Abstract
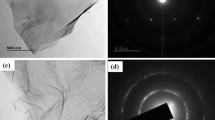
The authors describe nanoelectrodes based on the use of hierarchical carbon-nitrogen nanospheres and dual-head nickel oxide echinop flowers (CN@HDN) placed on indium tin oxide (ITO) electrodes. The modified electrodes enable sensitive detection of catecholamine neurotransmitters, specifically of epinephrine (EPI) in human serum samples. The modified electrodes possess many active sites along the {111} crystal plane and large contact surfaces. This enables a rapid EPI diffusion within a highly active transport surface. The geometrical and morphological structures of the NiO decorated with CN-nanospheres render superior electrocatalytic behavior at a relatively low working voltage of 0.12 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) which makes the sensor relatively specific. The use of CN also increases the electron transfer rate and facilitates mass transfer between electrolyte (EPI sample) and catalytically active sites. The electrode is sensitive, selective and works at near-physiological pH values. It has a detection limit as low as 4 nM of EPI.

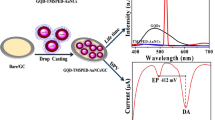
Assembling of modified electrode based on hierarchical carbon-nitrogen nanospheres@dual-head nickel oxide echinop flowers (CN@HDN) for monitoring epinephrine (EPI). EPI is electro-oxidized to its o-quinone form with charge transfer of 2e−/2H+ at the surface of CN@HDN.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robinson DL, Venton BJ, Heien MLAV, Wightman RM (2003) Detecting subsecond dopamine release with fast-scan cyclic voltammetry in vivo. Clin Chem 49:1763–1773. https://doi.org/10.1373/49.10.1763
Hefco V, Yamada K, Hefco A, Hritcu L, Tiron A, Nabeshima T (2003) Role of the mesotelencephalic dopamine system in learning and memory processes in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 475:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-2999(03)02115-0
Jemelkova Z, Barek J, Zima J (2010) Determination of epinephrine at different types of carbon paste electrodes. Anal Lett 43:1367–1376. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032710903518773
Shahrokhian S, Khafaji M (2010) Application of pyrolytic graphite modified with nano-diamond/graphite film for simultaneous voltammetric determination of epinephrine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid. Electrochim Acta 55:9090–9096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.08.043
Niu LM, Luo HQ, Li NB (2005) Electrochemical behavior of epinephrine at a Penicillamine self-assembled gold electrode, and its analytical application. Microchim Acta 150:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-005-0331-x
Lu X, Li Y, Du J, Zhou X, Xue Z, Liu X, Wang Z (2011) A novel nanocomposites sensor for epinephrine detection in the presence of uric acids and ascorbic acids. Electrochim Acta 56:7261–7266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.06.056
Ghica ME, Brett CMA (2013) Simple and efficient epinephrine sensor based on carbon nanotube modified carbon film electrodes. Anal Lett 46:1379–1393. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2012.762584
Beitollahi H, Karimi-Maleh H, Khabazzadeh H (2008) Nanomolar and selective determination of epinephrine in the presence of norepinephrine using carbon paste electrode modified with carbon nanotubes and novel 2-(4-oxo-3-phenyl-3, 4-dihydro-quinazolinyl)-N′-phenyl-hydrazinecarbothioamide. Anal Chem 80(9848–98):51. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac801854j
Goyal RN, Bishnoi S (2011) A novel multi-walled carbon nanotube modified sensor for the selective determination of epinephrine in smokers. Electrochim Acta 56:2717–2724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.12.047
Babaei A, Sohrabi M, Afrasiabi M (2012) A sensitive simultaneous determination of epinephrine and Piroxicam using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nickel hydroxide nanoparticles/multiwalled carbon nanotubes composite. Electroanalysis 2:2387–2394. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201200483
Justino DDA, Lage LA, Souto DEP, Silva JV, Santos WTP, Luz RCS, Damos FS (2013) Study of the effects of surface pKa and electron transfer kinetics of electroactive 4-nitrothiophenol/4-mercaptobenzoic acid binary SAM on the simultaneous determination of epinephrine and uric acid. J Electroanal Chem 703:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2013.05.024
Sanghavi BJ, Mobin SM, Mathur P, Lahiri GK, Srivastava AK (2013) Biomimetic sensor for certain catecholamines employing copper(II) complex and silver nanoparticle modified glassy carbon paste electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 39:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.07.008
Shahrokhian S, Ghalkhani M, Amini MK (2009) Application of carbon-paste electrode modified with iron phthalocyanine for voltammetric determination of epinephrine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid. Sensors Actuators B Chem 137:669–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2009.01.022
Zhang HM, Zhou XL, Hui RT, Li NQ, Liu DP (2002) Studies of the electrochemical behavior of epinephrine at a homocysteine self-assembled electrode. Talanta 56:1081–1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(01)00642-7
Fouad DM, El-Said WA (2016) Selective electrochemical detection of epinephrine using gold nanoporous film. J Nanomater 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6194230
