Summary
Background
The aim of this study was to investigate the antioxidant and radioprotective effects of propolis, caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), Nigella sativa oil (NSO), and thymoquinone (TQ) against ionizing radiation-induced cataracts in lens after total cranium irradiation of rats with single dose of 5-Gy cobalt-60 gamma rays.
Methods
A total of 74 Sprague–Dawley rats were divided into 8 groups to test the radioprotective effectiveness of Nigella sativa oil, thymoquine, propolis, or caffeic acid phenethyl ester administered by either orogastric tube or intraperitoneal injection. Appropriate control groups were also studied.
Results
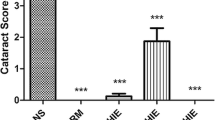
Chylack’s cataract classification was used in the study. At the end of the tenth day, cataracts developed in 80 % of the rats in the radiotherapy group. After irradiation, cataract rate dropped to 20 % in NSO, 30 % in propolis, 40 % in CAPE, and 50 % in TQ groups and was limited to grade 1 and grade 2. Cataract formation was observed the least in NSO group and the most in TQ group. In the irradiated (IR) group, superoxide dismutase activity was lower, while glutathione peroxidase and xanthine oxidase activities and malondialdehyde level were higher compared with the other groups. Total superoxide scavenger activity and nonenzymatic superoxide scavenger activity were not statistically significant in IR group compared with the other groups.
Conclusions
The findings obtained in the study might suggest that propolis, CAPE, NSO, and TQ could prevent cataractogenesis in ionizing radiation-induced cataracts in the lenses of rats, wherein propolis and NSO were found to be more potent.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taysi S, Okumus S, Akyuz M, Uzun N, Aksor A, Demir E, Orkmez M, Tarakcioglu M, Adli M. Zinc administration modulates radiation-induced oxidative injury in lens of rat. Pharmacogn Mag. 2012;8(32):245–9.
Taysi S, Memisogullari R, Koc M, Yazici AT, Aslankurt M, Gumustekin K, Al B, Ozabacigil F, Yilmaz A, Tahsin Ozder H. Melatonin reduces oxidative stress in the rat lens due to radiation-induced oxidative injury. Int J Radiat Biol. 2008;84(10):803–8.
Nair CK, Parida DK, Nomura T. Radioprotectors in radiotherapy. J Radiat Res. 2001;42(1):21–37.
Shirazi A, Haddadi GH, Asadi-Amoli F, Sakhaee S, Ghazi-Khansari M, Avand A. Radioprotective effect of melatonin in reducing oxidative stress in rat lenses. Cell J. 2011;13(2):79–82.
Fang YZ, Yang S, Wu G. Free radicals, antioxidants, and nutrition. Nutrition. 2002;18(10):872–9.
Trikha R, Morse LS, Zawadzki RJ, Werner JS, Park SS. Ten-year follow-up of eyes treated with stereotactic fractionated external beam radiation for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Retina. 2011;31(7):1303–15.
Manikandan R, Thiagarajan R, Beulaja S, Chindhu S, Mariammal K, Sudhandiran G, Arumugam M. Anti-cataractogenic effect of curcumin and aminoguanidine against selenium-induced oxidative stress in the eye lens of Wistar rat pups: an in vitro study using isolated lens. Chem Biol Interact. 2009;181(2):202–9.
Taysi S, Abdulrahman ZK, Okumus S, Demir E, Demir T, Akan M, Saricicek E, Saricicek V, Aksoy A, Tarakcioglu M. The radioprotective effect of Nigella sativa on nitrosative stress in lens tissue in radiation-induced cataract in rat. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 1–6.
Sankaranarayanan C, Pari L. Thymoquinone ameliorates chemical induced oxidative stress and beta-cell damage in experimental hyperglycemic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2011;190(2–3):148–54.
Gali-Muhtasib H, Roessner A, Schneider-Stock R. Thymoquinone: a promising anti-cancer drug from natural sources. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38(8):1249–53.
Ustun K, Taysi S, Sezer U, Demir E, Baysal E, Demir T, Saricicek E, Alkis H, Senyurt SZ, Tarakcioglu M, et al. Radio-protective effects of Nigella sativa oil on oxidative stress in tongue tissue of rats. Oral Dis. 2014;20(1):109–13.
