Abstract
Background
A new endoluminal fundoplication (ELF) technique performed transorally using the EsophyX™ device was evaluated for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in a prospective, feasibility clinical trial.
Methods
Nineteen patients were enrolled into the study. Inclusion criteria were chronic and symptomatic GERD, proton pump inhibitor (PPI) dependence, and the absence of esophageal motility disorder. Two patients were excluded due to esophageal stricture and a 6 cm hiatal hernia. The median duration of GERD symptoms and PPI use in the remaining 17 patients was 10 and 6 years, respectively. The ELF procedure was designed to partially reconstruct the antireflux barrier through the creation of a valve at the gastroesophageal junction.
Results
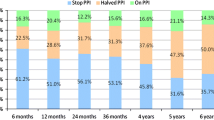
The ELF-created valves had a median length of 4 cm (range 3–5 cm) and circumference of 210° (180–270°). Adherence of the valves to the endoscope was tight (n = 14) or moderate (n = 3). Hiatal hernias present in 13 patients (76%) were all reduced. Adverse events were limited to mild or moderate pharyngeal irritation and epigastric pain, which resolved spontaneously. After 12 months, the ELF valves (n = 16) had a median length of 3 cm (1–4 cm) and a circumference of 200° (150–210°). Eighty-one percent of valves retained their tightness. The hiatal hernias present at the baseline remained reduced in 62% of patients. The median GERD-HRQL scores improved by 67% (17–6), and nine patients (53%) improved their scores by ≥50%. Eighty-two percent of patients were satisfied with the outcome of the procedure, 82% remained completely off PPIs, and 63% had normal pH.
Conclusion
The study demonstrated technical feasibility and safety of the ELF procedure using the EsophyX™ device. The study also demonstrated maintenance of the anatomical integrity of the ELF valves for 12 months and provided preliminary data on ELF efficacy in reducing the symptoms and medication use associated with GERD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fass R, Ofman JJ (2002) Gastroesophageal reflux disease–should we adopt a new conceptual framework? Am J Gastroenterol 97:1901–1909
Howard PJ, Heading RC (1992) Epidemiology of gastro-esophageal reflux disease. World J Surg 16:288–293
Moayyedi P, Talley NJ (2006) Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Lancet 367:2086–2100
Pace F, Bollani S, Molteni P, Bianchi Porro G (2004) Natural history of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease without oesophagitis (NERD)—a reappraisal 10 years on. Dig Liver Dis 36:111–115
Koop H (2006) Medical therapy of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. In: Granderath FA, Kamolz T, Pointner R (eds). Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Principles of Disease, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Springer, Wien, NewYork, pp 103–111
DeMeester TR, Bonavina L, Albertucci M (1986) Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Evaluation of primary repair in 100 consecutive patients. Ann Surg 204:9–20
Cadiere GB, Houben JJ, Bruyns J, Himpens J, Panzer JM, Gelin M (1994) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: Technique and preliminary results. Br J Surg 81:400–403
Hinder RA, Filipi CJ, Wetscher G, Neary P, DeMeester TR, Perdikis G (1994) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is an effective treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg 220:472–481
Weerts JM, Dallemagne B, Hamoir E, Demarche M, Markiewicz S, Jehaes C, Lombard R, Demoulin JC, Etienne M, Ferron PE, et al. (1993) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: detailed analysis of 132 patients. Surg Laparosc Endosc 3:359–364
Dallemagne B, Weerts J, Markiewicz S, Dewandre JM, Wahlen C, Monami B, Jehaes C (2006) Clinical results of laparoscopic fundoplication at ten years after surgery. Surg Endosc 20:159–165
Peters JH, DeMeester TR, Crookes P, Oberg S, de Vos Shoop M, Hagen JA, Bremner CG (1998) The treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: Prospective evaluation of 100 patients with “typical” symptoms. Ann Surg 228:40–50
Donahue PE, Carvalho PJ, Davis PE, Shen YJ, Miidla I, Bombeck CT, Nyhus LM (1990) Endoscopic sclerosis of the gastric cardia for prevention of experimental gastroesophageal reflux. Gastrointest Endosc 36:253–256
Arts J, Tack J, Galmiche JP (2004) Recent advances in clinical practice: Endoscopic antireflux procedures. Gut 53:1207–1214
Hogan WJ (2006) Clinical trials evaluating endoscopic GERD treatments. Is it time for a moratorium on the clinical use of these procedures? Am J Gastroenterol 101:437–439
Iqbal A, Salinas V, Filipi CJ (2006) Endoscopic therapies of gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Gastroenterol 12:2641–2655
Cipolletta L, Rotondano G, Dughera L, Repici A, Bianco MA, De Angelis C, Vingiani AM, Battaglia E (2005) Delivery of radiofrequency energy to the gastroesophageal junction (Stretta procedure) for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 19:849–853
Corley DA, Katz P, Wo JM, Stefan A, Patti M, Rothstein R, Edmundowicz S, Kline M, Mason R, Wolfe MM (2003) Improvement of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms after radiofrequency energy: A randomized, sham-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 125:668–676
Houston H, Khaitan L, Holzman M, Richards WO (2003) First year experience of patients undergoing the Stretta procedure. Surg Endosc 17:401–404
Lutfi RE, Torquati A, Kaiser J, Holzman M, Richards WO (2005) Three years’ experience with the Stretta procedure: Did it really make a difference? Surg Endosc 19:289–295
