sensation, oral stereognosis, and two-point discrimination with standardized protocols. Measurements were taken at three time points (within 48 h, and 7 and 14 days post-extubation) for patients with oral intubation but only once for the comparison group. The results show that independent of age, gender, tobacco used, and comorbidities, tongue strength was lower and its sensory functions were more impaired in patients who had oral intubation than in the comparison group. Sensory disturbances of the tongue gradually recovered, taking 14 days to be comparable with the comparison group, while weakness of the tongue persisted. In conclusion, patients with oral endotracheal intubation had weakness and somatosensory disturbances of the tongue lasting at least 14 days from extubation but whether is caused by intubation and whether is contributed to postextubation dysphagia should be further investigated.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calhoun KH, Gibson B, Hartley L, Minton J, Hokanson JA. Age-related changes in oral sensation. Laryngoscope. 1992;102(2):109–16.
Youmans S, Stierwalt JAG. Measures of tongue function related to normal swallowing. Dysphagia. 2006;21(2):102–11.
Goldsmith T. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders following endotracheal intubation and tracheostomy. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 2000;38(3):219–42.
Gutmann L, Blumenthal D, Gutmann L, Schochet SS. Acute type II myofiber atrophy in critical illness. Neurology. 1996;46(3):819–21.
Stierwalt JA, Youmans SR. Tongue measures in individuals with normal and impaired swallowing. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2007;16(2):148–56.
Adams V, Mathisen B, Baines S, Lazarus C, Callister R. Reliability of measurements of tongue and hand strength and endurance using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument with healthy adults. Dysphagia. 2014;29(1):83–95.
Solomon NP, Robin DA, Luschei ES. Strength, endurance, and stability of the tongue and hand in Parkinson disease. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2000;43(1):256–67.
Lazarus C, Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Helenowski IB, Vonesh EF, Maccracken E, Mittal BB, Vokes EE, Haraf DJ. Effects of radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy on tongue strength and swallowing in patients with oral cancer. Head Neck. 2007;29(7):632–7.
Lazarus CL, Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Larson CR, Mittal BB, Pierce M. Swallowing and tongue function following treatment for oral and oropharyngeal cancer. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2000;43(4):1011–23.
Palmer PM, Neel AT, Sprouls G, Morrison L. Swallow characteristics in patients with oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2010;53(6):1567–78.
SolomonNP Clark HM, Makashay MJ, Newman LA. Assessment of orofacial strength in patients with dysarthria. J Med Speech Lang Pathol. 2008;16(4):251–8.
Boliek CA, Rieger JM, Li SY, Mohamed Z, Kickham J, Amundsen K. Establishing a reliable protocol to measure tongue sensation. J Oral Rehabil. 2007;34(6):433–41.
Jacobs R, Wu CH, Van Loven K, Desnyder M, Kolenaar B, Van Steenberghed D. Methodology of oral sensory tests. J Oral Rehabil. 2002;29(8):720–30.
O’Day C, Frank E, Montgomery A, Nichols M, McDade H. Repeated tongue and hand strength measurements in normal adults and individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Int J Orofacial Myol. 2005;31:15.
Stierwalt JA, Youmans SR. Tongue measures in individuals with normal and impaired swallowing. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2007;16(4):148–56.
Vriens JP, Acosta R, Soutar DS, Webster MH. Recovery of sensation in the radial forearm free flap in oral reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996;98(4):649–56.
Kuriakose MA, Loree TR, Spies A, Meyers S, Hicks WL Jr. Sensate radial forearm free flaps in tongue reconstruction. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;127(12):1463–6.
Pow EH, Leung KC, McMillan AS, Wong MC, Li LS, Ho SL. Oral stereognosis in stroke and Parkinson’s disease: a comparison of partially dentate and edentulous individuals. Clin Oral Invest. 2001;5(2):112–7.
Bakke M, Larsen SL, Lautrup C, Karlsborg M. Orofacial function and oral health in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Oral Sci. 2011;119(1):27–32.
Burkhead LM. Applications of exercise science in dysphagia rehabilitation: perspectives on swallowing and swallowing disorders. Dysphagia. 2009;18(2):43–8.
Robbins J, Kays SA, Gangnon RE, Hind JA, Hewitt AL, Gentry LR, Taylor AJ. The effects of lingual exercise in stroke patients with dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88(2):150–8.
Robbins J, Gangnon RE, Theis SM, Kays SA, Hewitt AL, Hind JA. The effects of lingual exercise on swallowing in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53(9):1483–9.
Clark HM, O’Brien K, Calleja A, Corrie SN. Effects of directional exercise on lingual strength. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2009;52(4):1034–47.
Lazarus CL, Husaini H, Falciglia D, DeLacure M, Branski RC, Kraus D, Lee N, Ho M, Ganz C, Smith B, Sanfilippo N. Effects of exercise on swallowing and tongue strength in patients with oral and oropharyngeal cancer treated with primary radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;43(8):523–30.
Robbins J, Levine R, Wood J, Roecker EB, Luschei E. Age effects on lingual pressure generation as a risk factor for dysphagia. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1995;50(5):M257–62.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant # NSC-101-2314-B-002-131-MY3).
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Hsiao, TY., Ku, SC. et al. Tongue Weakness and Somatosensory Disturbance Following Oral Endotracheal Extubation. Dysphagia 30, 188–195 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-014-9594-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-014-9594-x