Abstract
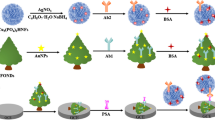
To increase the sensitivity of electrochemical sensor, Fe-MIL-88B-NH2 (Fe-MOF) with peroxidase-like activity is designed for the construction of immunoprobe. The Fe-MOF was prepared by one-step hydrothermalf method using 2-aminoterephthalic acid and iron(III) chloride. For the immunoprobe, it was fabricated by gold nanocomposite/Fe-MOF (Au/Fe-MOF) for the immobilization of labeling antibody (the antibody was used to conjuncting with label materials). The thin layer of Methylene Blue (MB) covered by reduced graphene oxide-gold nanocomposites (Au-rGO) serves as a substrate to covalently fix coating antibodies. The MB as a redox-active species was modified on the glass carbon electrode that can give a strong amperometric signal at 0.18 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). With the participation of H2O2, Fe-MOF can induce the Fenton reaction which degrades MB covered by Au-rGO on the substrate. The rest of MB on the surface of electrode becomes oxidized thereby generating a current signal. Square wave voltammetry (SWV) was used to quantify PSA. Under optimal conditions, the immunoassay is stable, specific and reproducible. It has a lower detection limit of 0.13 pg mL−1 (S/N = 3) and a wide analytical range that extends from 0.001 to 100 ng mL−1.

A sandwich-type amperometric immunoassay based on Fe-MOF-induced Fenton reaction was designed for sensitive determination of prostate specific antigen.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Y, Hong M, Qiu B, Lin Z, Chen Y, Cai Z (2014) Highly sensitive fluorescent immunosensor for detection of influenza virus based on Ag autocatalysis. Biosens Bioelectron 54:358–364
Pei H, Zhu S, Yang M, Kong R, Zheng Y, Qu F (2015) Graphene oxide quantum dots@silver core–shell nanocrystals as turn-on fluorescent nanoprobe for ultrasensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 74:909–914
Zheng H, Yi H, Lin W, Dai H, Hong Z, Lin Y (2018) A dual-amplified electrochemiluminescence immunosensor constructed on dual-roles of rutile TiO2 mesocrystals for ultrasensitive zearalenone detection. Electrochim Acta 260:847–854
Babamiri B, Bahari D, Salimi A (2019) Highly sensitive bioaffinity electrochemiluminescence sensors: recent advances and future directions. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111530
Saydam M, Rigsby P, Mawas F (2014) A novel enzyme-linked Immuno-sorbent assay (ELISA) for the quantification of total and free polysaccharide in Haemophilus influenzae b–tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccines in monovalent and combined vaccine formulations. Biologicals 42:29–33
Zhao LH, Ma ZF (2017) New immunoprobes based on bovine serum albumin-stabilized copper nanoclusters with triple signal amplification for ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensing for tumor marker. Sensors Actuators B Chem 241:849–854
Zheng Y, Zhao LH, Ma ZF (2018) pH responsive label-assisted click chemistry triggered sensitivity amplification for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of carbohydrate antigen 24-2. Biosens Bioelectron 115:30–36
Pastucha M, Farka Z, Lacina K, Mikušová Z, Skládal P (2019) Magnetic nanoparticles for smart electrochemical immunoassays: a review on recent developments. Microchim Acta 186(5):312
Macur K, Hagen L, Ciesielski TM, Konieczna L, Skokowski J, Jenssen BM (2019) A targeted mass spectrometry immunoassay to quantify osteopontin in fresh-frozen breast tumors and adjacent normal breast tissues. J Proteomics:103469
Wongkaew N, Simsek M, Griesche C, Baeumner AJ (2018) Functional nanomaterials and nanostructures enhancing electrochemical biosensors and lab-on-a-chip performances: recent progress, applications, and future perspective. Chem Rev 119:120–194
Liang XY, Han HL, Ma ZF (2019) pH responsive amperometric immunoassay for carcinoma antigen 125 based on hollow polydopamine encapsulating methylene blue. Sensors Actuators B Chem 290:625–630
Ding L, Yan J, Zhao Z, Li D (2019) Synthesis of NiGa2O4 nanosheets for non-enzymatic glucose electrochemical sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 296:126705
