Abstract
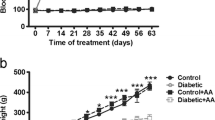
Due to the value of aging and its effect on body organs, it is necessary to study the factors that can have protective effects on this process. Curcumin is the active ingredient of Curcuma longa Turmeric, which has a strong antioxidant effect. We evaluated the curcumin treatment on testicular histopathology, apoptosis, and reproductive organs index in a mouse model of aging. Forty-eight mice divided into control, sham, d-galactose, and curcumin 1 to 3 groups. The d-galactose group was administered intraperitoneally 300 mg/kg d-galactose for 6 weeks. The curcumin 1 to 3 groups received d-galactose plus 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg of curcumin, respectively for 14 days. Then, testicular histopathology, apoptosis, and reproductive organs index were investigated after 6 weeks. The SPSS software was used for data analysis. Tunnel-positive cells in the d-galactose group were remarkably higher than the control group (p < 0.05). Administration of curcumin in all three doses reduced the number of positive tunnel cells, in comparison with the group that received d-galactose (p < 0.05). The epididymis weight index of the d-galactose group was significantly different from the control (p = 0.006), the sham (p = 0.01), the curcumin 1 (p = 0.003), the curcumin 2 (p = 0.003), and the curcumin 3 (p = 0.002) groups. Histological examination of the d-galactose group revealed a reduction in the thickness of the germinal epithelium, edema, and complete atrophy of germ cells in some seminiferous tubules. The histology of seminiferous tubules was near-normal appearance with the little disintegration of germ cells from their normal germinal epithelium in the curcumin 1 and 3 groups. The histology of seminiferous tubules was near-normal appearance with mild edema and congestion in some seminiferous tubules in the curcumin 2 group. Curcumin supplementation (2 weeks, 100 mg/kg) caused an improvement in biochemical markers and sperm parameters as well as a reduction in apoptosis in the testicular tissue of the aging mouse model.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal ML, Chacko KM, Kuruvilla BT (2015) Systematic and comprehensive investigation of the toxicity of curcuminoid-essential oil complex: a bioavailable turmeric formulation. Mol Med Rep 13(1):592–604. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.4579
Aktas C, Kanter M, Erboga M, Ozturk S (2012) Anti-apoptotic effects of curcumin on cadmium-induced apoptosis in rat testes. Toxicol Ind Health 28(2):122–130. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233711407242
Attari S, Mohammadi S, Ebrahimzadeh A, Hosseinzadeh H, Soukhtanloo M, Rajabzadeh A (2018) Effects of thymoquinone on sperm parameters, apoptosis, testosterone level, and oxidative stress in a mouse model of D-galactose-induced aging. Pharm Sci. 24 (2):180-186.
Chandra AK, Chatterjee A, Ghosh R, Sarkar M (2007) Effect of curcumin on chromium-induced oxidative damage in male reproductive system. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 24(2):160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2007.04.009
Cheraghi E, Golkar A, Roshanaei K, Alani B (2017) Aluminium-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis and alterations in testicular tissue and sperm quality in Wistar rats: ameliorative effects of curcumin. Int J Fertil Steril 11(3):166–175. https://doi.org/10.22074/ijfs.2017.4859
Głombik K, Basta-Kaim A, Sikora-Polaczek M, Kubera M, Starowicz G, Styrna J (2014) Curcumin influences semen quality parameters and reverses the di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP)-induced testicular damage in mice. Pharmacol Rep 66(5):782–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.04.010
Hamidabadi HG, Nazm Bojnordi M (2018) Co-culture of mouse spermatogonial stem cells with sertoli cell as a feeder layer, stimulates the proliferation and spermatogonial stemness profile. Middle East Fertility Society Journal. 23 (2):107–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mefs.2017.09.004
Kanter M, Aktas C, Erboga M (2013) Curcumin attenuates testicular damage, apoptotic germ cell death, and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Mol Nutr Food Res 57(9):1578–1585. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201200170
Karbalay-Doust S, Noorafshan A (2011) Ameliorative effects of curcumin on the spermatozoon tail length, count, motility and testosterone serum level in metronidazole-treated mice. Prague Med Rep 112(4):288–297
