Abstract
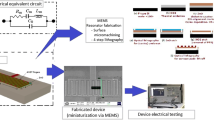
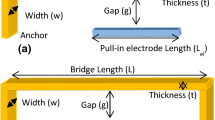
Microelectromechanical system (MEMS) based resonators can be used for filtering and frequency synthesis applications in many subcomponents of radio frequency wireless integrated circuits due to their small size, high level of frequency selectivity, low cost batch fabrication, ease of integration with CMOS circuits. Electroplated nickel is an attractive low cost material for CMOS compatible MEMS due to their low deposition temperatures. Among the different modes of vibration, radial-contour mode resonators are preferred for high frequency applications because they offer higher effective stiffness. Two different types of electroplated nickel based radial-contour bulk-mode circular disk resonator geometries which depend on capacitive actuation and readout technique is presented in this work. Material, mechanical and electrical characterizations were performed on these structures to show their functionality.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brand S, Czurratis P, Hoffrogge P, Petzold M (2010) Automated inspection and classification of flip–chip contacts using scanning acoustic microscopy. Microelectron Reliab 50(9–11):1469–1473
Chandorkar SA, Agarwal M, Melamud R, Candler RN, Goodson KE, Kenny TW (2008) Limits of quality factor in bulk-mode micromechanical resonators. In: Proceedings of the 21st IEEE international conference on microelectromechanical systems, Tucson, Arizona, pp 74–77
Clark JR, Hsu WT, Abdelmoneum MA, Nguyen CTC (2005) High-Q UHF micromechanical radial-contour mode disk resonators. J Microelectromech Syst 14(6):1298–1310
Cowen A, Mahadevan R, Johnson S, Hardy B (2009) MetalMUMPs design handbook, revision 3.0. MEMSCAP Inc.
Duwel A, Candler RN, Kenny TW, Varghese M (2006) Engineering MEMS resonators with low thermoelastic damping. J Microelectromech Syst 15(6):1437–1445
Hao Z, Ayazi F (2007) Support loss in the radial bulk-mode vibrations of center-supported micromechanical disk resonators. Sens Actuators A 134:582–593
Harris RW (1970) Electromechanical analogies in acoustics. Appl Acoust 3:265–281
Hsu WT, Clark JR, Nguyen CTC (2000) Mechanically temperature compensated flexural-mode micromechanical resonators. In: Technical digest of IEEE international electron devices meeting, San Francisco, pp 399–402
Huang WL, Ren Z, Lin YW, Chen HY, Lahann J, Nguyen CTC (2008) Fully monolithic CMOS nickel micromechanical resonator oscillator. In: Proceedings of the 21st IEEE international conference on microelectromechanical systems, Tucson, Arizona, pp 10–13
Lee JEY, Seshia AA (2009) 5.4-MHz single-crystal silicon wine glass mode disk resonator with quality factor of 2 million. Sens Actuators A 156:28–35
Lifshitz R, Roukes ML (2000) Thermoelastic damping in micro- and nanomechanical systems. Phys Rev B 61(8):5600–5609
Mohanty P, Harrington DA, Ekinci KL, Yang YT, Murphy MJ, Roukes ML (2002) Intrinsic dissipation in high-frequency micromechanical resonators. Phys Rev B 66:085416 (1–15)
Onoe M (1956) Contour vibrations of isotropic circular plates. J Acoust Soc Am 28(6):1158–1162
Senturia SD (2001) Microsystem design. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston
Wang J, Ren Z, Nguyen CTC (2004) 1.156-GHz self-aligned vibrating micromechanical disk resonator. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 51:1607–1628
Zuo C, Van der Spiegel J, Piazza G (2010) 1.05-GHz CMOS oscillator based on lateral-field-excited piezoelectric AlN contour-mode MEMS resonators. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 57:82–87
Acknowledgments
The work presented here is supported by the National Programme on Micro and Smart Systems (NPMASS), Govt. of India. The authors would like to express their deep gratitude to Prof. Rudra Pratap and Prof. Navakanta Bhat for extending the infrastructure of characterization at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhuri, R.R., Bhattacharyya, T.K. Electroplated nickel based micro-machined disk resonators for high frequency applications. Microsyst Technol 19, 525–535 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1645-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1645-3