Abstract
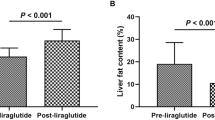
Ectopic accumulation of lipids in nonadipose tissues plays a primary role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study was to examine the effects of exenatide, insulin, and pioglitazone on liver fat content and body fat distributions in T2DM. Thirty-three drug-naive T2DM patients (age 52.7 ± 1.7 years, HbA1c 8.7 ± 0.2 %, body mass index 24.5 ± 0.5 kg/m2) were randomized into exenatide, insulin, or pioglitazone for 6 months. Intrahepatic fat (IHF), visceral fat (VF), and subcutaneous fat (SF) were measured using proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Plasma tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and adiponectin were assayed by ELISA. HbA1c declined significantly in all three groups. Body weight, waist, and serum triglycerides decreased with exenatide. After interventions, IHF significantly reduced with three treatments (exenatide Δ = −68 %, insulin Δ = −58 %, pioglitazone Δ = −49 %). Exenatide reduced VF (Δ = −36 %) and SF (Δ = −13 %), and pioglitazone decreased VF (Δ = −30 %) with no impact on SF, whereas insulin had no impact on VF or SF. Levels of TNFα (exenatide/insulin/pioglitazone) decreased, and levels of adiponectin (exenatide/pioglitazone) increased. Analysis showed that ΔIHF correlated with ΔHbA1c and Δweight. Besides, ΔIHF correlated with Δtriglycerides and ΔTNFα, but the correlations fell short of significance after BMI adjustment. By linear regression analysis, ΔHbA1c alone explained 41.5 % of the variance of ΔIHF, and ΔHbA1c + Δweight explained 57.6 % of the variance. Liver fat content can be significantly reduced irrespective of using exenatide, insulin, and pioglitazone. Early glycaemic control plays an important role in slowing progression of fatty liver in T2DM.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGarry JD (2001) Banting lecture 2001: dysregulation of fatty acid metabolism in the etiology of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 51:7–18
Unger RH (2008) Reinventing type 2 diabetes: pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention. JAMA 299:1185–1187
Vilsbøll T, Christensen M, Junker AE, Knop FK, Gluud LL (2012) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on weight loss: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 344:d7771
Jendle J, Nauck MA, Matthews DR, Frid A, Hermansen K, Düring M, Zdravkovic M, Strauss BJ, Garber AJ (2009) LEAD-2 and LEAD-3 study groups weight loss with liraglutide, a once-daily human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue for type 2 diabetes treatment as monotherapy or added to metformin, is primarily as a result of a reduction in fat tissue. Diabetes Obes Metab 11:1163–1172
Cuthbertson DJ, Irwin A, Gardner CJ, Daousi C, Purewal T, Furlong N, Goenka N, Thomas EL, Adams VL, Pushpakom SP, Pirmohamed M, Kemp GJ (2012) Improved glycaemia correlates with liver fat reduction in obese, type 2 diabetes, patients given glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. PLoS One 7:e50117
Sathyanarayana P, Jogi M, Muthupillai R, Krishnamurthy R, Samson SL, Bajaj M (2011) Effects of combined exenatide and pioglitazone therapy on hepatic fat content in type 2 diabetes. Obesity (Silver Spring) 19:2310–2315
Lindberg M, Astrup A (2007) The role of glitazones in management of type 2 diabetes. A dream or a nightmare? Obes Rev 8:381–384
Bajaj M, Suraamornkul S, Pratipanawatr T, Hardies LJ, Pratipanawatr W, Glass L, Cersosimo E, Miyazaki Y, DeFronzo RA (2003) Pioglitazone reduces hepatic fat content and augments splanchnic glucose uptake in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 52:1364–1370
Weng J, Li Y, Xu W, Shi L, Zhang Q, Zhu D, Hu Y, Zhou Z, Yan X, Tian H, Ran X, Luo Z, Xian J, Yan L, Li F, Zeng L, Chen Y, Yang L, Yan S, Liu J, Li M, Fu Z, Cheng H (2008) Effect of intensive insulin therapy on beta-cell function and glycaemic control in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a multicentre randomised parallel-group trial. Lancet 371:1753–1760