Ahlatci A, Kuzhan A, Taysi S, Demirtas OC, Alkis HE, Tarakcioglu M, Demirci A, Caglayan D, Saricicek E, Cinar K. Radiation-modifying abilities of Nigella sativa and thymoquinone on radiation-induced nitrosative stress in the brain tissue. Phytomedicine. 2014;21(5):740–4.
Akyol S, Ginis Z, Armutcu F, Ozturk G, Yigitoglu MR, Akyol O. The potential usage of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) against chemotherapy-induced and radiotherapy-induced toxicity. Cell Biochem Funct. 2012;30(5):438–43.
Taysi S, Cikman O, Kaya A, Demircan B, Gumustekin K, Yilmaz A, Boyuk A, Keles M, Akyuz M, Turkeli M. Increased oxidant stress and decreased antioxidant status in erythrocytes of rats fed with zinc-deficient diet. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2008;123(1–3):161–7.
Taysi S. Oxidant/antioxidant status in liver tissue of vitamin B6 deficient rats. Clin Nutr. 2005;24(3):385–9.
Merriam GR, Jr., Focht EF. A clinical study of radiation cataracts and the relationship to dose. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1957;77(5):759–85.
Kocer I, Taysi S, Ertekin MV, Karslioglu I, Gepdiremen A, Sezen O, Serifoglu K. The effect of L-carnitine in the prevention of ionizing radiation-induced cataracts: a rat model. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007;245(4):588–94.
Aktan B, Taysi S, Gumustekin K, Bakan N, Sutbeyaz Y. Evaluation of oxidative stress in erythrocytes of guinea pigs with experimental otitis media and effusion. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2003;33(2):232–6.
Chylack LT, Jr., Wolfe JK, Singer DM, Leske MC, Bullimore MA, Bailey IL, Friend J, McCarthy D, Wu SY. The lens opacities classification system III. The longitudinal study of cataract study group. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993;111(6):831–6.
Durak I, Canbolat O, Kacmaz M, Ozgen G, Ozturk HS. Antioxidant interferences in superoxide dismutase activity methods using superoxide radical as substrate. Clin Chem Lab Med. 1998;36(6):407–8.
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y. A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem. 1988;34(3):497–500.
Paglia DE, Valentine WN. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med. 1967;70(1):158–69.
Hashimoto S. A new spectrophotometric assay method of xanthine oxidase in crude tissue homogenate. Anal Biochem. 1974;62(2):426–35.
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K. Reaction of linoleic acid hydroperoxide with thiobarbituric acid. J Lipid Res. 1978;19(8):1053–7.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Yagci R, Aydin B, Erdurmus M, Karadag R, Gurel A, Durmus M, Yigitoglu R. Use of melatonin to prevent selenite-induced cataract formation in rat eyes. Curr Eye Res. 2006;31(10):845–50.
Hosseinimehr SJ. Trends in the development of radioprotective agents. Drug Discov Today. 2007;12(19–20):794–805.
Hu Y, Cao JJ, Liu P, Guo DH, Wang YP, Yin J, Zhu Y, Rahman K. Protective role of tea polyphenols in combination against radiation-induced haematopoietic and biochemical alterations in mice. Phytother Res. 2011;25(12):1761–9.
Vitolo JM, Cotrim AP, Sowers AL, Russo A, Wellner RB, Pillemer SR, Mitchell JB, Baum BJ. The stable nitroxide tempol facilitates salivary gland protection during head and neck irradiation in a mouse model. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(5):1807–12.
Karslioglu I, Ertekin MV, Kocer I, Taysi S, Sezen O, Gepdiremen A, Balci E. Protective role of intramuscularly administered vitamin E on the levels of lipid peroxidation and the activities of antioxidant enzymes in the lens of rats made cataractous with gamma-irradiation. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2004;14(6):478–85.
Okumus S, Taysi S, Orkmez M, Saricicek E, Demir E, Adli M, Al B. The effects of oral Ginkgo biloba supplementation on radiation-induced oxidative injury in the lens of rat. Pharmacogn Mag. 2011;7(26):141–5.
