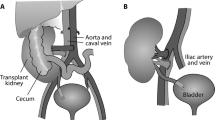
Abstract
En bloc renal transplantation (EBT) from infant donors is an option for children with end-stage renal failure. Owing to potential complications, EBT is not performed in all paediatric nephrology centres. We evaluated the perioperative and long-term course of five children undergoing EBT. Primary diagnosis was atypical (diarrhoea-negative) haemolytic uraemic syndrome (n=2), interstitial nephropathy (two siblings) and branchio-oto-renal syndrome (n=1). Recipient and donor ages ranged between 5.9 and 11.1 years and 0.3 and 2.5 years, respectively. Follow-up time after EBT was 2.1–13.2 years. Perioperative complications included (1) a renal artery thrombosis, with immediate intraoperative reconstruction and primary non-functioning of the graft, with recovery after 10 days, and (2) a vesico-ureteric obstruction, successfully managed with temporary insertion of a JJ-catheter. All grafts had good long-term function. Absolute glomerular filtration rate (GFR; millilitres/minute) increased in all patients, whereas relative GFR (millilitres/minute per 1.73 m2 body surface area) remained stable during the follow-up period in all but one. Kidney size increased significantly, with maximal growth during the first year after EBT; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed normal structure and vasculature. EBT is a safe and effective option for young children with end-stage renal failure. Absolute GFR and graft size increase and adapt to the children’s growing body mass.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Creagh TA, McLean PA, Spencer S, Cunningham P, Donovan MG, Walshe JJ, Murphy DM (1991) Transplantation of kidneys from pediatric cadaver donors to adult recipients. J Urol 146:951–952
Marques M, Prats D, Sanchez-Fructuoso A, Naranjo P, Herrero JA, Contreras E, Barrientos A (2001) Incidence of renal artery stenosis in pediatric en bloc and adult single kidney transplants. Transplantation 71:164–166
Bretan PN, Friese C, Goldstein RB, Osorio RW, Tamlanovich S, Amend W, Mathur V, Vincenti F (1997) Immunologic and patient selection strategies for successful utilization of less than 15 kg pediatric donor kidneys—long-term experience with 40 transplants. Transplantation 63:233–237
Ratner LE, Cigarroa FG, Bender JS, Magnuson T, Kraus ES (1997) Transplantation of single and paired pediatric kidneys into adult recipients. J Am Coll Surg 185:437–445
Hobart MG, Modlin CS, Kapoor A, Boparai N, Mastroianni B, Papajcik D, Flechner SM, Goldfarb DA, Fischer R, O’Malley KJ, Novick AC (1998) Transplantation of pediatric en bloc cadaver kidneys into adult recipients. Transplantation 66:1689–1694
Strey C, Grotz W, Mutz C, Pisarski P, Furtwaengler A, Bluemke M, Kirste G (2002) Graft survival and graft function of pediatric en bloc kidneys in paraaortal position. Transplantation 73:1095–1099
Ruff T, Reddy KS, Johnston TD, Waid T, McKeown W, Khan T, Ranjan D, Lucas BA (2002) Transplantation of pediatric en bloc cadaver kidney into adult recipients: a single-center experience. Am Surg 68:857–859
Satterthwaite R, Aswad S, Sunga V, Shidban H, Mendez RG, Bogaard T, Asai P, Khetan U, Magpayo M, Mendez R (1997) Outcome of en bloc and single kidney transplantation from very young cadaveric donors. Transplantation 63:1405–1410
Hiramoto JS, Freise CE, Randall HR, Bretan PN, Tomlanovich S, Stock PG, Hirose R (2002) Successful long-term outcomes using pediatric en bloc kidneys for transplantation. Am J Transplant 2:337–342
Ruder H, Schäfer F, Gretz N, Mohring S, Schärer K (1989) Donor kidneys of infants and very young children are unacceptable for transplantation. Lancet 15:168
Singh A, Stablein D, Tejani A (1997) Risk factors for vascular thrombosis in pediatric renal transplantation: a special report of the North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study. Transplantation 63:1263–1266
Dubourg L, Cochat P, Hadj-Aissa A, Tyden G, Berg UB (2002) Better long-term functional adaptation to the child’s size with pediatric compared to adult kidney donors. Kidney Int 62:1454–1460
Pape L, Offner G, Ehrich J, De Boer J, Persijn G (2004) Renal allograft function in matched pediatric and adult recipient pairs of the same donor. Transplantation 77:1191–1194
Berg UB, Bohlin AB, Tyden G (1997) Influence of donor and recipient ages and sex on graft function after pediatric renal transplantation. Transplantation 64:1424–1428
Bergmeijer JF, Cransberg K, Nijman JM, Molenaar JC, Wolff ED, Provoost AP (1994) Functional adaptation of en bloc-transplanted pediatric kidneys into pediatric recipients. Transplantation 58:623–625
Maranes A, Herrero JA, Marron B, Marques M, Cruceyra A, Portoles J, Prats D, Sanchez-Fructuoso AI, Barrientos A (1998) Functional glomerular reserve in recipients of en bloc pediatric transplant kidneys. Transplantation 65:677–680
Chantler C, Barratt TM (1972) Estimation of glomerular filtration rate from plasma clearance of 51-chromium edetic acid. Arch Dis Child 47:613–617
Prader A, Largo RH, Molinari L, Issler C (1989) Physical growth of Swiss children from birth to 20 years of age. Helvetic Paediatr Acta Suppl 52:1–125
Vester U, Offner G, Hoyer PF, Oldhafer K, Fangmann J, Pichlmayr R, Brodehl J (1998) End-stage renal failure in children younger than 6 years: renal transplantation is the therapy of choice. Eur J Pediatr 157:239–242
Han BK, Babcock DS (1985) Sonographic measurements and appearance of normal kidneys in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol 145:611–616
Nashan B (2004) Renal allograft allocation for children: are we penalizing children to not penalize adults ? Transplantation 77:1145–1146
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laube, G.F., Kellenberger, C.J., Kemper, M.J. et al. Transplantation of infant en bloc kidneys into paediatric recipients. Pediatr Nephrol 21, 408–412 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-2129-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-2129-9