Hu Y, Li L, Xu Y, Yu T, Tong G, Huang H, Bi Y, Weng J, Zhu D (2011) Short-term intensive therapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes partially restores both insulin sensitivity and β-cell function in subjects with long-term remission. Diabetes Care 34:1848–1853
Juurinen L, Tiikkainen M, Häkkinen AM, Hakkarainen A, Yki-Järvinen H (2007) Effects of insulin therapy on liver fat content and hepatic insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292:E829–E835
Shah PK, Mudaliar S, Chang AR, Aroda V, Andre M, Burke P, Henry RR (2011) Effects of intensive insulin therapy alone and in combination with pioglitazone on body weight, composition, distribution and liver fat content in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 13:505–510
Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ (1998) Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med 15:539–553
Xu W, Bi Y, Sun Z, Li J, Guo L, Yang T, Wu G, Shi L, Feng Z, Qiu L, Li Q, Guo X, Luo Z, Lu J, Shan Z, Yang W, Ji Q, Yan L, Li H, Yu X, Li S, Zhou Z, Lv X, Liang Z, Lin S, Zeng L, Yan J, Ji L, Weng J (2014) Comparison of the effects on glycaemic control and β-cell function in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients of treatment with exenatide, insulin or pioglitazone: a multicentre randomized parallel-group trial (the CONFIDENCE study). J Intern Med Jul 16, Epub ahead of print
Bi Y, Zeng LY, Zhu DL, Yan J, Zhang Y, Tong G, Mu P, Shen S, Hu Y, Yu Q, Liang H, Weng J (2012) Association of β-cell function and insulin sensitivity with fasting and 2 h plasma glucose in a large Chinese population. Diabetes Obes Metab 14:174–180
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Matsuda M, DeFronzo RA (1999) Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 22:1462–1470
Thomas EL, Hamilton G, Patel N, O’Dwyer R, Doré CJ, Goldin RD, Bell JD, Taylor-Robinson SD (2005) Hepatic triglyceride content and its relation to body adiposity: a magnetic resonance imaging and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Gut 54:122–127
Liska D, Dufour S, Zern TL, Taksali S, Calí AM, Dziura J, Shulman GI, Pierpont BM, Caprio S (2007) Interethnic differences in muscle, liver, and abdominal fat partitioning in obese adolescents. PLoS One 2:e569
Hwang JH, Stein DT, Barzilai N, Cui MH, Tonelli J, Kishore P, Hawkins M (2007) Increased intrahepatic triglyceride is associated with peripheral insulin resistance: in vivo MR imaging and spectroscopy studies. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E1663–E1669
Porepa L, Ray JG, Sanchez-Romeu P, Booth GL (2010) Newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for serious liver disease. CMAJ 182:E526–E531
Musso G, Cassader M, Rosina F, Gambino R (2012) Impact of current treatments on liver disease, glucose metabolism and cardiovascular risk in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Diabetologia 55:885–904
Petersen KF, Dufour S, Befroy D, Lehrke M, Hendler RE, Shulman GI (2005) Reversal of nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis, hepatic insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia by moderate weight reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 54:603–608
Kenny PR, Brady DE, Torres DM, Ragozzino L, Chalasani N, Harrison SA (2010) Exenatide in the treatment of diabetic patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a case series. Am J Gastroenterol 105:2707–2709
Lim EL, Hollingsworth KG, Aribisala BS, Chen MJ, Mathers JC, Taylor R (2011) Reversal of type 2 diabetes: normalisation of beta cell function in association with decreased pancreas and liver triacylglycerol. Diabetologia 54:2506–2514
Asrih M, Jornayvaz F (2013) Inflammation as a link between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. J Endocrinol 218:R25–R36
Daniele G, Guardado Mendoza R, Winnier D, Fiorentino TV, Pengou Z, Cornell J, Andreozzi F, Jenkinson C, Cersosimo E, Federici M, Tripathy D, Folli F (2014) The inflammatory status score including IL-6, TNF-α, osteopontin, fractalkine, MCP-1 and adiponectin underlies whole-body insulin resistance and hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol 51:123–131