Gao N, He C, Ma M, Cai Z, Zhou Y, Chang G (2019) Electrochemical co-deposition synthesis of Au-ZrO2-graphene nanocomposite for a nonenzymatic methyl parathion sensor. Anal Chim Acta 1072:25–34
Li X, Dou B, Yuan R, Xiang Y (2019) Mismatched catalytic hairpin assembly and ratiometric strategy for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of microRNA from tumor cells. Sensors Actuators B Chem 286:191–197
Das J, Aziz MA, Yang H (2006) Nanocatalyst-based assay for proteins: DNA-free ultrasensitive electrochemical detection using catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol by gold-nanoparticle labels. J Am Chem Soc 128(50):16022–16023
Attar F, Shahpar MG, Rasti B, Sharifi M, Saboury AA, Rezayat SM (2019) Nanozymes with intrinsic peroxidase-like activities. J Mol Liq 278:130–144
Song W, Zhao B, Wang C, Ozaki Y, Lu X (2019) Functional nanomaterials with unique enzyme-like characteristics for sensing applications. J Mater Chem B 7:850–875
Wu J, Wang X, Wang Q, Lou Z, Li S, Zhu Y (2019) Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem Soc Rev 48:1004–1076
Yang H (2012) Enzyme-based ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensors. Curr Opin Chem Biol 16:422–428
Mano N (2019) Engineering glucose oxidase for bioelectrochemical applications. Bioelectrochemistry 128:218–240
Huo X, Liu P, Zhu J, Liu X, Ju H (2016) Electrochemical immunosensor constructed using TiO2 nanotubes as immobilization scaffold and tracing tag. Biosens Bioelectron 85:698–706
Wang HQ, Ma ZF (2018) A cascade reaction signal-amplified amperometric immunosensor platform for ultrasensitive detection of tumour marker. Sensors Actuators B Chem 254:642–647
Sharma MK, Narayanan J, Pardasani D, Srivastava DN, Upadhyay S, Goel AK (2016) Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunoassay for surface array protein, a Bacillus anthracis biomarker using Au-Pd nanocrystals loaded on boron-nitride nanosheets as catalytic labels. Biosens Bioelectron 80:442–449
Pei F, Wang P, Ma E, Yu H, Gao C, Yin H (2018) A sandwich-type amperometric immunosensor fabricated by Au@Pd NDs/Fe2+-CS/PPy NTs and Au NPs/NH2-GS to detect CEA sensitively via two detection methods. Biosens Bioelectron 122:231–238
Yuan R, Yue C, Qiu J, Liu F, Li A (2019) Highly efficient sunlight-driven reduction of Cr(VI) by TiO2@NH2-MIL-88B (Fe) heterostructures under neutral conditions. Appl Catal, B 251:229–239
He JC, Zhang Y, Zhang XD, Huang YM (2018) Highly efficient Fenton and enzyme-mimetic activities of NH2-MIL-88B(Fe) metal organic framework for methylene blue degradation. Sci Rep 8:51–59
Tang ZX, Wang LY, Ma ZF (2017) Triple sensitivity amplification for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 92:577–582
Pham MH, Vuong GT, Vu AT, Do TO (2011) Novel route to size-controlled Fe-MIL-88B-NH2 metal-organic framework nanocrystals. Langmuir 27:15261–15267
Zhang C, Zhang DS, Ma ZF, Han HL (2019) Cascade catalysis-initiated radical polymerization amplified impedimetric immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of carbohydrate antigen 15-3. Biosens Bioelectron 137:1–7
Liu N, Chen X, Ma ZF (2013) Ionic liquid functionalized graphene/Au nanocomposites and its application for electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 48:33–38
Xu W, Jiao L, Yan H, Wu Y, Chen L, Gu W (2019) Glucose oxidase-integrated metal-organic framework hybrids as biomimetic cascade nanozymes for ultrasensitive glucose biosensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:22096–22101
Acknowledgements
This research was financed by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21673143), Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality (2172016), and Capacity Building for Sci-Tech Innovation-Fundamental Scientific Research Funds (19530050179).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1640 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, J., Wang, H. & Ma, Z. Ultrasensitive amperometric immunosensor for the prostate specific antigen by exploiting a Fenton reaction induced by a metal-organic framework nanocomposite of type Au/Fe-MOF with peroxidase mimicking activity. Microchim Acta 187, 95 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4075-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4075-4