Ertekin MV, Kocer I, Karslioglu I, Taysi S, Gepdiremen A, Sezen O, Balci E, Bakan N. Effects of oral Ginkgo biloba supplementation on cataract formation and oxidative stress occurring in lenses of rats exposed to total cranium radiotherapy. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2004;48(5):499–502.
Shirazi A, Haddadi GH, Asadi-Amoli F, Sakhaee S, Ghazi-Khansari M, Avand A. Radioprotective effect of melatonin in reducing oxidative stress in rat lenses. Cell J. 2011;13(2):79–82.
Diplock AT, Charleux JL, Crozier-Willi G, Kok FJ, Rice-Evans C, Roberfroid M, Stahl W, Vina-Ribes J. Functional food science and defence against reactive oxidative species. Br J Nutr. 1998;80(Suppl. 1):77–112.
Sud’ina GF, Mirzoeva OK, Pushkareva MA, Korshunova GA, Sumbatyan NV, Varfolomeev SD. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester as a lipoxygenase inhibitor with antioxidant properties. FEBS Lett. 1993;329(1–2):21–4.
Chen MF, Wu CT, Chen YJ, Keng PC, Chen WC. Cell killing and radiosensitization by caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) in lung cancer cells. J Radiat Res. 2004;45(2):253–60.
Hehlgans S, Lange I, Eke I, Kammerer B, Cordes N. Human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines are differentially radiosensitised by the honeybee product Propolis. Int J Radiat Biol. 2011;87(3):243–53.
Benkovic V, Knezevic AH, Orsolic N, Basic I, Ramic S, Viculin T, Knezevic F, Kopjar N. Evaluation of radioprotective effects of propolis and its flavonoid constituents: in vitro study on human white blood cells. Phytother Res. 2009;23(8):1159–68.
Buyukokuroglu ME, Taysi S, Polat F, Gocer F. Mechanism of the beneficial effects of dantrolene sodium on ethanol-induced acute gastric mucosal injury in rats. Pharmacol Res. 2002;45(5):421–5.
Woo CC, Kumar AP, Sethi G, Tan KH. Thymoquinone: potential cure for inflammatory disorders and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83(4):443–51.
Karslioglu I, Ertekin MV, Taysi S, Kocer I, Sezen O, Gepdiremen A, Koc M, Bakan N. Radioprotective effects of melatonin on radiation-induced cataract. J Radiat Res. 2005;46(2):277–82.
Koc M, Taysi S, Emin Buyukokuroglu M, Bakan N. The effect of melatonin against oxidative damage during total-body irradiation in rats. Radiat Res. 2003;160(2):251–5.
Taysi S, Okumus S, Ezirmik S, Uzun N, Yilmaz A, Akyuz M, Tekelioglu U, Dirier A, Al B. The protective effects of L-carnitine and vitamin E in rat lenses in irradiation-induced oxidative injury. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2011;20(1):15–21.
Nagi MN, Mansour MA. Protective effect of thymoquinone against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats: a possible mechanism of protection. Pharmacol Res. 2000;41(3):283–9.
Mansour MA, Nagi MN, El-Khatib AS, Al-Bekairi AM. Effects of thymoquinone on antioxidant enzyme activities, lipid peroxidation and DT-diaphorase in different tissues of mice: a possible mechanism of action. Cell Biochem Funct. 2002;20(2):143–51.
Cemek M, Enginar H, Karaca T, Unak P. In vivo radioprotective effects of Nigella sativa L oil and reduced glutathione against irradiation-induced oxidative injury and number of peripheral blood lymphocytes in rats. Photochem Photobiol. 2006;82(6):1691–6.
Acknowledgments
This study has been supported by the Research Foundation of the Gaziantep University, Gaziantep, Turkey.
Conflict of interest
No author has a financial or proprietary interest in any material or method mentioned.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demir, E., Taysi, S., Al, B. et al. The effects of Nigella sativa oil, thymoquinone, propolis, and caffeic acid phenethyl ester on radiation-induced cataract. Wien Klin Wochenschr 128 (Suppl 8), 587–595 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-015-0736-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-015-0736-4