Kim SH, Lee JW, Yeo IH (2000) Spectroelectrochemical and electrochemical behavior of epinephrine at a gold electrode. Electrochim Acta 45:2889–2895. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(00)00364-9
Zhang H, Wang X, Wan L, Liu Y, Bai C (2004) Electrochemical behavior of multi-wall carbon nanotubes and electrocatalysis of toluene-filled nanotube film on gold electrode. Electrochim Acta 49:715–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2003.09.023
Valentini F, Palleschi G, Lopez Morales E, Orlanducci S, Tamburri E, Terranova ML (2007) Functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes modified microsensors for the selective response of epinephrine in presence of ascorbic acid. Electroanalysis 19:859–865. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200603788
Agboola BO, Ozoemena KI (2008) Efficient Electrocatalytic detection of epinephrine at gold electrodes modified with self-assembled Metallo-Octacarboxyphthalocyanine complexes. Electroanalysis 20:1696–1707. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200804240
Hoa ND, El-Safty SA (2001) Synthesis of mesoporous NiO Nanosheets for the detection of toxic NO2 gas. Chem A Eur J 17:12896–12901. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201101122
Shenashen MA, El-Safty SA, Elshehy EA (2011) Architecture of optical sensor for recognition of multiple toxic metal ions from water. J Hazard Mater 260:833–843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.06.025
EL-Safty SA, Abdelllatef A, Ismeal M, Shahat A (2013) Optical Nanosphere sensor based on Shell-by-Shell fabrication for removal of toxic metals from human blood. Adv Healthc Mater 2:854–862. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201200326
Das SK, El-Safty SA (2013) Development of mesoscopically assembled sulfated zirconia nanoparticles as promising heterogeneous and recyclable biodiesel catalysts. Chem Cat Chem 5:3050–3059. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201300192
Hassen D, Shenashen MA, El-Safty SA, Selim MM, Isago H, Elmarakbi A, El-Safty A, Yamaguchi H (2016) Nitrogen-doped carbon-embedded TiO2 nanofibers as promising oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysts. J Power Sources 330:292–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.08.140
Yu S, Peng X, Cao G, Zhou M, Qiao L, Yao J, He H (2012) Ni nanoparticles decorated titania nanotube arrays as efficient nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Electrochim Acta 76:512–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.05.079
Khairy M, El-Safty SA, Ismael M, Kawarada H (2012) Multidirectional porous NiO nanoplatelet-like mosaics as catalysts for green chemical transformations. Appl Catal B Environ 123-124:162–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.04.021
Khairy M, El-Safty SA (2013) Mesoporous NiO Nanosheets for the catalytic conversion of organic contaminants. Current Catalysis 2:17–26. https://doi.org/10.2174/2211544711302010005
Khairy M, El-Safty SA, Shenashen MA, Elshehy EA, Warkocki W, Sakai M (2015) Optical mesoscopic membrane sensor layouts for water-free and blood-free toxicants. Nano Res 8(10):3150–3163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0815-x
Khairy M, El-Safty SA (2013) Mesoporous NiO nanoarchitectures for electrochemical energy storage: influence of size, porosity, and morphology. RSC Adv 3:23801–23809. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA44465A
Khairy M, El-Safty SA (2015) Promising supercapacitor electrodes based immobilization of proteins onto macroporous Ni foam materials. Journal of Energy Chemistry 24:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-4956(15)60281-9
Zhao S, Zhang J, Li Z, Zhang P, Li Y, Liu G, Wang Y, Yue Z (2017) Photoelectrochemical determination of hydrogen peroxide using a gold electrode modified with fluorescent gold nanoclusters and graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 184:677–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2035-9
Xi X, Li J, Wang H, Zhao Q, Li H (2015) Non-enzymatic photoelectrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide using hierarchically structured zinc oxide hybridized with graphite-like carbon nitride. Microchim Acta 182:1273–1279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1448-10
Chen Z, Zhang C, Zhou T, Ma H (2015) Gold nanoparticle based colorimetric probe for dopamine detection based on the interaction between dopamine and melamine. Microchim Acta 182:1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1417-0
Li Y, Lin H, Peng H, Qi R, Luo C (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with MoS2 nanosheets and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Microchim Acta 183:2517–2523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1897-1
Kavitha T, Yuvaraj H (2011) Facile approach to the synthesis of high-quality NiO nanorods: electrochemical and antibacterial properties. J Mater Chem 21(39):15686–15691. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1JM13278D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 795 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emran, M.Y., Khalifa, H., Gomaa, H. et al. Hierarchical C-N doped NiO with dual-head echinop flowers for ultrasensitive monitoring of epinephrine in human blood serum. Microchim Acta 184, 4553–4562 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2498-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2498-3