Tripathy D, Daniele G, Fiorentino TV, Perez-Cadena Z, Chavez-Velasquez A, Kamath S, Fanti P, Jenkinson C, Andreozzi F, Federici M, Gastaldelli A, Defronzo RA, Folli F (2013) Pioglitazone improves glucose metabolism and modulates skeletal muscle TIMP-3-TACE dyad in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, mechanistic study. Diabetologia 56:2153–2163
Lesmana CR, Hasan I, Budihusodo U, Gani RA, Krisnuhoni E, Akbar N, Lesmana LA (2009) Diagnostic value of a group of biochemical markers of liver fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Did Dis 10:201–206
Speliotes EK, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Vasan RS, Meigs JB, Sahani DV, Hirschhorn JN, O’Donnell CJ, Fox CS (2010) Fatty liver is associated with dyslipidemia and dysglycemia independent of visceral fat: the Framingham heart study. Hepatology 51:1979–1987
Fernández-Miranda C, Pérez-Carreras M, Colina F, López-Alonso G, Vargas C, Solís-Herruzo JA (2008) A pilot trial of fenofibrate for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis 40:200–205
Spadaro L, Magliocco O, Spampinato D, Piro S, Oliveri C, Alagona C, Papa G, Rabuazzo AM, Purrello F (2008) Effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis 40:194–199
Deurenberg P, Yap M, van Staveren WA (1998) Body mass index and percent body fat: a meta analysis among different ethnic groups. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 22:1164–1171
Chiu KC, Cohan P, Lee NP, Chuang LM (2000) Insulin sensitivity differs among ethnic groups with a compensatory response in beta-cell function. Diabetes Care 23:1353–1358
Ma RC, Chan JC (2013) Type 2 diabetes in East Asians: similarities and differences with populations in Europe and the United States. Ann NY Acad Sci 1281:64–91
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J, Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, Zhu D, Ge J, Lin L, Chen L, Guo X, Zhao Z, Li Q, Zhou Z, Shan G, He J (2010) China National Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders study group prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med 362:1090–1101
Bazzocchi A, Diano D, Ponti F, Salizzoni E, Albisinni U, Marchesini G, Battista G (2014) A 360-degree overview of body composition in healthy people: relationships among anthropometry, ultrasonography, and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Nutrition 30:696–701
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the participating patients. This study was sponsored by Grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant Award (81270906, 81070636), 973 project (2012CB517506), the China postdoctoral Science Foundation (2012M521050), Jiangsu postdoctoral Science Foundation, Jiangsu Province’s Key Provincial Talents Program (RC2011011), the Key Project of Nanjing Medical Science and Technology Development Foundation (ZKX11017, YKK11092), the Project of National Key Clinical Division, Jiangsu Province’s Key Discipline of Medicine (XK201105), National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (81025005), and New Drug Development, Construction and management of Clinical Biobank for Major Disease (2011ZX0907-001-08).
Conflict of interest
Yan Bi, Bing Zhang, Wen Xu, Huijie Yang, Wenhuan Feng, Cuiliu Li, Guoyu Tong, Ming Li, Xin Wang, Shanmei Shen, Bin Zhu, Jianping Weng, and Dalong Zhu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Managed by Massimo Federici.
Yan Bi and Bing Zhang contributed equally to the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, Y., Zhang, B., Xu, W. et al. Effects of exenatide, insulin, and pioglitazone on liver fat content and body fat distributions in drug-naive subjects with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 51, 865–873 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0638-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0638-3