Khorsandi L, Mirhoseini M, Mohamadpour M, Orazizadeh M, Khaghani S (2013) Effect of curcumin on dexamethasone-induced testicular toxicity in mice. Pharm Biol 51(2):206–212. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2012.716854
Kumar A, Prakash A, Dogra S (2011) Protective effect of curcumin (Curcuma longa) against D-galactose-induced senescence in mice. J Asian Nat Prod Res 13(1):42–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2010.544253
Liao VH, Yu CW, Chu YJ, Li WH, Hsieh YC, Wang TT (2011) Curcumin-mediated lifespan extension in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech Ageing Dev 132(10):480–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2011.07.008
Lonare M, Kumar M, Raut S, More A, Doltade S, Badgujar P, Telang A (2016) Evaluation of ameliorative effect of curcumin on imidacloprid-induced male reproductive toxicity in wistar rats. Environ Toxicol 31(10):1250–1263. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22132
Mohammadi S, Khakbaz M, Shoraka M, Vakil S, Moghimian M, Mohammadzadeh F (2016a) Effects of different doses of manganese on lead poisoning in the kidney of adult male mice. Koomesh 18(1):203–210
Mohammadi S, Safari F, Seyedi Z, Seyed Hosseini E, Karimi F, Mohammadi M, Karimi M, Delshad A, Abtahi H, Mohammadzadeh F (2016b) Effect of different doses of N-acetyl cysteine on biochemical and histopathological parameters in kidney of formalin-treated. JKMU 3(5):607–617
Mohammadi S, Golamin M, Mohammadi M, Mansouri A, Mahmoodian R, Attari S (2018a) Down-regulation of CatSper 1 and CatSper 2 genes by lead and mercury. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 59:82–86
Mohammadi S, Golamin M, Mohammadi M, Mansouri A, Mahmoodian R, Attari S, Kebriaei SM, Zibaei B, Roshanaei M, Daneshvar F, Khandehro M, Khodadadegan MA, Delshad A, Mohammadzadeh F, Peyvandi M, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Tavallaie S, Boroumand-Noughabi S, Ferns AAG (2018b) Down-regulation of CatSper 1 and CatSper 2 genes by lead and mercury. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 59:82–86
Momtaz S, Abdollahi M (2012) A comprehensive review of biochemical and molecular evidences from animal and human studies on the role of oxidative stress in aging: an epiphenomenon or the cause. Asian J Anim Vet Adv 7:1–19
Mu Y, Yan WJ, Yin TL, Yang J (2016) Curcumin ameliorates high-fat diet-induced spermatogenesis dysfunction. Mol Med Rep 14(4):3588–3594. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5712
Shen LR, Parnell LD, Ordovas JM, Lai CQ (2013a) Curcumin and aging. Biofactors 39(1):133–140
Shen LR, Xiao F, Yuan P, Chen Y, Gao QK, Parnell LD (2013b) Curcumin-supplemented diets increase superoxide dismutase activity and mean lifespan in Drosophila. Age (Dordr) 35(4):1133–1142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-012-9438-2
Sikora E, Scapagnini G, Barbagallo M (2010) Curcumin, inflammation, ageing and age-related diseases. Immun Ageing 7(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4933-7-1
Singh S, Das Roy L, Giri S (2013) Curcumin protects metronidazole and X-ray induced cytotoxicity and oxidative stress in male germ cells in mice. Prague Med Rep 114(2):92–102
Tajaddini S, Ebrahimi S, Shirinbayan P, Bakhtiari M, Behnam B, Joghataei MT (2013) Protective effects of manganese on the testis structure and sperm parameters of formalin treated mice. J Isfahan Med Sch 31(243):1018–1032
Tvrdá E, Tušimová E, Kováčik A, Paál D, Greifová H, Abdramanov A, Lukáč N (2016) Curcumin has protective and antioxidant properties on bull spermatozoa subjected to induced oxidative stress. Anim Reprod Sci 172:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anireprosci.2016.06.008
Wang W, Li S, Dong H-P, Lv S, Tang Y-Y (2009) Differential impairment of spatial and nonspatial cognition in a mouse model of brain aging. Life Sci 85(3):127–135
Acknowledgments
This article was derived from the MSc thesis in Anatomy Sciences (code 951445). We also thank Azam Amini and Fatemeh Tajik for her skilled assistance.
Funding
This study was funded by Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (grant number 951445).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taba, M.Y., Mohammadi, S., Jalali, M. et al. Effects of different doses of curcumin on testicular histopathology, apoptosis, and reproductive organs weight index in mice d-galactose-induced aging model. Comp Clin Pathol 28, 997–1002 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2870-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2870-7