Abstract
Background/purpose
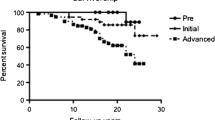
Rotational acetabular osteotomy (RAO) is a joint-conserving surgery in which femoral head coverage is improved using autologous cartilage to stabilize the joint. For advanced coxarthrosis, it has been reported that radical surgery should be selected, compared to the pre- and early stages. The objective of this study was to determine the clinical outcomes of patients in whom coxarthrosis progressed after RAO and came to undergo total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Methods
We compared 24 total hip arthroplasties done in dysplastic hips after previous rotational acetabular osteotomy (RAO group) with a well-matched control group of 24 primary arthroplasties (control group) done during the same period at an average follow-up of 85 months (range 15–195).
Results
RAO group required significantly longer operative times and had more intraoperative blood loss. There was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of Harris Hip Score and radiographic outcome. Revision was performed in four and one joints in the RAO and control groups, respectively, showing no significant difference between the two groups (p = 0.165).
Conclusion
THA after previous RAO leads to midterm results similar to those of other dysplastic hips. RAO does not seem to compromise the midterm clinical and radiographic outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ninomiya S, Tagawa H (1984) Rotational acetabular osteotomy for the dysplastic hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 66:430–436
Shindo H, Igarashi H, Taneda H, Azuma H (1996) Rotational acetabular osoteotomy for severe dysplasia of the hip with a false acetabulum. J Bone Joint Surg Br 78-B:871–877
Nakamura S, Ninomiya S, Takatori Y, Morimoto S, Umeyama T (1998) Long-term outcome of rotational acetabular osteotomy: 145 hips followed for 10–23 years. Acta Orthop Scand 69:259–265
Nozawa M, Shitoto K, Matsuda K, Maezawa K, Kuroswa H (2002) Rotational acetabular osteotomy for acetabular dysplasia. A follow-up for more than ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:59–65
Yasunaga Y, Ochi M, Shimogaki K, Yamamoto S, Iwamori H (2004) Rotational acetabular osteotomy for hip dysplasia: 61 hips followed for 8–15 years. Acta Orthop Scand 75:10–15
Yasunaga Y, Ochi M, Terayama H, Tanaka R, Yamasaki T, Ishii Y (2006) Rotational acetabular osteotomy for advanced osteoarthritis secondary to dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg A 88:1915–1919
Nozawa M, Maezawa K, Matsuda K, Kim SG, Shitoto K, Kurosawa H (2009) Rotational acetabular osteotomy for advanced osteoarthritis of the hip joint with acetabular dysplasia. Int Orthop 33:1549–1553
Parvizi J, Burmeister H, Ganz R (2004) Previous bernese periacetabular osteotomy does not compromise the results of total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 423:118–122
Peters CL, Beck M, Dunn HK (2001) Total hip arthroplasty in young adults after failed triple innominate osteotomy. J Arthroplasty 16:188–195
Hashemi-Nejad A, Haddad FS, Tong KM, Muirhead-Allwood SK, Catterall A (2002) Does Chiari osteotomy compromise subsequent total hip arthroplasty? J Arthroplsaty 17:731–739
Tokunaga K, Aslam N, Zredo R, Schemitsh EH, Waddwll JP (2011) Effect of prior Salter or Chiari osteotomy on THA with developmental hip dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:237–243
Minoda Y, Kadowaki T, Kim M (2006) Total hip arthroplasty of dysplastic hip after previous pelvic osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 126:394–400
Harris WH (1969) Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 51:737–755
DeLee JG, Charnley J (1976) Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 121:20–32
Gruen TA, McNiece GM, Amstutz HC (1979) “Modes of failure” of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res 141:17–27
Nozawa M, Shitoto K, Mastuda K, Maezawa K, Ogawa S, Yuasa T, Aritomi K, Kurosawa H (2006) Original methods to move femoral head medially and caudally after rotational acetabular osteotomy: especially to use ceramic spacer. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 126:421–424
Conflict of interest
No.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuasa, T., Maezawa, K., Nozawa, M. et al. Total hip arthroplasty after previous rotational acetabular osteotomy. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 25, 1057–1060 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1657-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-015-1657-7