Triadafilopoulos G, DiBaise JK, Nostrant TT, Stollman NH, Anderson PK, Wolfe MM, Rothstein RI, Wo JM, Corley DA, Patti MG, Antignano LV, Goff JS, Edmundowicz SA, Castell DO, Rabine JC, Kim MS, Utley DS (2002) The Stretta procedure for the treatment of GERD: 6 and 12 month follow-up of the U.S. open label trial. Gastrointest Endosc 55:149–156
Wolfsen HC, Richards WO (2002) The Stretta procedure for the treatment of GERD: a registry of 558 patients. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 12:395–402
Cohen LB, Johnson DA, Ganz RA, Aisenberg J, Deviere J, Foley TR, Haber GB, Peters JH, Lehman GA (2005) Enteryx implantation for GERD: expanded multicenter trial results and interim postapproval follow-up to 24 months. Gastrointest Endosc 61:650–658
Deviere J, Costamagna G, Neuhaus H, Voderholzer W, Louis H, Tringali A, Marchese M, Fiedler T, Darb-Esfahani P, Schumacher B (2005) Nonresorbable copolymer implantation for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a randomized sham-controlled multicenter trial. Gastroenterology 128:532–540
Fockens P, Bruno MJ, Gabbrielli A, Odegaard S, Hatlebakk J, Allescher HD, Rosch T, Rhodes M, Bastid C, Rey J, Boyer J, Muehldorffer S, van den Hombergh U, Costamagna G (2004) Endoscopic augmentation of the lower esophageal sphincter for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: Multicenter study of the Gatekeeper Reflux Repair System. Endoscopy 36:682–689
Johnson DA, Ganz R, Aisenberg J, Cohen LB, Deviere J, Foley TR, Haber GB, Peters JH, Lehman GA (2003) Endoscopic, deep mural implantation of Enteryx for the treatment of GERD: 6-month follow-up of a multicenter trial. Am J Gastroenterol 98:250–258
Falk GW, Fennerty MB, Rothstein RI (2006) AGA Institute medical position statement on the use of endoscopic therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 131:1313–1314
Annese V, Caletti G, Cipolletta L, Costamagna G, D’Onofrio V, Leandro G, Koch M, Pace F, Penagini R, Repici A, Ricci E, Vigneri S, Zaninotto G (2005) Endoscopic treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Endoscopy 37:470–478
Falk GW, Fennerty MB, Rothstein RI (2006) AGA Institute technical review on the use of endoscopic therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 131:1315–1336
Pleskow D, Rothstein R, Lo S, Hawes R, Kozarek R, Haber G, Gostout C, Lembo A (2004) Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of GERD: A multicenter trial. Gastrointest Endosc 59:163–171
Pleskow D, Rothstein R, Lo S, Hawes R, Kozarek R, Haber G, Gostout C, Lembo A (2005) Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of GERD: 12-month follow-up for the North American open-label trial. Gastrointest Endosc 61:643–649
Rothstein R, Filipi C, Caca K, Pruitt R, Mergener K, Torquati A, Haber G, Chen Y, Chang K, Wong D, Deviere J, Pleskow D, Lightdale C, Ades A, Kozarek R, Richards W, Lembo A (2006) Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a randomized, sham-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 131:704–712
Cadiere GB, Rajan A, Rqibate M, Germay O, Dapri G, Himpens J, Gawlicka AK (2006) Endoluminal fundoplication (ELF) - evolution of EsophyX, a new surgical device for transoral surgery. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 15:348–355
Chandrasoma PT, DeMeester TR (2006) The Past, Present, and Future of Columnar-Lined (Barrett) Esophagus (eds). GERD: Reflux to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Boston, Elsevier, pp 11–39
Velanovich V, Vallance SR, Gusz JR, Tapia FV, Harkabus MA (1996) Quality of life scale for gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 183:217–224
Hill LD, Kozarek RA, Kraemer SJ, Aye RW, Mercer CD, Low DE, Pope CE 2nd (1996) The gastroesophageal flap valve: In vitro and in vivo observations. Gastrointest Endosc 44:541–547
Jobe BA, Kahrilas PJ, Vernon AH, Sandone C, Gopal DV, Swanstrom LL, Aye RW, Hill LD (2004) Endoscopic appraisal of the gastroesophageal valve after antireflux surgery. Am J Gastroenterol 99:233–243
Thor KB, Hill LD, Mercer DD, Kozarek RD (1987) Reappraisal of the flap valve mechanism in the gastroesophageal junction. A study of a new valvuloplasty procedure in cadavers. Acta Chir Scand 153:25–28
Pandolfino JE, Richter JE, Ours T, Guardino JM, Chapman J, Kahrilas PJ (2003) Ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring using a wireless system. Am J Gastroenterol 98:740–749
Tseng D, Rizvi AZ, Fennerty MB, Jobe BA, Diggs BS, Sheppard BC, Gross SC, Swanstrom LL, White NB, Aye RW, Hunter JG (2005) Forty-eight-hour pH monitoring increases sensitivity in detecting abnormal esophageal acid exposure. J Gastrointest Surg 9:1043–1051
Tutuian R, Castell DO (2006) Diagnostic procedures in GERD: Principles and values of esophageal manometry and pH-monitoring In: Granderath FA, Kamolz T, Pointner R (eds). Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Principles of Disease, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Springer-Verlag, Wien, New York, pp 121–138
Cadiere GB, Rajan A, Dapri G, Rqibate M, Germay O, Himpens J (2006) Nouvelle technique du traitement par voie endoscopique du reflux gastro-oesophagien: La fundoplicature endoluminale. J Coelio-Chirurgie 57:14–19
Disclosure
The study was sponsored by EndoGastric Solutions, Inc., Redmond, WA, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cadière, G.B., Rajan, A., Germay, O. et al. Endoluminal fundoplication by a transoral device for the treatment of GERD: A feasibility study. Surg Endosc 22, 333–342 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9618-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9618-9